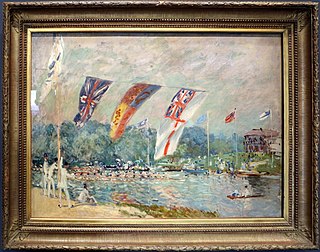Berthe Marie Pauline Morisot was a French painter and a member of the circle of painters in Paris who became known as the Impressionists.

Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities, ordinary subject matter, unusual visual angles, and inclusion of movement as a crucial element of human perception and experience. Impressionism originated with a group of Paris-based artists whose independent exhibitions brought them to prominence during the 1870s and 1880s.

Pierre-Auguste Renoir was a French artist who was a leading painter in the development of the Impressionist style. As a celebrator of beauty and especially feminine sensuality, it has been said that "Renoir is the final representative of a tradition which runs directly from Rubens to Watteau."

The Musée d'Orsay is a museum in Paris, France, on the Left Bank of the Seine. It is housed in the former Gare d'Orsay, a Beaux-Arts railway station built between 1898 and 1900. The museum holds mainly French art dating from 1848 to 1914, including paintings, sculptures, furniture, and photography. It houses the largest collection of Impressionist and post-Impressionist masterpieces in the world, by painters including Berthe Morisot, Claude Monet, Édouard Manet, Degas, Renoir, Cézanne, Seurat, Sisley, Gauguin, and van Gogh. Many of these works were held at the Galerie nationale du Jeu de Paume prior to the museum's opening in 1986. It is one of the largest art museums in Europe.

Henri Fantin-Latour was a French painter and lithographer best known for his flower paintings and group portraits of Parisian artists and writers.

Gustave Caillebotte was a French painter who was a member and patron of the Impressionists, although he painted in a more realistic manner than many others in the group. Caillebotte was known for his early interest in photography as an art form.

Alfred Sisley was an Impressionist landscape painter who was born and spent most of his life in France, but retained British citizenship. He was the most consistent of the Impressionists in his dedication to painting landscape en plein air. He deviated into figure painting only rarely and, unlike Renoir and Pissarro, he found that Impressionism fulfilled his artistic needs.

Eva Gonzalès was a French Impressionist painter. She was one of the four most notable female Impressionists in the nineteenth century, along with Mary Cassatt (1844–1926), Berthe Morisot (1841–95), and Marie Bracquemond (1840–1916).

Félix Henri Bracquemond was a French painter, etcher, and printmaker. He played a key role in the revival of printmaking, encouraging artists such as Édouard Manet, Edgar Degas and Camille Pissarro to use this technique.

Les Choristes is an 1877 pastel on monotype by French artist Edgar Degas. Part of a series of similar works depicting daily public entertainment at the time, it shows a group of singers performing a scene from the opera Don Giovanni, the only work by Degas depicting an operatic performance without dancers.

Marie Bracquemond was a French Impressionist artist. She was one of four notable women in the Impressionist movement, along with Mary Cassatt (1844-1926), Berthe Morisot (1841-1895), and Eva Gonzalès (1847-1883). Bracquemond studied drawing as a child and began showing her work at the Paris Salon when she was still an adolescent. She never underwent formal art training, but she received limited instruction from Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres (1780–1867) and advice from Paul Gauguin (1848–1903) which contributed to her stylistic approach.

Portrait of Gustave Geffroy is a c. 1895 painting by the French Post-Impressionist artist Paul Cézanne. It portrays Gustave Geffroy, a French novelist and art critic noted as one of the earliest historians of Impressionism.

Les raboteurs de parquet is an oil painting by French Impressionist Gustave Caillebotte. The canvas measures 102 by 146.5 centimetres. It was originally given by Caillebotte's family in 1894 to the Musée du Luxembourg, then transferred to the Musée du Louvre in 1929. In 1947, it was moved to the Galerie nationale du Jeu de Paume, and in 1986, it was transferred again to the Musée d'Orsay in Paris, where it is currently displayed.

Edma Morisot was a French artist and the older sister of the Impressionist painter Berthe Morisot.

The Canal du Loing or The Canal du Loing at Moret is an 1892 painting by Alfred Sisley, donated to the Musée du Luxembourg after the painter's death in 1899 by a group of the painter's friends headed by Claude Monet. It is now in the Musée d'Orsay. A similar work, painted in winter 1891, is now in the National Museum of Fine Arts of Algiers.
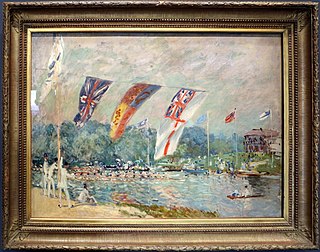
Regatta at Molesey near Hampton Court is an 1874 painting by Alfred Sisley, now in the Musée d'Orsay, to which it was allocated in 1986. The work shows the Molesey Regatta on the River Thames, begun by an amateur sportsman in 1873 and still in existence. The viewpoint looks upstream from Molesey Boat Club, with the recently-constructed Island Hotel visible on Tagg's Island.

Under the Lamp, also known as Sous la lampe - Afred Sisley et sa femme, chez Bracquemond à Sèvres, is an 1887 oil-on-canvas painting by French artist Marie Bracquemond. It is held in a private collection.

Afternoon Tea is an 1880 oil-on-canvas painting by French artist Marie Bracquemond. It is a portrait of the artist's half-sister Louise Quivoron, who often served as a model for her paintings, reading in a garden at Bracquemond's home in the Parisian suburb of Sèvres. The work was shown during an exhibition in 1919 and purchased by the French government from Bracquemond's son Pierre. It is now in the collection of the Petit Palais, Musée des Beaux-Arts de la Ville de Paris. It is one of her few works held in a public collection. The theme of the work reflects the intellectual activities of the lives of women, and can be compared to related works such as Mary Cassatt’s The Reader (1877) and Harriet Backer’s Evening (1890).

The Lady in White, also known as The Woman in White, is an 1880 oil-on-canvas painting by French artist Marie Bracquemond. It depicts the artist's half-sister Louise Quivoron, who often served as a model for her paintings. It was one of three paintings by Bracquemond shown at the fifth Impressionist exhibition in April 1880. A previous painting, Woman in the Garden (1877), may have been a study for The Lady in White. Like the other Impressionists of the time, Bracquemond worked outside en plein air, mostly in her garden at Sèvres.

On the Terrace at Sèvres is the title of at least two 1880 oil-on-canvas paintings with the same subject by French artist Marie Bracquemond. A larger version is held by the Musée du Petit Palais in Geneva, Switzerland, while a smaller version is held by the Artizon Museum, Ishibashi Foundation, in Tokyo, Japan.