Related Research Articles
Extractive metallurgy is a branch of metallurgical engineering wherein process and methods of extraction of metals from their natural mineral deposits are studied. The field is a materials science, covering all aspects of the types of ore, washing, concentration, separation, chemical processes and extraction of pure metal and their alloying to suit various applications, sometimes for direct use as a finished product, but more often in a form that requires further working to achieve the given properties to suit the applications.

In industrial process engineering, mixing is a unit operation that involves manipulation of a heterogeneous physical system with the intent to make it more homogeneous. Familiar examples include pumping of the water in a swimming pool to homogenize the water temperature, and the stirring of pancake batter to eliminate lumps (deagglomeration).

A chemical reactor is an enclosed volume in which a chemical reaction takes place. In chemical engineering, it is generally understood to be a process vessel used to carry out a chemical reaction, which is one of the classic unit operations in chemical process analysis. The design of a chemical reactor deals with multiple aspects of chemical engineering. Chemical engineers design reactors to maximize net present value for the given reaction. Designers ensure that the reaction proceeds with the highest efficiency towards the desired output product, producing the highest yield of product while requiring the least amount of money to purchase and operate. Normal operating expenses include energy input, energy removal, raw material costs, labor, etc. Energy changes can come in the form of heating or cooling, pumping to increase pressure, frictional pressure loss or agitation.

Crystallization is the process by which solids form, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposition directly from a gas. Attributes of the resulting crystal depend largely on factors such as temperature, air pressure, cooling rate, and in the case of liquid crystals, time of fluid evaporation.

Froth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in mineral processing, paper recycling and waste-water treatment industries. Historically this was first used in the mining industry, where it was one of the great enabling technologies of the 20th century. It has been described as "the single most important operation used for the recovery and upgrading of sulfide ores". The development of froth flotation has improved the recovery of valuable minerals, such as copper- and lead-bearing minerals. Along with mechanized mining, it has allowed the economic recovery of valuable metals from much lower-grade ore than previously.

Mineral processing is the process of separating commercially valuable minerals from their ores in the field of extractive metallurgy. Depending on the processes used in each instance, it is often referred to as ore dressing or ore milling.
Hydrometallurgy is a technique within the field of extractive metallurgy, the obtaining of metals from their ores. Hydrometallurgy involve the use of aqueous solutions for the recovery of metals from ores, concentrates, and recycled or residual materials. Processing techniques that complement hydrometallurgy are pyrometallurgy, vapour metallurgy, and molten salt electrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy is typically divided into three general areas:
Carbon in pulp (CIP) is an extraction technique for recovery of gold which has been liberated into a cyanide solution as part of the gold cyanidation process.

A phase-change material (PCM) is a substance which releases/absorbs sufficient energy at phase transition to provide useful heat or cooling. Generally the transition will be from one of the first two fundamental states of matter - solid and liquid - to the other. The phase transition may also be between non-classical states of matter, such as the conformity of crystals, where the material goes from conforming to one crystalline structure to conforming to another, which may be a higher or lower energy state.
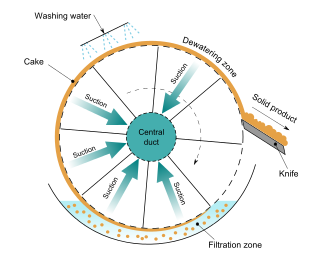
A Rotary Vacuum Filter Drum consists of a cylindrical filter membrane that is partly sub-merged in a slurry to be filtered. The inside of the drum is held lower than the ambient pressure. As the drum rotates through the slurry, the liquid is sucked through the membrane, leaving solids to cake on the membrane surface while the drum is submerged. A knife or blade is positioned to scrape the product from the surface.
A high-shear mixer disperses, or transports, one phase or ingredient into a main continuous phase (liquid), with which it would normally be immiscible. A rotor or impeller, together with a stationary component known as a stator, or an array of rotors and stators, is used either in a tank containing the solution to be mixed, or in a pipe through which the solution passes, to create shear. A high-shear mixer can be used to create emulsions, suspensions, lyosols, and granular products. It is used in the adhesives, chemical, cosmetic, food, pharmaceutical, and plastics industries for emulsification, homogenization, particle size reduction, and dispersion.

The Fernald Feed Materials Production Center is a Superfund site located within Crosby Township in Hamilton County, Ohio, as well as Ross Township in Butler County, Ohio, in the United States. It was a uranium processing facility located near the rural town of New Baltimore, about 20 miles (32 km) northwest of Cincinnati, which fabricated uranium fuel cores for the U.S. nuclear weapons production complex from 1951 to 1989. During that time, the plant produced 170,000 metric tons uranium (MTU) of metal products and 35,000 MTU of intermediate compounds, such as uranium trioxide and uranium tetrafluoride.

An industrial filter press is a tool used in separation processes, specifically to separate solids and liquids. The machine stacks many filter elements and allows the filter to be easily opened to remove the filtered solids, and allows easy cleaning or replacement of the filter media.

Leaching is the process of a solute becoming detached or extracted from its carrier substance by way of a solvent.
A vacuum ceramic filter is designed to separate liquids from solids for dewatering of ore concentrates purposes. The device consists of a rotator, slurry tank, ceramic filter plate, distributor, discharge scraper, cleaning device, frame, agitating device, pipe system, vacuum system, automatic acid dosing system, automatic lubricating system, valve and discharge chute. The operation and construction principle of vacuum ceramic filter resemble those of a conventional disc filter, but the filter medium is replaced by a finely porous ceramic disc. The disc material is inert, has a long operational life and is resistant to almost all chemicals. Performance can be optimized by taking into account all those factors which affect the overall efficiency of the separation process. Some of the variables affecting the performance of a vacuum ceramic filter include the solid concentration, speed rotation of the disc, slurry level in the feed basin, temperature of the feed slurry, and the pressure during dewatering stages and filter cake formation.

Pumpable icetechnology (PIT) uses thin liquids, with the cooling capacity of ice. Pumpable ice is typically a slurry of ice crystals or particles ranging from 5 micrometers to 1 cm in diameter and transported in brine, seawater, food liquid, or gas bubbles of air, ozone, or carbon dioxide.
A slurry pump is a type of pump designed for pumping liquid containing solid particles. Slurry pumps changes in design and construction to adjust to multiple type of slurry which varies in concentration of solids, size of solid particles, shape of solid particles, and composition of solution. Slurry pump are more robust than liquid pumps; they have added sacrificial material and replaceable wear parts to withstand wear due to abrasion.
Sepro Mineral Systems Corp. is a Canadian company founded in 1987 and headquartered in British Columbia, Canada. The outcome of the acquisition of Sepro Mineral Processing International by Falcon Concentrators in 2008, the company's key focus is the production of mineral processing equipment for the mining and aggregate industries. Sepro Mineral Systems Corp. also provides engineering and process design services. Products sold by Sepro include grinding mills, ore scrubbers, vibrating screens, centrifugal gravity concentrators, agglomeration drums, and dense media separators. The company is also a supplier of single source modular pre-designed and custom designed plants and circuits.

The Jameson Cell is a high-intensity froth flotation cell that was invented by Laureate Professor Graeme Jameson of the University of Newcastle (Australia) and developed in conjunction with Mount Isa Mines Limited.

A pusher centrifuge is a type of filtration technique that offers continuous operation to de-water and wash materials such as relatively in-compressible feed solids, free-draining crystalline, polymers and fibrous substances. It consists of a constant speed rotor and is fixed to one of several baskets. This assembly is applied with centrifugal force that is generated mechanically for smaller units and hydraulically for larger units to enable separation.
References
- ↑ Altman, K., Schaffner, M., & McTavish, S. (2002). D. J. Barrat; H. N. Doug; A. L. Mular (eds.). Mineral Processing Plant Design, Practice and Control. Littleton, Colorado, USA: Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration, Inc. (SME). pp. 1631–1643.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)