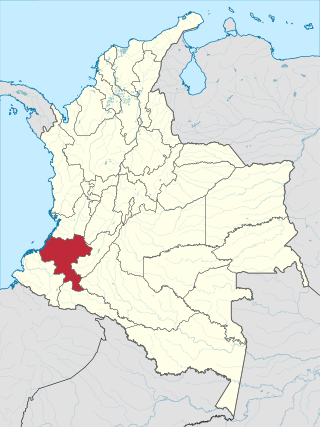
Cauca Department is a department of Southwestern Colombia. Located in the southwestern part of the country, facing the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Valle del Cauca Department to the north, Tolima Department to the northeast, Huila Department to the east, and Nariño Department to the south. Putumayo and Caqueta Departments border the southeast portion of Cauca Department as well. It covers a total area of 29,308 km2 (11,316 sq mi), the 13th largest in Colombia. Its capital is the city of Popayán. The offshore island of Malpelo belongs to the department. It is located in the southwest of the country, mainly in the Andean and Pacific regions plus a tiny part (Piamonte) in the Amazonian region. The area makes up 2.56% of the country.
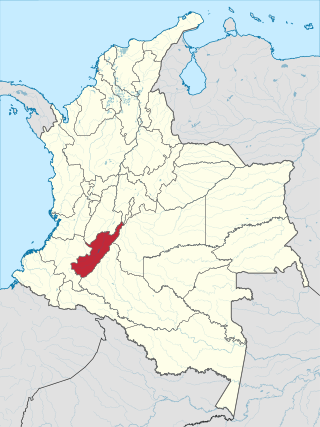
Huila is one of the departments of Colombia. It is located in the southwest of the country, and its capital is Neiva.

Neiva is the capital of the Department of Huila. It is located in the valley of the Magdalena River in south central Colombia with a municipal population of 357,392. It is one of the most important cities in southern Colombia, mainly because of its strategic geographical location.
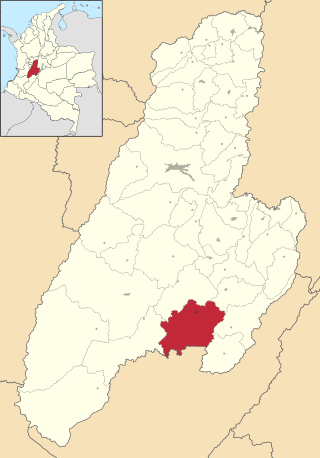
Natagaima is a town and municipality in the Tolima department of Colombia, on the shore of the Magdalena River, at 326 meters (1,070 ft) above sea level. The population of the municipality was 21,324 as of the 1993 census, and its average temperature is 26 °C (79 °F). Natagaima was founded in 1606 by Spanish conqueror Juan de Borja y Armendia.

La Unión is a municipality in Colombia, located in the Eastern subregion of the department of Antioquia. It is bordered to the north by the municipalities of La Ceja and El Carmen de Viboral, to the east by El Carmen de Viboral, to the south by the municipality of Abejorral, and to the west by the municipality of La Ceja. Its capital is 57 kilometers away from Medellín, the capital of the department of Antioquia. The municipality covers an area of 198 square kilometers.
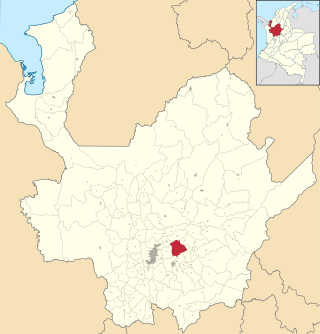
San Vicente Ferrer is a town and municipality in Antioquia Department, Colombia. The population was 18,051 at the 2018 census. The town of San Vicente is part of the sub-region of Eastern Antioquia.

Titiribí is a town and municipality in the Colombian department of Antioquia. Located at an elevation of 1,550 m above sea level, it is part of the sub-region of Southwestern Antioquia.

Rionegro is a city and municipality in Antioquia Department, Colombia, located in the subregion of Eastern Antioquia. The official name of the city is Ciudad Santiago de Arma de Rionegro. Rio Negro means "Black River" in Spanish, as the city received its name after a river that looks black because of the shadows cast by trees. The river traverses the city and it is the most prominent geographical feature of the municipality. Rionegro is also sometimes called the Cuna de la democracia as it was one of the most important cities during the era of the Colombia's struggle for independence and the 1863 constitution was written in the city.

La Guajira is a department of Colombia. It occupies most of the Guajira Peninsula in the northeast region of the country, on the Caribbean Sea and bordering Venezuela, at the northernmost tip of South America. The capital city of the department is Riohacha.

Tolima is one of the 32 departments of Colombia, located in the Andean region, in the center-west of the country. It is bordered on the north and the west by the department of Caldas; on the east by the department of Cundinamarca; on the south by the department of Huila, and on the west by the departments of Cauca, Valle del Cauca, Quindío and Risaralda. Tolima has a surface area of 23,562 km2, and its capital is Ibagué. The department of Tolima was created in 1861 from a part of what was previously Cundinamarca.

Acandí is a town in Colombia at the northern extremity of the department of Chocó in the northwest of Colombia, bordering Panama and the Caribbean Sea. It is 366 km (227 mi) from the department's capital, Quibdó. Its average temperature is 28 degrees Celsius (82 °F). It was founded around the year 1887, and it became a municipality in 1905, previously being part of Turbo. The name "Acandí" is a corruption of the indigenous word "Acanti", which means "River of Stone".

Caquetá Department is a department of Colombia. Located in the Amazonas region, Caquetá borders with the departments of Cauca and Huila to the west, the department of Meta to the north, the department of Guaviare to the northeast, the department of Vaupés to the east, the departments of Amazonas and Putumayo to the south covering a total area of 88,965 km², the third largest in the country. Its capital is the city of Florencia.

Viterbo is a town and municipality in the Colombian Department of Caldas. Formally constituted as a municipality on December 31, 1951, it was founded on April 19, 1911 by Presbítero Nazario Restrepo Botero. The current mayor is Jhon Mario Giraldo Arrubla. They call it "El Paraiso Turistico de Caldas" (The Touristic Paradise of The Colombian Department of Caldas. It is known as this due to its all year through warm climate, Villas, Farms and Condominiums around the surrounding land, and the welcoming people of the 'Viterbeños'.

Timbiqui is a town and municipality in the Cauca Department, Colombia. It is located on the Pacific Coast of Colombia on the estuary of the Timbiqui River. An earthquake affected its inhabitants on the first of October, 2012.

Baraya is a town and municipality in the Huila Department of Colombia.

Garzon is a town and municipality in the Huila Department, Colombia.
Iquira is a town and municipality in the Huila Department, Colombia.

Santa María is a town and municipality in the Huila Department, Colombia.

Florencia is a municipality and the capital city of the Department of Caquetá, Colombia. It is the most populous city in the Amazon Region of Colombia. It lies on the Orteguaza River which flows into the Caqueta River. Its population is 177,946 in 2023.

La Ceja del Tambo, known as La Ceja, is a town and municipality in the Antioquia Department of Colombia. It is part of the subregion of Eastern Antioquia. La Ceja borders the Rionegro and Carmen de Viboral municipalities to the north, La Unión to the east, and Montebello and Retiro to the west. It is located approximately 41 kilometers from Medellín, the department capital.






















