
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tension.
Tendinopathy is a type of tendon disorder that results in pain, swelling, and impaired function. The pain is typically worse with movement. It most commonly occurs around the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle.
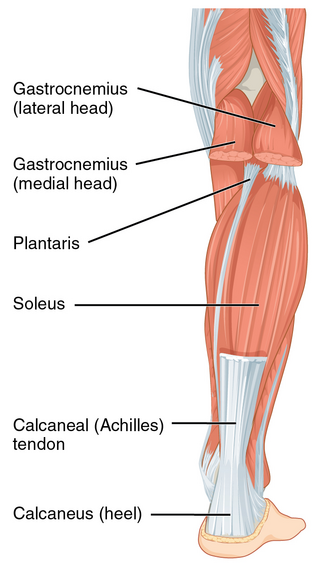
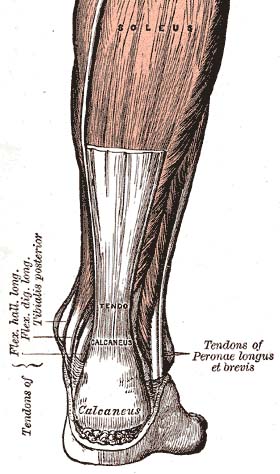
The Achilles tendon or heel cord, also known as the calcaneal tendon, is a tendon at the back of the lower leg, and is the thickest in the human body. It serves to attach the plantaris, gastrocnemius (calf) and soleus muscles to the calcaneus (heel) bone. These muscles, acting via the tendon, cause plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle joint, and flexion at the knee.
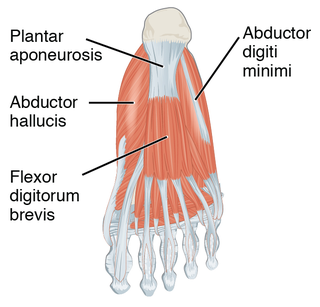
The plantar fascia or plantar aponeurosis is the thick connective tissue aponeurosis which supports the arch on the bottom of the foot. Recent studies suggest that the plantar fascia is actually an aponeurosis rather than true fascia. It runs from the tuberosity of the calcaneus forward to the heads of the metatarsal bones.

Achilles tendinitis, also known as achilles tendinopathy, occurs when the Achilles tendon, found at the back of the ankle, becomes sore. Achilles tendinopathy is accompanied by alterations in the tendon's structure and mechanical properties. The most common symptoms are pain and swelling around the affected tendon. The pain is typically worse at the start of exercise and decreases thereafter. Stiffness of the ankle may also be present. Onset is generally gradual.

Rotator cuff tendinopathy is a process of senescence. The pathophysiology is mucoid degeneration. Most people develop rotator cuff tendinopathy within their lifetime.

Nintendo thumb, also known as gamer's thumb and similar names, is a form of repetitive strain injury (RSI) caused by excessive playing video games with the traditional Nintendo controller. This injury mainly occurs due to repeated thumb movements while playing video games. The symptoms are blistering, paraesthesia, and swelling of the thumbs, though any finger can be affected. This can lead to stress on tendons, nerves, and ligaments in the hands, and further onto lateral epicondylitis, tendinitis, bursitis, and carpal tunnel syndrome. Similar injuries can occur with other gaming systems, such as PlayStation thumb from playing Sony PlayStation. The general recommendation for the treatment is to rest and stop the repetitive motion of the affected finger. In more severe and painful cases, using NSAIDs is also recommended.

Achilles tendon rupture is when the Achilles tendon, at the back of the ankle, breaks. Symptoms include the sudden onset of sharp pain in the heel. A snapping sound may be heard as the tendon breaks and walking becomes difficult.

Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction is a surgical tissue graft replacement of the anterior cruciate ligament, located in the knee, to restore its function after an injury. The torn ligament can either be removed from the knee, or preserved before reconstruction through an arthroscopic procedure. ACL repair is also a surgical option. This involves repairing the ACL by re-attaching it, instead of performing a reconstruction. Theoretical advantages of repair include faster recovery and a lack of donor site morbidity, but randomised controlled trials and long-term data regarding re-rupture rates using contemporary surgical techniques are lacking.

The palmaris longus is a muscle visible as a small tendon located between the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris, although it is not always present. It is absent in about 14 percent of the population; this number can vary in African, Asian, and Native American populations, however. Absence of the palmaris longus does not have an effect on grip strength. The lack of palmaris longus muscle does result in decreased pinch strength in fourth and fifth fingers. The absence of palmaris longus muscle is more prevalent in females than males.

The plantaris is one of the superficial muscles of the superficial posterior compartment of the leg, one of the fascial compartments of the leg.
A negative repetition is the repetition of a technique in weight lifting in which the lifter performs the eccentric phase of a lift. Instead of pressing the weight up slowly, in proper form, a spotter generally aids in the concentric, or lifting, portion of the repetition while the lifter slowly performs the eccentric phase for 3–6 seconds.

Patellar tendon rupture is a tear of the tendon that connects the knee cap (patella) to the tibia. Often there is sudden onset of pain and walking is difficult. In a complete rupture, the ability to extend that knee is decreased. A pop may be felt when it occurs.

An anterior cruciate ligament injury occurs when the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is either stretched, partially torn, or completely torn. The most common injury is a complete tear. Symptoms include pain, an audible cracking sound during injury, instability of the knee, and joint swelling. Swelling generally appears within a couple of hours. In approximately 50% of cases, other structures of the knee such as surrounding ligaments, cartilage, or meniscus are damaged.

The patellar tendon is the distal portion of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris, which is continued from the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It is also sometimes called the patellar ligament as it forms a bone to bone connection when the patella is fully ossified.

The unhappy triad, also known as a blown knee among other names, is an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and meniscus. Analysis during the 1990s indicated that this 'classic' O'Donoghue triad is actually an unusual clinical entity among athletes with knee injuries. Some authors mistakenly believe that in this type of injury, "combined anterior cruciate and medial collateral ligament disruptions that were incurred during athletic endeavors" always present with concomitant medial meniscus injury. However, the 1990 analysis showed that lateral meniscus tears are more common than medial meniscus tears in conjunction with sprains of the ACL.

In human anatomy, the quadriceps tendon works with the quadriceps muscle to extend the leg. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the shin via the patella, where the quadriceps tendon becomes the patellar ligament. It attaches the quadriceps to the top of the patella, which in turn is connected to the shin from its bottom by the patellar ligament. A tendon connects muscle to bone, while a ligament connects bone to bone.

Tendon rupture is a condition in which a tendon separates in whole or in part from tissue to which it is attached, or is itself torn or otherwise divided in whole or in part.
Franklin Adin Simmonds F.R.C.S. was a British orthopaedic surgeon for whom the Simmonds' test on rupture of the Achilles tendon is named. He also worked with the pioneering surgeon John Charnley on hip replacement surgery and became an expert in this field.

A biceps tendon rupture or bicep tear is a complete or partial rupture of a tendon of the biceps brachii muscle. It can affect any of the three biceps brachii tendons - the proximal tendon of the short head of the muscle belly, the proximal tendon of the long head of the muscle belly, or the distal tendon. The characteristic finding of a biceps tendon rupture is the Popeye sign. Patients often report an audible pop at the time of injury as well as pain, bruising, and swelling. Provocative physical exam maneuvers to assess for a rupture include Ludington's test, Hook test, and the Ruland biceps squeeze test. Treatment and prognosis are highly dependent on the site of the injury described in further detail below.
















