
An octopus is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda. The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the center point of the eight limbs. The soft body can radically alter its shape, enabling octopuses to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their eight appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used both for respiration and for locomotion, by expelling a jet of water. Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse of all invertebrates.

A squid is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius or pen, made of chitin.

A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology.
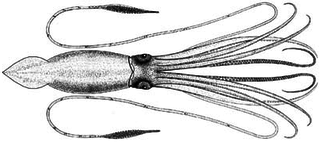
The giant squid is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum size at around 12–13 m (39–43 ft) for females and 10 m (33 ft) for males, from the posterior fins to the tip of the two long tentacles. The mantle of the giant squid is about 2 m long, and the length of the squid excluding its tentacles rarely exceeds 5 m (16 ft). Claims of specimens measuring 20 m (66 ft) or more have not been scientifically documented.

Grimpoteuthis is a genus of pelagic cirrate (finned) octopods known as the dumbo octopuses. The name "dumbo" originates from their resemblance to the title character of Disney's 1941 film Dumbo, having two prominent ear-like fins which extend from the mantle above each eye. There are 17 species recognized in the genus. Prey include crustaceans, bivalves, worms and copepods. The average life span of various Grimpoteuthis species is 3–5 years.

Umbrella octopuses are a group of pelagic octopuses. Umbrella octopuses are characterized by a web of skin between the arms, causing them to somewhat resemble an opened umbrella when the arms are spread.

Vitreledonella richardi, also known as the glass octopus, is an incirrate octopus. It is in the genus Vitreledonella and of the family Amphitretidae.

Tremoctopus is a genus of pelagic cephalopods, containing four species that occupy surface to mid-waters in subtropical and tropical oceans. They are commonly known as blanket octopuses, in reference to the long, transparent webs that connect the dorsal and dorsolateral arms of the adult females. The other arms are much shorter and lack webbing.

The mimic octopus is a species of octopus from the Indo-Pacific region. Like other octopuses, it uses its chromatophores to disguise itself. It is noteworthy for being able to impersonate a wide variety of other marine animals. While many animals mimic either their environment or other animals to avoid predation, the mimic octopus and its close relative the wunderpus are the only ones known to actively imitate several animals in order to elude predators.

Enteroctopus is an octopus genus whose members are sometimes known as giant octopuses.

Cephalopods, which include squids and octopuses, vary enormously in size. The smallest are only about 1 centimetre (0.39 in) long and weigh less than 1 gram (0.035 oz) at maturity, while the giant squid can exceed 10 metres (33 ft) in length and the colossal squid weighs close to half a tonne (1,100 lb), making them the largest living invertebrates. Living species range in mass more than three-billion-fold, or across nine orders of magnitude, from the lightest hatchlings to the heaviest adults. Certain cephalopod species are also noted for having individual body parts of exceptional size.

Callistoctopus macropus, also known as the Atlantic white-spotted octopus, white-spotted octopus, grass octopus or grass scuttle, is a species of octopus found in shallow areas of the Mediterranean Sea, the warmer parts of the eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea, and the Indo-Pacific region. This octopus feeds on small organisms which lurk among the branches of corals.

Macroctopus maorum is known more commonly as the Maori octopus or the New Zealand octopus. It is found in the waters around New Zealand and southern Australia. M. maorum is one of the largest and most aggressive octopus species living in the New Zealand and Australian waters. They feed mainly on crustaceans and fish. Although they have a short life span, the females lay thousands of eggs and are very protective of them.

Cirroteuthis muelleri, also known as the big-finned jellyhead, was the first cirrate octopus species to be scientifically described. It is closely related to the genus Cirrothauma within the family Cirroteuthidae. At present the genus contains a single recognized species restricted to the Arctic Ocean and northern basins of the Atlantic and Pacific, but other species may be present in the southern hemisphere.

The curled octopus, also known as the horned octopus, lesser octopus or northern octopus, is a species of cephalopod found in the northeast Atlantic, ranging from Norway to the Mediterranean, including the British Isles. The total length of an adult is around 50 cm, but their arms are often tightly curled. It immobilises and eats large crustaceans by drilling a hole through their shell. It is mainly by-catch in commercial fisheries of the north eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean, where the common octopus is the preferred species.

Bathypolypus arcticus, the North Atlantic octopus, deep sea octopus or spoonarm octopus is a small species of demersal octopus of the North Atlantic. It is usually found at depths of 200 to 600 m (660–1,970 ft) where the temperature is between 2 and 6 °C (36–43 °F).
Sasakiopus is a genus of octopus containing only one species, Sasakiopus salebrosus, the rough octopus. It is part of the family Enteroctopodidae. Genetic analysis appeared to show that S. salebrosus is the sister taxon of the genera Benthoctopus and Vulcanoctopus, although the former is now considered a synonym of Bathypolypus, the only genus in the family Bathypolypodidae, and the latter as a synonym of Muusoctopus.

Wunderpus photogenicus, the wunderpus octopus, is a small-bodied species of octopus with distinct white and rusty brown coloration. 'Wunderpus' from German “wunder” meaning ‘marvel or wonder’.
Opisthoteuthis calypso or calypso flapjack octopus is a species of genus Opisthoteuthis, which are known as the cirrate octopuses. Octopuses in this genus are known as the flapjack octopuses and can be found in a variety of oceans across the world.

Opisthoteuthis agassizii is a lesser-known, deep-sea octopus first described in 1883 by Addison E. Verrill.

















