Related Research Articles

Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the local mean time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, counted from midnight. At different times in the past, it has been calculated in different ways, including being calculated from noon; as a consequence, it cannot be used to specify a particular time unless a context is given. The term "GMT" is also used as one of the names for the time zone UTC+00:00 and, in UK law, is the basis for civil time in the United Kingdom.

A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it is convenient for areas in frequent communication to keep the same time.

Japan Standard Time, or Japan Central Standard Time, is the standard time zone in Japan, 9 hours ahead of UTC (UTC+09:00). Japan does not observe daylight saving time, though its introduction has been debated on several occasions. During World War II, the time zone was often referred to as Tokyo Standard Time.

The Alaska Time Zone observes standard time by subtracting nine hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC−09:00). During daylight saving time its time offset is eight hours (UTC−08:00). The clock time in this zone is based on mean solar time at the 135th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory.

Central European Time (CET) is a standard time of Central, and parts of Western Europe, which is one hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The time offset from UTC can be written as UTC+01:00. It is used in most parts of Europe and in a few North African countries. CET is also known as Middle European Time and by colloquial names such as Amsterdam Time, Berlin Time, Brussels Time, Budapest Time, Madrid Time, Paris Time, Rome Time, Prague time, Warsaw Time or Romance Standard Time (RST).
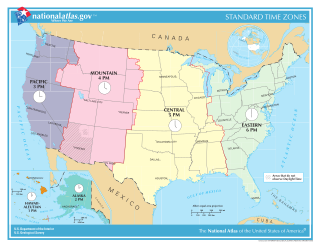
In the United States, time is divided into nine standard time zones covering the states, territories and other US possessions, with most of the country observing daylight saving time (DST) for approximately the spring, summer, and fall months. The time zone boundaries and DST observance are regulated by the Department of Transportation, but no single map of those existed until the agency announced intentions to make one in September 2022. Official and highly precise timekeeping services (clocks) are provided by two federal agencies: the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) ; and the United States Naval Observatory (USNO). The clocks run by these services are kept synchronized with each other as well as with those of other international timekeeping organizations.

Moscow Time is the time zone for the city of Moscow, Russia, and most of western Russia, including Saint Petersburg. It is the second-westernmost of the eleven time zones of Russia. It has been set to UTC+03:00 without DST since 26 October 2014; before that date it had been set to UTC+04:00 year-round on 27 March 2011.

UTC−04:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −04:00.
Time in Chile is divided into three time zones. Most of Continental Chile uses the time offset UTC−04:00 in winter time and UTC−03:00 in summer time, while the Magallanes and Chilean Antarctica region uses the time offset UTC−03:00 the whole year. Additionally, Easter Island uses the time offset UTC−06:00 in winter time and UTC−05:00 in summer time.
Malaysian Standard Time or Malaysian Time (MYT) is the standard time used in Malaysia. It is 8 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Malaysia does not observe daylight saving time.

Iran Standard Time (IRST) or Iran Time (IT) is the time zone used in Iran. Iran uses a UTC offset UTC+03:30. IRST is defined by the 52.5 degrees east meridian, the same meridian which defines the Iranian calendar and is the official meridian of Iran.
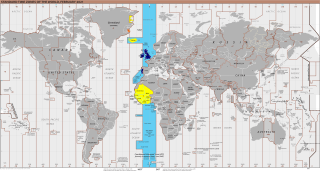
UTC+00:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +00:00. This time zone is the basis of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and all other time zones are based on it. In ISO 8601, an example of the associated time would be written as 2069-01-01T12:12:34+00:00. It is also known by the following geographical or historical names:

Mexico uses four time zones:

UTC−04:30 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −04:30.

Metropolitan France uses Central European Time as its standard time, and observes Central European Summer Time from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. With its overseas territories, France uses 12 different time zones, more than any other country in the world.

Portugal has two time zones and observes daylight saving time. Continental Portugal and Madeira use UTC+00:00, while the Azores use UTC–01:00. Daylight saving time is observed nationwide from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October, when continental Portugal and Madeira advance one hour to UTC+01:00, and the Azores advances one hour to UTC+00:00.

The Astronomical and Meteorological Observatory of Caracas, was created by decree of President Juan Pablo Rojas Paul on September 8, 1888. The observatory was established on Quintana Hill, later changed to Cagigal Hill in honor of the astronomer and mathematician, Colonel Juan Manuel Cagigal, who was the founder of mathematical studies in Venezuela. The hill is also known as Observatory Hill.

Denmark, including its dependencies of Faroe Islands and Greenland, uses six time zones.

Finland uses Eastern European Time (EET) during the winter as standard time and Eastern European Summer Time (EEST) during the summer as daylight saving time. EET is two hours ahead of coordinated universal time (UTC+02:00) and EEST is three hours ahead of coordinated universal time (UTC+03:00). Finland adopted EET on 30 April 1921, and has observed daylight saving time in its current alignment since 1981 by advancing the clock forward one hour at 03:00 EET on the last Sunday in March and back at 04:00 EET on the last Sunday in October, doing so an hour earlier for the first two years.
Nigeria observes West Africa Time (WAT), which is one hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC+01:00), year-round as standard time. Nigeria has never observed daylight saving time. It shares WAT with fourteen other countries in Africa. Nigeria's local mean time was UTC+00:13:35.
References
- 1 2 3 "Venezuela Changes Time Zone to Save Electricity". Sky News. 16 April 2016. Archived from the original on 16 April 2016. Retrieved 28 June 2018.
- 1 2 3 "Venezuela's Legal Time Service" (in Spanish). Cagigal Naval Observatory, Caracas: Venezuela's Navigation and Hydrography Service. Archived from the original on 7 April 2014. Retrieved 2 April 2014.
- ↑ Cawthorne, Andrew; Kai, Daniel (15 April 2016). "Venezuela scraps half-hour time difference set by Chavez". Reuters . Retrieved 19 April 2016.
