
The aardwolf is an insectivorous species of hyena, native to East and Southern Africa. Its name means "earth-wolf" in Afrikaans and Dutch. It is also called the maanhaar-jackal, termite-eating hyena and civet hyena, based on its habit of secreting substances from its anal gland, a characteristic shared with the African civet.

Edible mushrooms are the fleshy fruit bodies of several species of macrofungi. Edibility may be defined by criteria including the absence of poisonous effects on humans and desirable taste and aroma. Edible mushrooms are consumed for their nutritional and culinary value. Mushrooms, especially dried shiitake, are sources of umami flavor.

Termitomyces, the termite mushrooms, is a genus of basidiomycete fungi belonging to the family Lyophyllaceae. All of which are completely dependent on fungus-growing termites, the Macrotermitinae, to survive, and vice versa. They are the food source for these termites, who enjoy an obligate symbiosis with the genus similar to that between Atta ants and Attamyces mushrooms. Termitomyces mushrooms are edible, and are highly regarded for their flavor.

Fungivory or mycophagy is the process of organisms consuming fungi. Many different organisms have been recorded to gain their energy from consuming fungi, including birds, mammals, insects, plants, amoebas, gastropods, nematodes, bacteria and other fungi. Some of these, which only eat fungi, are called fungivores whereas others eat fungi as only part of their diet, being omnivores.

The Macrotermitinae, the fungus-growing termites, constitute a subfamily of the family Termitidae that is only found within the Old World tropics.

Termitomyces titanicus is a species of fungus in the Lyophyllaceae family. Found in West Africa, it has a cap that may reach 1 metre (3 ft) in diameter on a stipe up to 22 inches (57 cm) in length. Termitomyces is symbiotic with termites of the genus Macrotermes who raise the hyphae upon partially digested leaves as their primary foodstuff. T. titanicus was unknown to Western science prior to 1980, even though it was a common item in the native markets. Pegler and Piearce made no attempt to explain its late discovery.

Termitomyces le-testui is a species of agaric fungus in the family Lyophyllaceae. It was first described scientifically from Africa by French mycologist Narcisse Théophile Patouillard in 1916, and transferred to the genus Termitomyces by Roger Heim in 1942. The mushroom is edible and used as food.

Termitomyces microcarpus is a species of agaric fungus in the family Lyophyllaceae. An edible species, it is found in Africa and Asia, where it grows in groups or clusters in deciduous forests near the roots of bamboo stumps associated with termite nests.

Termitomyces reticulatus is a species of agaric fungus in the family Lyophyllaceae. Found in southern Africa, it was described as new to science in 1990. It is associated with the termite species Odontotermes badius and O. transvaalensis, which are widely distributed in South Africa.

Termitomyces heimii is a species of agaric fungus in the family Lyophyllaceae. It has symbiotic relationship with termites. Described as new to science in 1979, it is found in India. The specific epithet heimii honors French mycologist Roger Heim. The fruit bodies (mushrooms) produced by the fungus are edible.

Termitomyces schimperi is a large mushroom associated with the termite species Macrotermes michaelseni. It grows in the northern part of Southern Africa, from northern Namibia up to Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), eastwards to Malawi and Mozambique, and westwards to Ivory Coast.
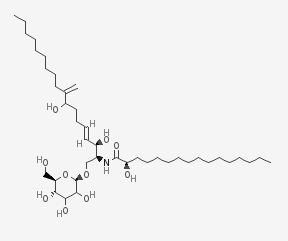
Termitomycesphins A-H are neuritogenic cerebrosides isolated from the mushroom Termitomyces albuminosus.
Hypotermes makhamensis is a species of termite in the subfamily Macrotermitinae of the family Termitidae. It lives in dry evergreen forests in tropical south-eastern Asia and builds termite mounds in which it cultivates fungus for use as food.

Macrotermes michaelseni is a species of termite in the family Termitidae, found in sub-Saharan Africa. It is associated with the fungus Termitomyces schimperi.
Termitomyces robustus is a mushroom in the genus Termitomyces. Attempts at cultivation by humans have failed in past trials.

Termitomyces umkowaan is a species of agaric fungus in the family Lyophyllaceae. Found in South Africa, it was described as new to science in 1889 by Mordecai Cubitt Cooke and George Edward Massee from collections made in Durban. Cooke noted that was "called Umkowaan by the natives, and is delicious when cooked, much superior to the common mushroom." Derek Reid transferred the fungus to the genus Termitomyces in 1975.

Macrotermes is a genus of termites belonging to the subfamily Macrotermitinae and widely distributed throughout Africa and South-East Asia. Well-studied species include Macrotermes natalensis and M. bellicosus.

Termitomyces eurrhizus species of agaric fungus in the family Lyophyllaceae native to Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka, Burma, southwestern China and Malaysia. The fungus has a symbiotic relationship with termites, its mushrooms growing out of mounds after periods of rainfall. It is eaten in Malaysia and the Indian subcontinent.

Macrotermes natalensis is a fungus-growing termite species that belongs to the genus Macrotermes. This species is associated with the Termitomyces fungal genus. M. natalensis has domesticated Termitomyces to produce food for the colony. Both termite species- fungal genus- are obligate and mutually beneficial where termite relies on the fungus to break down for plant materiel and nutrient resource. In contrast, the fungal species obtain plant material and optimal conditions for growth.

Odontotermes is a termite genus belonging to subfamily Macrotermitinae, which is native to the Old World. They are most destructive in wooden homes, and are agricultural pests in the tropics and subtropics of Africa and Asia. It is the most diverse termite genus in Africa, with 78 species recorded.















