
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Hepatitis is acute if it resolves within six months, and chronic if it lasts longer than six months. Acute hepatitis can resolve on its own, progress to chronic hepatitis, or (rarely) result in acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may progress to scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), liver failure, and liver cancer.

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and yellow tinged skin. The virus persists in the liver, becoming chronic, in about 70% of those initially infected. Early on, chronic infection typically has no symptoms. Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop serious complications such as liver failure, liver cancer, or dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach.
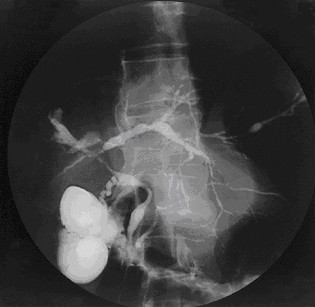
Hepatology is the branch of medicine that incorporates the study of liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas as well as management of their disorders. Although traditionally considered a sub-specialty of gastroenterology, rapid expansion has led in some countries to doctors specializing solely on this area, who are called hepatologists.

Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.

Alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also called alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), is a term that encompasses the liver manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.

Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, although availability of donor organs is a major limitation. The most common technique is orthotopic transplantation, in which the native liver is removed and replaced by the donor organ in the same anatomic position as the original liver. The surgical procedure is complex, requiring careful harvest of the donor organ and meticulous implantation into the recipient. Liver transplantation is highly regulated, and only performed at designated transplant medical centers by highly trained transplant physicians and supporting medical team. Favorable outcomes require careful screening for eligible recipients, as well as a well-calibrated live or deceased donor match.

Alcoholic hepatitis is hepatitis due to excessive intake of alcohol. Patients typically have a history of at least 10 years of heavy alcohol intake, typically 8-10 drinks per day. It is usually found in association with fatty liver, an early stage of alcoholic liver disease, and may contribute to the progression of fibrosis, leading to cirrhosis. Symptoms may present acutely after a large amount of alcoholic intake in a short time period, or after years of excess alcohol intake. Signs and symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis include jaundice, ascites, fatigue and hepatic encephalopathy. Mild cases are self-limiting, but severe cases have a high risk of death. Severe cases may be treated with glucocorticoids. The condition often comes on suddenly and may progress in severity very rapidly.

Autoimmune hepatitis, formerly known as lupoid hepatitis, plasma cell hepatitis, or autoimmune chronic active hepatitis, is a chronic, autoimmune disease of the liver that occurs when the body's immune system attacks liver cells, causing the liver to be inflamed. Common initial symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, muscle aches, or weight loss or signs of acute liver inflammation including fever, jaundice, and right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Individuals with autoimmune hepatitis often have no initial symptoms and the disease may be detected by abnormal liver function tests and increased protein levels during routine bloodwork or the observation of an abnormal-looking liver during abdominal surgery.

Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is an autoimmune disease of the liver. It results from a slow, progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver, causing bile and other toxins to build up in the liver, a condition called cholestasis. Further slow damage to the liver tissue can lead to scarring, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis.

Portal hypertension is defined as increased portal venous pressure, with a hepatic venous pressure gradient greater than 5 mmHg. Normal portal pressure is 1-4mmHg; clinically insignificant portal hypertension is present at portal pressures 5-9mmHg; clinically significant portal hypertension is present at portal pressures greater than 10mmHg. The portal vein and its branches supply most of the blood and nutrients from the intestine to the liver.
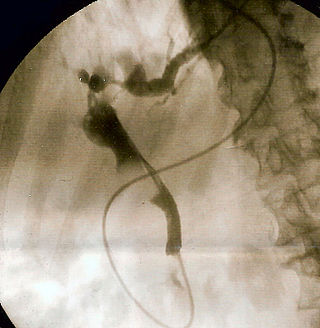
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a long-term progressive disease of the liver and gallbladder characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, which normally allow bile to drain from the gallbladder. Affected individuals may have no symptoms or may experience signs and symptoms of liver disease, such as yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes, itching, and abdominal pain.

Fatty liver disease (FLD), also known as hepatic steatosis and steatotic liver disease (SLD), is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Often there are no or few symptoms. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Complications may include cirrhosis, liver cancer, and esophageal varices.

Hepatorenal syndrome is a life-threatening medical condition that consists of rapid deterioration in kidney function in individuals with cirrhosis or fulminant liver failure. HRS is usually fatal unless a liver transplant is performed, although various treatments, such as dialysis, can prevent advancement of the condition.

Liver biopsy is the biopsy from the liver. It is a medical test that is done to aid diagnosis of liver disease, to assess the severity of known liver disease, and to monitor the progress of treatment.

Cholestasis is a condition where the flow of bile from the liver to the duodenum is impaired. The two basic distinctions are:

Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage to the liver leads to repair of liver tissue and subsequent formation of scar tissue. Over time, scar tissue can replace normal functioning tissue, leading to the impaired liver function of cirrhosis. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years. Early symptoms may include tiredness, weakness, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and discomfort in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. As the disease worsens, symptoms may include itchiness, swelling in the lower legs, fluid build-up in the abdomen, jaundice, bruising easily, and the development of spider-like blood vessels in the skin. The fluid build-up in the abdomen may develop into spontaneous infections. More serious complications include hepatic encephalopathy, bleeding from dilated veins in the esophagus, stomach, or intestines, and liver cancer.
Sander S. Florman is an American transplant surgeon and Director of the Recanati/Miller Transplantation Institute at The Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City. He is a member of the American Society of Transplant Surgeons, the American Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association, the American Society of Transplantation and the American College of Surgeons.
A liver support system or diachysis is a type of therapeutic device to assist in performing the functions of the liver. Such systems focus either on removing the accumulating toxins, or providing additional replacement of the metabolic functions of the liver through the inclusion of hepatocytes to the device. This system is in trial to help people with acute liver failure (ALF) or acute-on-chronic liver failure.

MELD-Plus is a risk score to assess severity of chronic liver disease that was resulted from a collaboration between Massachusetts General Hospital and IBM. The score includes nine variables as effective predictors for 90-day mortality after a discharge from a cirrhosis-related admission. The variables include all Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD)'s components, as well as sodium, albumin, total cholesterol, white blood cell count, age, and length of stay.

Melissa Palmer is an American hepatologist. She is recognized for her research and treatment of hepatitis and liver disease. Palmer is the Chief Medical Officer of Gannex Pharma, a wholly owned company of Ascletis Pharma.
















