
A larva is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.

Silphidae is a family of beetles that are known commonly as large carrion beetles, carrion beetles or burying beetles. There are two subfamilies: Silphinae and Nicrophorinae. Members of Nicrophorinae are sometimes known as burying beetles or sexton beetles. The number of species is relatively small, at around two hundred. They are more diverse in the temperate region although a few tropical endemics are known. Both subfamilies feed on decaying organic matter such as dead animals. The subfamilies differ in which uses parental care and which types of carcasses they prefer. Silphidae are considered to be of importance to forensic entomologists because when they are found on a decaying body they are used to help estimate a post-mortem interval.

The insects of the beetle family Chrysomelidae are commonly known as leaf beetles, and include over 37,000 species in more than 2,500 genera, making up one of the largest and most commonly encountered of all beetle families. Numerous subfamilies are recognized, but the precise taxonomy and systematics are likely to change with ongoing research.

The cinnabar moth is a brightly coloured arctiid moth found as a native species in Europe and western and central Asia then east across the Palearctic to Siberia to China. It has been introduced into New Zealand, Australia and North America to control ragwort, on which its larvae feed. The moth is named after the red mineral cinnabar because of the red patches on its predominantly black wings. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. Cinnabar moths are about 20 mm (0.79 in) long and have a wingspan of 32–42 mm (1.3–1.7 in).
The Prodoxidae are a family of moths, generally small in size and nondescript in appearance. They include species of moderate pest status, such as the currant shoot borer, and others of considerable ecological and evolutionary interest, such as various species of "yucca moths".

The caddisflies, or order Trichoptera, are a group of insects with aquatic larvae and terrestrial adults. There are approximately 14,500 described species, most of which can be divided into the suborders Integripalpia and Annulipalpia on the basis of the adult mouthparts. Integripalpian larvae construct a portable casing to protect themselves as they move around looking for food, while annulipalpian larvae make themselves a fixed retreat in which they remain, waiting for food to come to them. The affinities of the small third suborder Spicipalpia are unclear, and molecular analysis suggests it may not be monophyletic. Also called sedge-flies or rail-flies, the adults are small moth-like insects with two pairs of hairy membranous wings. They are closely related to the Lepidoptera which have scales on their wings; the two orders together form the superorder Amphiesmenoptera.
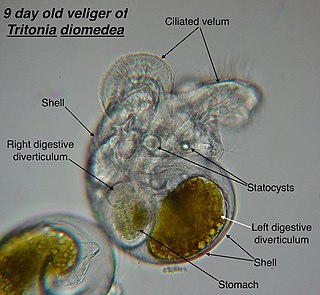
A veliger is the planktonic larva of many kinds of sea snails and freshwater snails, as well as most bivalve molluscs (clams) and tusk shells.

Notodontidae is a family of moths with approximately 3,800 known species. The family was described by James Francis Stephens in 1829. Moths of this family are found in all parts of the world, but they are most concentrated in tropical areas, especially in the New World.

The Tenebrionoidea are a very large and diverse superfamily of beetles. It generally corresponds to the Heteromera of earlier authors.

The Asilidae are the robber fly family, also called assassin flies. They are powerfully built, bristly flies with a short, stout proboscis enclosing the sharp, sucking hypopharynx. The name "robber flies" reflects their expert predatory habits; they feed mainly or exclusively on other insects and, as a rule, they wait in ambush and catch their prey in flight.

The soldier flies are a family of flies. The family contains over 2,700 species in over 380 extant genera worldwide. Larvae are found in a wide array of locations, mostly in wetlands, damp places in soil, sod, under bark, in animal excrement, and in decaying organic matter. Adults are found near larval habitats. They are diverse in size and shape, though they commonly are partly or wholly metallic green, or somewhat wasplike mimics, marked with black and yellow or green and sometimes metallic. They are often rather inactive flies which typically rest with their wings placed one above the other over the abdomen.

Phyllophaga is a very large genus of New World scarab beetles in the subfamily Melolonthinae. Common names for this genus and many other related genera in the subfamily Melolonthinae are May beetles, June bugs, and July beetles. They range in size from 12 to 35 mm and are blackish or reddish-brown in colour, without prominent markings, and often rather hairy ventrally. These beetles are nocturnal, and are attracted to artificial lights in great numbers.

The family Oedemeridae is a cosmopolitan group of beetles commonly known as false blister beetles, though some recent authors have coined the name pollen-feeding beetles. There are some 100 genera and 1,500 species in the family, mostly associated with rotting wood as larvae, though adults are quite common on flowers. The family was erected by Pierre André Latreille in 1810.

Gracillariidae is an important family of insects in the order Lepidoptera and the principal family of leaf miners that includes several economic, horticultural or recently invasive pest species such as the horse-chestnut leaf miner, Cameraria ohridella.

Cleridae are a family of beetles of the superfamily Cleroidea. They are commonly known as checkered beetles. The family Cleridae has a worldwide distribution, and a variety of habitats and feeding preferences.

Miletinae is a subfamily of the family Lycaenidae of butterflies, commonly called harvesters and woolly legs, and virtually unique among butterflies in having predatory larvae. Miletinae are entirely aphytophagous. The ecology of the Miletinae is little understood, but adults and larvae live in association with ants, and most known species feed on Hemiptera, though some, like Liphyra, feed on the ants themselves. The butterflies, ants, and hemipterans, in some cases, seem to have complex symbiotic relationships benefiting all.

The Megalopodidae are a small family of leaf beetles, previously included as a subfamily within the Chrysomelidae. One of its constituent subfamilies, Zeugophorinae, has also frequently been treated as a subfamily within Chrysomelidae. The family contains approximately 30 genera worldwide, primarily in the nominate subfamily Megalopodinae, and mostly circumtropical.

Anthribidae is a family of beetles also known as fungus weevils. The antennae are not elbowed, may occasionally be longer than the body and thread-like, and can be the longest of any members of Curculionoidea. As in the Nemonychidae, the labrum appears as a separate segment to the clypeus, and the maxillary palps are long and projecting.

Eristalinae are one of the four subfamilies of the fly family Syrphidae, or hoverflies. A well-known species included in this subfamily is the dronefly, Eristalis tenax.

The Erebidae are a family of moths in the superfamily Noctuoidea. The family is among the largest families of moths by species count and contains a wide variety of well-known macromoth groups. The family includes the underwings (Catocala); litter moths (Herminiinae); tiger, lichen, and wasp moths (Arctiinae); tussock moths (Lymantriinae), including the arctic woolly bear moth ; fruit-piercing moths ; micronoctuoid moths (Micronoctuini); snout moths (Hypeninae); and zales, though many of these common names can also refer to moths outside the Erebidae. Some of the erebid moths are called owlets.


















