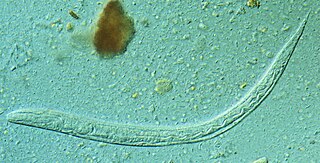
Strongyloides stercoralis is a human pathogenic parasitic roundworm causing the disease strongyloidiasis. Its common name in the US is threadworm. In the UK and Australia, however, the term threadworm can also refer to nematodes of the genus Enterobius, otherwise known as pinworms.

Spercheus is a genus of aquatic beetles which are placed in a family of their own, Spercheidae. About 20 species are known from around the world, with the majority being from the Oriental and Afrotropical Realms.

Sawflies are the insects of the suborder Symphyta within the order Hymenoptera alongside ants, bees and wasps. The common name comes from the saw-like appearance of the ovipositor, which the females use to cut into the plants where they lay their eggs. The name is associated especially with the Tenthredinoidea, by far the largest superfamily in the suborder, with about 7,000 known species; in the entire suborder, there are 8,000 described species in more than 800 genera. Symphyta is paraphyletic, consisting of several basal groups within the order Hymenoptera, each one rooted inside the previous group, ending with the Apocrita which are not sawflies.

Botflies, also known as warble flies, heel flies, and gadflies, are a family of flies technically known as the Oestridae. Their larvae are internal parasites of mammals, some species growing in the host's flesh and others within the gut. Dermatobia hominis is the only species of botfly known to parasitize humans routinely, though other species of flies cause myiasis in humans.

Buprestidae is a family of beetles known as jewel beetles or metallic wood-boring beetles because of their glossy iridescent colors. Larvae of this family are known as flatheaded borers. The family is among the largest of the beetles, with some 15,500 species known in 775 genera. In addition, almost 100 fossil species have been described.
Glowworm or glow-worm is the common name for various groups of insect larvae and adult larviform females that glow through bioluminescence. They include the European common glow-worm and other members of the Lampyridae, but bioluminescence also occurs in the families Elateridae, Phengodidae, and Rhagophthalmidae among beetles; as well as members of the genera Arachnocampa, Keroplatus, and Orfelia among keroplatid fungus gnats.

Myiasis is the parasitic infestation of the body of a live animal by fly larvae (maggots) which grow inside the host while feeding on its tissue. Although flies are most commonly attracted to open wounds and urine- or feces-soaked fur, some species can create an infestation even on unbroken skin and have been known to use moist soil and non-myiatic flies as vector agents for their parasitic larvae.
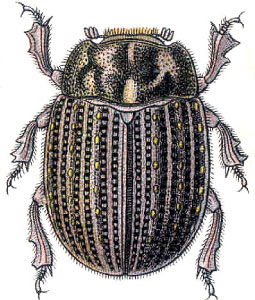
Trogidae, sometimes called hide beetles, is a family of beetles with a distinctive warty or bumpy appearance. Found worldwide, the family includes about 300 species contained in four or five genera.

The Cucujidae, "flat bark beetles," are a family of distinctively flat beetles found worldwide under the bark of dead trees. The family has received considerable taxonomic attention in recent years and now consists of 59 species distributed in four genera. It was indicated Cucujus species are scavengers, only feeding on pupae and larvae of other insects and on other subcortical beetles such as their own. Since the Cucujidae prey on larvae of potentially tree damaging beetles that spread fungal diseases, they are considered to be beneficial to the health of living trees.
Gnathostomiasis is the human infection caused by the nematode (roundworm) Gnathostoma spinigerum and/or Gnathostoma hispidum, which infects vertebrates.

The witchetty grub is a term used in Australia for the large, white, wood-eating larvae of several moths. In particular, it applies to the larvae of the cossid moth Endoxyla leucomochla, which feeds on the roots of the witchetty bush that is widespread throughout the Northern Territory and also typically found in parts of Western Australia and South Australia, although it is also found elsewhere throughout Australia.

Ceratopogonidae is a family of flies commonly known as no-see-ums, or biting midges, generally 1–3 mm in length. The family includes more than 5,000 species, distributed worldwide, apart from the Antarctic and the Arctic.

Psychodidae, called drain flies, sink flies, filter flies, sewer flies, or sewer gnats, is a family of true flies. Some genera have short, hairy bodies and wings giving them a "furry" moth-like appearance, hence one of their common names, moth flies. Members of the sub-family Phlebotominae which are hematophagous may be called sand flies in some countries, although this term is also used for other unrelated flies.
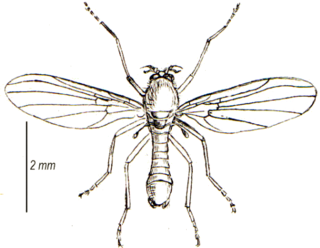
Thaumaleidae, the solitary midges or trickle midges, are a group of nematoceran flies related to the Ceratopogonidae, Chironomidae, and the Simuliidae. They are small, stocky, yellow to brown flies (3–4 mm). Very few species are known for this family. Larvae are found in films on rocks and the nonfeeding adults are usually found on foliage along the same streams in which the larvae are found. A few solitary midges are found in the Southern Hemisphere, but Thaumaleidae are generally an Holarctic family.

Fungus gnats are small, dark, short-lived gnats, of the families Sciaridae, Diadocidiidae, Ditomyiidae, Keroplatidae, Bolitophilidae, and Mycetophilidae ; they comprise six of the seven families placed in the superfamily Sciaroidea.

The Heleomyzidae is a small family of true flies in the insect order Diptera. Over 740 described species of Heleomyzidae occur in about 76 genera distributed throughout the world.

The Keroplatidae are a family of small flies known as fungus gnats. About 950 species are described, but the true number of species is undoubtedly much higher. They are generally forest dwellers found in the damp habitats favoured by their host fungi. They can also often be found in caves. Larvae both feed on fungi and are predatory - they can spin webs by secreting acid fluids, which they use to kill smaller invertebrates and capture spores. Some of the predatory larvae cannibalize pupa of their own species.
Cyclotorna is a genus of moths, the sole one of family Cyclotornidae, with five recognized species, all endemic to Australia. This family and the closely related Epipyropidae are unique among the Lepidoptera in that the larvae are ectoparasites, the hosts in this case typically being leafhoppers, sometimes scale insects. The larvae of cyclotornids, however, leave the hemipteran host and become predatory on the brood in ant nests, apparently using chemical cues to induce the ants to carry the larvae into the ant nest.
Agathiphaga is a genus of moths, known as kauri moths. It is the only living in the family Agathiphagidae. This caddisfly-like lineage of primitive moths was first reported by Lionel Jack Dumbleton in 1952, as a new genus of Micropterigidae.
Hygrobia is a genus of aquatic beetles native to Europe, North Africa, China and Australia. It is the only genus in the family Hygrobiidae, also known as the Paelobiidae. These are known commonly as squeak beetles or screech-beetles.














