Antinuclear antibodies are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human proteins (autoantigens). In some cases, antibodies to human antigens are produced.

Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids. Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins.
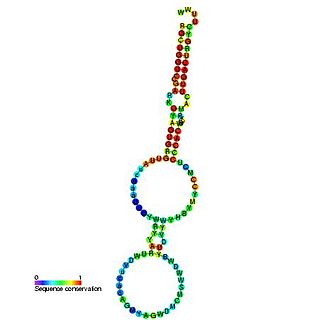
Y RNAs are small non-coding RNAs. They are components of the Ro60 ribonucleoprotein particle which is a target of autoimmune antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. They are also reported to be necessary for DNA replication through interactions with chromatin and initiation proteins. However, mouse embryonic stem cells lacking Y RNAs are viable and have normal cell cycles.

rRNA 2'-O-methyltransferase fibrillarin is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FBL gene.

Ku70 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the XRCC6 gene.

Ku80 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the XRCC5 gene. Together, Ku70 and Ku80 make up the Ku heterodimer, which binds to DNA double-strand break ends and is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair. It is also required for V(D)J recombination, which utilizes the NHEJ pathway to promote antigen diversity in the mammalian immune system.

Interleukin enhancer-binding factor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ILF3 gene.

Sjögren syndrome type B antigen (SS-B) also known as Lupus La protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SSB gene.

Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein-associated proteins B and B' is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNRPB gene.

60 kDa SS-A/Ro ribonucleoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TROVE2 gene.

Tripartite motif-containing protein 25 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRIM25 gene.

Cerebellar degeneration-related protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDR2 gene.

GTP-binding protein ARD-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRIM23 gene.

E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM33, also known as (ectodermin homolog and tripartite motif-containing 33) is a protein encoded in the human by the gene TRIM33, a member of the tripartite motif family.

Tripartite motif-containing protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRIM6 gene.

Tripartite motif-containing protein 11 is a protein found in humans that is encoded by the TRIM11 gene.

Anti-double stranded DNA (Anti-dsDNA) antibodies are a group of anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) the target antigen of which is double stranded DNA. Blood tests such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunofluorescence are routinely performed to detect anti-dsDNA antibodies in diagnostic laboratories. They are highly diagnostic of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and are implicated in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis.
Intracellular antibody-mediated degradation (IAMD) is a neutralization mechanism of intracellular antibody-mediated immunity whereby an effector protein, TRIM21, directs antibody bound virions to the proteasome where they are degraded. As yet, it has only been observed to act against the adenovirus but is likely to also be effective against other non-enveloped viruses.

Anti-SSA autoantibodies are a type of anti-nuclear autoantibodies that are associated with many autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), SS/SLE overlap syndrome, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), neonatal lupus and primary biliary cirrhosis. They are often present in Sjögren's syndrome (SS). Additionally, Anti-Ro/SSA can be found in other autoimmune diseases such as systemic sclerosis (SSc), polymyositis/dermatomyositis (PM/DM), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), and are also associated with heart arrhythmia.

In molecular biology, the La domain is a conserved protein domain.