
Chrysolepis is a small genus of plants in the family Fagaceae, endemic to the western United States. Its two species have the common name chinquapin. The genus occurs from western Washington south to the Transverse Ranges in Southern California, and east into Nevada.

Manglares de Tumbes National Sanctuary is a protected natural area located in the region of Tumbes, Peru. Established in 1988, it protects the largest area of mangrove forest in Peru.

Sophora chrysophylla, known as māmane in Hawaiian, is a species of flowering plant in the pea and bean family, Fabaceae, that is endemic to Hawaii. It is highly polymorphic, growing as a shrub or tree, and able to reach a height of 15 m (49 ft) in tree form. Yellow flowers are produced in winter and spring.
Tephrosia odorata is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in Yemen. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry lowland grassland.

Tephrosia is a genus of flowering plants in the pea family, Fabaceae. It is widespread in both the Eastern and Western Hemisphere, where it is found in tropical and warm-temperate regions.
Tephrosia socotrana is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae.

Tephrosia purpurea is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, that has a pantropical distribution. It is a common wasteland weed. In many parts it is under cultivation as green manure crop. It is found throughout India and Sri Lanka in poor soils.

Tephrosia virginiana, also known as goat-rue, goat's rue, catgut, rabbit pea, and Virginia tephrosia, is a perennial dicot in family Fabaceae. This subshrub has alternate compound leaves. Its leaves are imparipinnate, with relatively wide pinnae. All parts of the plant are pubescent giving it a silvery, hoary appearance. The terminal, compact racemes of cream and deep pink flowers bloom May to August. This plant prefers acidic soils, in part to full sun. It grows throughout the Midwest, New England and southeastern United States. Not easy to propagate, this plant can be found in sand savannas, open woods and glades, prairies and rocky soils. All tissues of this plant are toxic, and should not be eaten by people or livestock. Crushed stems were previously used as a fish poison.
Tephrosia clementii is a plant species, endemic to the north-west of Western Australia. It is an annual with a prostrate, spreading habit, growing to between 0.1 and 0.25 metres high. Orange or red flowers are produced between January and March in the species' native range.

Tephrosia rosea, commonly known as Flinders River poison, is a plant species, endemic to northern Australia. It is a shrub with an erect or sprawling habit, growing to between 0.2 and 2 metres high. Pink to purple flowers are produced throughout the year in the species' native range.

Tephrosia vogelii, the Vogel's tephrosia, fish-poison-bean or Vogel tephrosia (English), tefrósia (Portuguese) or barbasco guineano (Spanish), is a flowering plant species in the genus Tephrosia.

Chrysolepis chrysophylla is a species of flowering shrub or tree in the beech family known by the common names golden chinquapin, giant chinquapin, and western chinquapin. It is native to the Pacific coast of the United States.

Heteropterys chrysophylla is a plant species that grows in South America and can be found from Brazil to Argentina.

Phlomis chrysophylla, the golden-leaved Jerusalem sage, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae, native to southwest Asia. It is an evergreen shrub growing to 1 m (3 ft) tall by 1.2 m (4 ft) wide, with woolly-textured, sage-like leaves that turn lime green with age, and yellow flowers carried in the leaf axils in early summer.
James Francis Macbride was an American botanist who devoted most of his professional life to the study of the flora of Peru. Born on 19 May 1892 in Rock Valley, Iowa, Macbride graduated from the University of Wyoming in 1914 and worked briefly at the Gray Herbarium, Harvard University.

Tephrosia apollinea is a legume species, native to southwest Asia and northeast Africa.
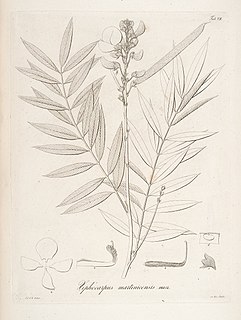
Tephrosia candida, the white hoarypea, is a perennial shrub, native to India, in the legume family. It has been introduced to Malesia, South America, Africa, South East Asia and Australia.

Roosfontein Nature Reserve is a protected nature area in Durban, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Threatened protected species such as the Dwarf Chameleon and Tephrosia inandensis are found in the reserve, which is an example of North Coast Grassland.

Tephrosia glomeruliflora, or pink tephrosia, is a perennial (non-climbing) herb in the family Fabaceae, endemic to South Africa. It is also found on the eastern coast of Australia, in New South Wales and Queensland, where it is considered an environmental weed.

Tephrosia onobrychoides, commonly called multi-bloom hoary pea, is a species of plant in the pea family that is native to Texas, Louisiana, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Mississippi, and Alabama in the United States of America.















