Related Research Articles

STS-51-G was the 18th flight of NASA's Space Shuttle program, and the fifth flight of Space Shuttle Discovery. The seven-day mission launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on June 17, 1985, and landed at Edwards Air Force Base, California, on June 24. Sultan bin Salman Al Saud of Saudi Arabia was on board as a payload specialist; Al Saud became the first Arab, the first Muslim, and the first member of a royal family to fly into space. It was also the first Space Shuttle mission which flew without at least one astronaut from the pre-Shuttle era among its crew.
Telstar 301 is an American communications satellite launched in July 1983 and operated by AT&T. It was one of three Telstar 3 satellites, followed by Telstar 302 in 1984 and Telstar 303 in 1985.
AlphaStar Digital Television was a direct-to-home satellite broadcasting service for the United States market developed by Canadian firm Tee-Comm Electronics. It was the first direct-to-home satellite broadcasting service in the United States to use the internationally accepted DVB-S broadcasting standard and used 39" satellite dish receivers. AlphaStar service launched in July 1996 but was discontinued completely by September 1997 with 40,000 subscribers as the company went through bankruptcy proceedings. The American assets of AlphaStar was used under the auspices of the Champion Telecom Platform which used to own the AlphaStar brand. AlphaStar would also have alleviated a shortage of Canadian satellite capacity by using foreign (US) satellite capacity to fill Canadian needs—indeed this was a requirement for the Canadian company to obtain its license from Canada to commence broadcasting. Tee-Comm, the parent company of AlphaStar had originally co-founded the partnership that created ExpressVu as technology supplier but later divested all interest in ExpressVu.
AsiaSat 2 was a Hong Kong communications satellite, which was owned, and was initially operated, by the Hong Kong based Asia Satellite Telecommunications Company. It was positioned in geostationary orbit at a longitude of 17° East of the Greenwich Meridian, on lease to Spacecom. It spent most of its operational life at 100.5° East, from where it was used to provide fixed satellite services, including broadcasting, audio and data transmission, to Asia and the Pacific Ocean.
NEXTSat, or Next Generation Satellite and Commodities Spacecraft (NEXTSat/CSC) is an American technology demonstration satellite which was operated as part of the Orbital Express programme. It was used as a target spacecraft for a demonstration of autonomous servicing and refueling operations performed by the ASTRO satellite. Launched in March 2007, it was operated for four months, and then deactivated in orbit.
Galaxy 26 is a communications satellite owned by Intelsat. It was built by Space Systems/Loral, as part of its FS-1300 line. Galaxy 26 was formerly known as Intelsat Americas 6 and Telstar 6. It was launched aboard a Proton-K/DM3 from Baykonur LC81.

This article outlines notable events occurring in 1994 in spaceflight, including major launches and EVAs.

Telstar is the name of various communications satellites. The first two Telstar satellites were experimental and nearly identical. Telstar 1 launched on top of a Thor-Delta rocket on July 10, 1962. It successfully relayed through space the first television pictures, telephone calls, and telegraph images, and provided the first live transatlantic television feed. Telstar 2 launched May 7, 1963. Telstar 1 and 2—though no longer functional—still orbit the Earth.
Telstar 14R, also known as Estrela do Sul 2 is a commercial communications satellite in the Telstar series built by Space Systems/Loral for Telesat to provide Ku-band communications to South America and the Southern United States. It is a replacement for Telstar 14, whose north solar array failed to open after launch, limiting its mission effectiveness. Telstar 14R experienced the same problem, with its north solar array failing to open too, but is now in service despite that failure.
Telstar 14 or Estrela do Sul 1 is a commercial communications satellite in the Telstar series built by Space Systems/Loral (SS/L) for Telesat to provide Ku-band communications to South America and the Southern United States. Estrela do Sul 1 was launched by Sea Launch using a Zenit-3SL carrier rocket on 11 Jan 2004 for geosynchronous orbit at 63 degrees west.
Yamal-402 is a Russian geostationary communications satellite. It was launched on 8 December 2012, 13:13:43 UTC from Site 200/39 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. It was built by Thales Alenia Space, and is based on the Spacebus 4000C3 satellite bus. It is equipped with 46 J band transponders. It has a design life of 15 years, but reducing to 11 years expected after launch partial failure.

USA-256, also known as GPS IIF-7, GPS SVN-68 and NAVSTAR 71, is an American navigation satellite which forms part of the Global Positioning System. It was the seventh of twelve Block IIF satellites to be launched.

USA-258, also known as GPS IIF-8, GPS SVN-69 and NAVSTAR 72, is an American navigation satellite which forms part of the Global Positioning System. It was the eighth of twelve Block IIF satellites to be launched.
Yamal-401 is a Russian geostationary communications satellite operated by Gazprom Space Systems. It was built by ISS Reshetnev and is based on the Ekspress-2000 satellite bus. It is equipped with 17 C band and 36 Ku band transponders. It has a design life of 15 years.

Telstar 303 is a U.S. communications satellite launched from Space ShuttleDiscovery during STS-51-G on 17 June 1985. Owned by AT&T and operated by Loral Skynet Hughes, it was one of three Telstar 3 satellites, Preceded by Telstar 301 in 1983 and Telstar 302 in 1984.
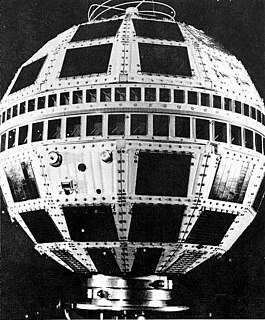
Telstar 2 was a communications satellite launched by NASA on May 7, 1963. It remained active for 2 years.
Telstar 18V(Telstar 18 Vantage / APStar 5C) is a communication satellite in the Telstar series of the Canadian satellite communications company Telesat. T18V will be equipped with C and Ku-band transponders and operate from 138° East. At 7,060 kilograms (15,560 lb), it is the second-heaviest communication satellite ever launched, weighing slightly less than its sibling Telstar 19V.
Telstar 402 was a communications satellite owned by AT&T Corporation.
Telstar 4 was a communications satellite owned by AT&T Corporation.
References
- ↑ McDowell, Jonathan. "Satellite Catalog". Jonathan's Space Page. Retrieved 24 October 2013.