Psilocybe is a genus of gilled mushrooms, growing worldwide, in the family Hymenogastraceae. Most or nearly all species contain the psychedelic compounds psilocybin and psilocin.

The Caribbean hermit crab, also known as the soldier crab, West Atlantic crab, tree crab, or purple pincher, is a species of land hermit crab native to the west Atlantic, Belize, southern Florida, Venezuela, and the West Indies.

Macrolepiota is a genus of white spored, gilled mushrooms of the family Agaricaceae. The best-known member is the parasol mushroom (M. procera). The widespread genus contains about 40 species.

Rigidoporus microporus is a plant pathogen, known to cause white root rot disease on various tropical crops, such as cacao, cassava, tea, with economical importance on the para rubber tree.

Termitomyces, the termite mushrooms, is a genus of basidiomycete fungi belonging to the family Lyophyllaceae. All of which are completely dependent on fungus-growing termites, the Macrotermitinae, to survive, and vice versa. They are the food source for these termites, who enjoy an obligate symbiosis with the genus similar to that between Atta ants and Attamyces mushrooms. Termitomyces mushrooms are edible, and are highly regarded for their flavor.
Roger Heim was a French botanist specialising in mycology and tropical phytopathology. He was known for his studies describing the anatomy of the mushroom hymenium, the systematics and phylogeny of higher fungi, the mycology of tropical fungi such as Termitomyces, as well as ethnomycological work on hallucinogenic fungi, like Psilocybe and Stropharia. In his career, he published over 560 articles, scientific reviews, and major works in fields like botany, chemistry, education, forestry, horticulture, liberal arts, medicine and zoology.
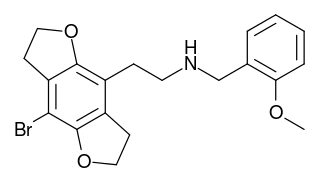
2CBFly-NBOMe is a compound indirectly derived from the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, and related to benzodifurans like 2C-B-FLY and N-benzylphenethylamines like 25I-NBOMe. It was discovered in 2002, and further researched by Ralf Heim at the Free University of Berlin, and subsequently investigated in more detail by a team at Purdue University led by David E. Nichols. It acts as a potent partial agonist for the 5-HT2A serotonin receptor subtype.
Macrolepiota albuminosa is a species of agaric fungus in the family Agaricaceae, found in Peradeniya, Ceylon.

25TFM-NBOMe is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-TFM, discovered in 2004 by Ralf Heim at the Free University of Berlin. It acts as a potent partial agonist for the 5-HT2A receptor, though its relative potency is disputed, with some studies finding it to be of lower potency than 25I-NBOMe, while others show it to be of similar or higher potency, possibly because of differences in the assay used. 2C-TFM-NB2OMe can be taken to produce psychedelic effects similar to 2C-I-NB2OMe and 2C-D-NB2OMe.

Termitomyces le-testui is a species of agaric fungus in the family Lyophyllaceae. It was first described scientifically from Africa by French mycologist Narcisse Théophile Patouillard in 1916, and transferred to the genus Termitomyces by Roger Heim in 1942. The mushroom is edible and used as food.

Termitomyces tylerianus is a species of agaric fungus in the family Lyophyllaceae. Found in Africa and China, it was first formally described in 1964. Fruit bodies (mushrooms) grow in groups or clusters near termite nests in deciduous forests. The mushrooms are edible.

Termitomyces microcarpus is a species of agaric fungus in the family Lyophyllaceae. An edible species, it is found in Africa and Asia, where it grows in groups or clusters in deciduous forests near the roots of bamboo stumps associated with termite nests.

Termitomyces heimii is a species of agaric fungus in the family Lyophyllaceae. It has symbiotic relationship with termites. Described as new to science in 1979, it is found in India. The specific epithet heimii honors French mycologist Roger Heim. The fruit bodies (mushrooms) produced by the fungus are edible.

Termitomyces schimperi is a large mushroom associated with the termite species Macrotermes michaelseni. It grows in the northern part of Southern Africa, from northern Namibia up to Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), eastwards to Malawi and Mozambique, and westwards to Ivory Coast.

Termitomyces eurrhizus species of agaric fungus in the family Lyophyllaceae native to Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka, Burma, southwestern China and Malaysia. The fungus has a symbiotic relationship with termites, its mushrooms growing out of mounds after periods of rainfall. It is eaten in Malaysia and the Indian subcontinent.

Macrotermes natalensis is a fungus-growing termite species that belongs to the genus Macrotermes. This species is associated with the Termitomyces fungal genus. M. natalensis has domesticated Termitomyces to produce food for the colony. Both termite species- fungal genus- are obligate and mutually beneficial where termite relies on the fungus to break down for plant materiel and nutrient resource. In contrast, the fungal species obtain plant material and optimal conditions for growth.

Louise Payton Heims Beck, sometimes referred to as Mrs. Martin Beck, was an American librarian who became a vaudeville performer and the wife of theatre impresario Martin Beck. She assisted her husband in his theatrical enterprises until his death in 1940, after which she took over the management of his eponymous Broadway theatre. Along with Antoinette Perry and several other women, she co-founded the American Theater Wing (ATW) in its revived and revised version in 1940. She served as one of the directors of the ATW in its early years, and played a critical role in establishing both the Stage Door Canteen during World War II and the Tony Awards in 1947. She was chairman of the governing board of the Actors' Fund of America from 1960 until her death in 1978.