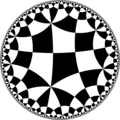
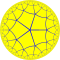
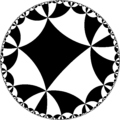
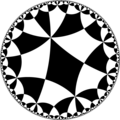
| Tetraoctagonal tiling | |
|---|---|
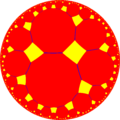
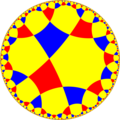
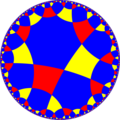
 Poincaré disk model of the hyperbolic plane | |
| Type | Hyperbolic uniform tiling |
| Vertex configuration | (4.8)2 |
| Schläfli symbol | r{8,4} or rr{8,8} rr(4,4,4) t0,1,2,3(∞,4,∞,4) |
| Wythoff symbol | 2 | 8 4 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | [8,4], (*842) [8,8], (*882) [(4,4,4)], (*444) [(∞,4,∞,4)], (*4242) |
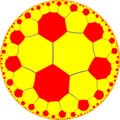
| Dual | Order-8-4 quasiregular rhombic tiling |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive edge-transitive |
In geometry, the tetraoctagonal tiling is a uniform tiling of the hyperbolic plane.