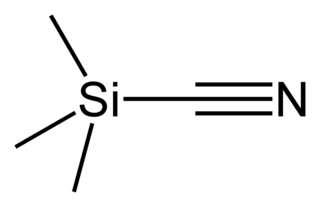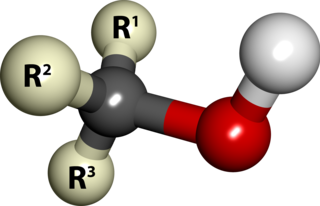
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sucrose and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of hydrocarbons, conferring hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur.

In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.
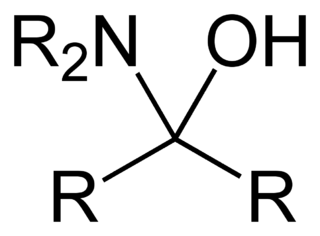
In organic chemistry, a hemiaminal is a functional group or type of chemical compound that has a hydroxyl group and an amine attached to the same carbon atom: −C(OH)(NR2)−. R can be hydrogen or an alkyl group. Hemiaminals are intermediates in imine formation from an amine and a carbonyl by alkylimino-de-oxo-bisubstitution. Hemiaminals can be viewed as a blend of aminals and geminal diol. They are a special case of amino alcohols.

In organic chemistry, an aminal or aminoacetal is a functional group or type of organic compound that has two amine groups attached to the same carbon atom: −C(NR2)(NR2)−.. A common aminal is bis(dimethylamino)methane, a colorless liquid that is prepared by the reaction of dimethylamine and formaldehyde:

Organotin chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organotin compounds or stannanes, which are organometallic compounds containing tin–carbon bonds. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide, discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory.
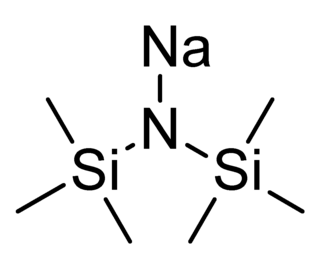
Sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide is the organosilicon compound with the formula NaN(Si 3)2. This species, usually called NaHMDS, is a strong base used for deprotonation reactions or base-catalyzed reactions. Its advantages are that it is commercially available as a solid and it is soluble not only in ethers, such as THF or diethyl ether, but also in aromatic solvents, like benzene and toluene by virtue of the lipophilic TMS groups.
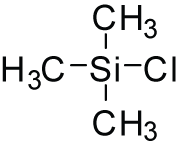
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound, with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry.
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Eschenmoser's salt</span> Ionic compound with the formula [(H3C–)2N–CH2]I](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/28/Eschenmosersalz.png/320px-Eschenmosersalz.png)
In organic chemistry, Eschenmoser's salt is the ionic, organic compound [(CH3)2NCH2]I. It is the iodide salt of the dimethylaminomethylene cation [(CH3)2NCH2]+.
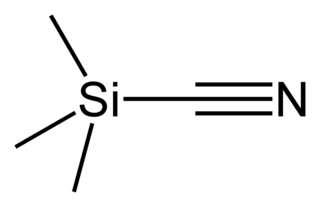
Trimethylsilyl cyanide is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3SiCN. This volatile liquid consists of a cyanide group, that is CN, attached to a trimethylsilyl group. The molecule is used in organic synthesis as the equivalent of hydrogen cyanide. It is prepared by the reaction of lithium cyanide and trimethylsilyl chloride:

Bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride is the chemical compound with the formula [( 3P)2N]Cl, often abbreviated [(Ph3P)2N]Cl, where Ph is phenyl C6H5, or even abbreviated [PPN]Cl or [PNP]Cl or PPNCl or PNPCl, where PPN or PNP stands for (Ph3P)2N. This colorless salt is a source of the [(Ph3P)2N]+ cation, which is used as an unreactive and weakly coordinating cation to isolate reactive anions. [(Ph3P)2N]+ is a phosphazene.
tert-Butyl chloride is the organochloride with the formula (CH3)3CCl. It is a colorless, flammable liquid. It is sparingly soluble in water, with a tendency to undergo hydrolysis to the corresponding tert-butyl alcohol. It is produced industrially as a precursor to other organic compounds.
Dimethyldichlorosilane is a tetrahedral organosilicon compound with the formula Si(CH3)2Cl2. At room temperature it is a colorless liquid that readily reacts with water to form both linear and cyclic Si-O chains. Dimethyldichlorosilane is made on an industrial scale as the principal precursor to dimethylsilicone and polysilane compounds.

The Jones oxidation is an organic reaction for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to carboxylic acids and ketones, respectively. It is named after its discoverer, Sir Ewart Jones. The reaction was an early method for the oxidation of alcohols. Its use has subsided because milder, more selective reagents have been developed, e.g. Collins reagent.

tert-Butylthiol, also known as tert-butyl mercaptan (TBM), and abbreciated t-BuSH, is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)3CSH. This thiol is used as an odorant for natural gas, which is otherwise odorless. It may also have been used as a flavoring agent.

N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylformamidinium chloride is the simplest representative of quaternary formamidinium cations of the general formula [R2N−CH=NR2]+ with a chloride as a counterion in which all hydrogen atoms of the protonated formamidine [HC(=NH2)NH2]+ are replaced by methyl groups.

Tris(dimethylamino)methane (TDAM) is the simplest representative of the tris(dialkylamino)methanes of the general formula (R2N)3CH in which three of the four of methane's hydrogen atoms are replaced by dimethylamino groups (−N(CH3)2). Tris(dimethylamino)methane can be regarded as both an amine and an orthoamide.

3-Dimethylaminoacrolein is an organic compound with the formula Me2NC(H)=CHCHO. It is a pale yellow water-soluble liquid. The compound has a number of useful and unusual properties, e.g. it "causes a reversal of the hypnotic effect of morphine in mice" and has a "stimulating effect in humans".
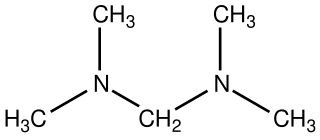
Bis(dimethylamino)methane is the organic compound with the formula [(CH3)2N]2CH2. It is classified as an aminal as well as a ditertiary amine, in fact the simplest. It is a colorless liquid that is widely available. It is prepared by the reaction of dimethylamine and formaldehyde:

tert-Butyl nitrite is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3CONO. A colorless liquid, it is the tert-butyl ester of nitrous acid. It is typically employed as a solution with tert-butyl alcohol.









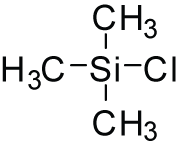
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Eschenmoser's salt</span> Ionic compound with the formula [(H3C–)2N–CH2]I](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/28/Eschenmosersalz.png/320px-Eschenmosersalz.png)