
Terminalia is a genus of large trees of the flowering plant family Combretaceae, comprising nearly 300 species distributed in tropical regions of the world. The genus name derives from the Latin word terminus, referring to the fact that the leaves appear at the very tips of the shoots.

Terminalia catappa is a large tropical tree in the leadwood tree family, Combretaceae, native to Asia, Australia, the Pacific, Madagascar and Seychelles. Common names in English include country almond, Indian almond, Malabar almond, sea almond, tropical almond, beach almond and false kamani.
Heneicosane is the organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)19CH3. It is the straight chain, saturated C21 hydrocarbon. It is a white wax.

Citrullus colocynthis, with many common names including Abu Jahl's melon, colocynth, bitter apple, bitter cucumber, egusi, vine of Sodom, or wild gourd, is a poisonous desert viny plant native to the Mediterranean Basin and West Asia, especially the Levant, Turkey, and Nubia.

Kainji National Park is a national park in Niger State and Kwara State, Nigeria. Established in 1978, it covers an area of about 5,341 km2 (2,062 sq mi). The park includes three distinct sectors: a part of the Kainji Lake in which fishing is restricted, the Borgu Game Reserve to the west of the lake, and the Zugurma Game Reserve to the southeast.

Punicalagin (Pyuni-cala-jen) is an ellagitannin, a type of phenolic compound. It is found as alpha and beta isomers in pomegranates, Terminalia catappa, Terminalia myriocarpa, and in Combretum molle, the velvet bushwillow, a plant species found in South Africa. These three genera are all Myrtales and the last two are both Combretaceae.

Terminalia chebula, commonly known as black- or chebulic myrobalan, is a species of Terminalia, native to South Asia from Pakistan, India and Nepal east to southwest China (Yunnan), and south to Sri Lanka, Malaysia, and Vietnam.

Galba truncatula is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Lymnaeidae, the pond snails.
Terminalia schimperiana is a species of Terminalia, native to tropical Africa from Guinea and Sierra Leone east to Uganda and Ethiopia.

Terminalia leiocarpa is a species of tree in the genus Terminalia. It is a deciduous tree native of tropical Africa from Senegal and Guinea in the west to Eritrea in the east and as far south as the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Bao BolongWetland Reserve is a protected area in The Gambia. Established in 1996, it covers 296.5 square kilometres.
Plasmodium megaglobularis is a species of malaria-causing parasite in the genus Plasmodium, subgenus Novyella. As in all Plasmodium species, P. megaglobularis has both vertebrate and insect hosts. The vertebrate hosts for this parasite are birds.

Chrysomya megacephala, more commonly known as the oriental latrine fly or oriental blue fly, is a member of the family Calliphoridae (blowflies). It is a warm-weather fly with a greenish-blue metallic box-like body. The fly infests corpses soon after death, making it important to forensic science. This fly is implicated in some public health issues; it can be the cause of myiasis, and also infects fish and livestock.

Mole National Park, one of Ghana's seven national parks, is the country's largest wildlife refuge. The park is located in the Savannah region of Ghana on savanna and riparian ecosystems at an elevation of 50 m, with a sharp escarpment forming the southern boundary of the park. The Park is 24 km from Damongo, the district capital, 146 km south east of Tamale, the Regional capital. The park is 700 km from Accra and 430 km from Kumasi. The park's entrance is reached through the nearby town of Larabanga. It covers an area of about 4,577 square kilometers of fairly undisturbed Guinea savannah in the northern part of Ghana. The Levi and Mole Rivers are ephemeral rivers flowing through the park, leaving behind only drinking holes during the long dry season. This area of Ghana receives over 10 mm per year of rainfall. A long-term study has been done on Mole National Park to understand the impact of human hunters on the animals in the preserve.

Castalagin is an ellagitannin, a type of hydrolyzable tannin, found in oak and chestnut wood and in the stem barks of Terminalia leiocarpa and Terminalia avicennoides.

Terminalia arjuna is a tree of the genus Terminalia. It is commonly known as arjuna or arjun tree in English. It is used as a traditional medicinal plant.
Tergallic acids are trimers of gallic acid, often found naturally in the form of glycosides. Tergallic acid O- or C-glucosides that can be found in acorns of several Quercus (oak) species. The dehydrated tergallic acid C-glucoside and tergallic acid O-glucoside can be characterised in the acorns of Quercus macrocarpa. Dehydrated tergallic-C-glucoside can be found in the cork from Quercus suber.
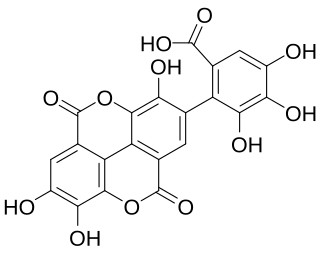
Flavogallonic acid dilactone is a hydrolysable tannin that can be found in Rhynchosia volubilis seeds, in Shorea laevifolia, in Anogeissus leiocarpus and Terminalia avicennoides.

Terminalia macroptera is a species of flowering plant in the Combretaceae known by the Hausa common name kwandari. It is native to Africa, where it can be found in Benin, Burkina Faso, Ghana, Senegal, Sudan, Uganda, and Nigeria.
Haemoproteus vacuolatus is a parasite. It was found in Andropadus latirostris in Ghana and Cameroon.














