Related Research Articles
Hinduism is an umbrella-term for a broad range of Indian religious and spiritual traditions (sampradayas) that are unified by the concept of dharma, a universal order maintained by its followers through rituals and righteous living. The word Hindu is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, it has also been described as Sanātana Dharma, a modern usage, based on the belief that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym for Hinduism is Vaidika Dharma.

Indian religions, sometimes also termed Dharmic religions or Indic religions, are the religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent. These religions, which include Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism, and Sikhism, are also classified as Eastern religions. Although Indian religions are connected through the history of India, they constitute a wide range of religious communities, and are not confined to the Indian subcontinent.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the history of South Asia.
Kalki, also called Kalkin, is the prophesied tenth and final incarnation of the Hindu god Vishnu. According to Vaishnava cosmology, Kalki is destined to appear at the end of the Kali Yuga, the last of the four ages in the cycle of existence (Krita). His arrival will mark the end of the Kali Yuga and herald the beginning of the Satya Yuga, the most virtuous age, before the ultimate dissolution of the universe (Mahapralaya).

The historical Vedic religion, also called Vedicism or Vedism, and sometimes ancient Hinduism or Vedic Hinduism, constituted the religious ideas and practices prevalent amongst some of the Indo-Aryan peoples of the northwest Indian subcontinent during the Vedic period. These ideas and practices are found in the Vedic texts, and some Vedic rituals are still practiced today. The Vedic religion is one of the major traditions which shaped modern Hinduism, though present-day Hinduism is significantly different from the historical Vedic religion.
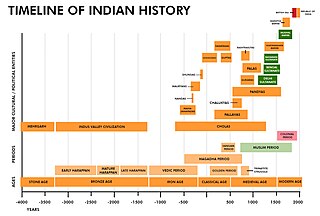
This is a timeline of Indian history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in India and its predecessor states. To read about the background to these events, see History of India. Also see the list of governors-general of India, list of prime ministers of India and list of years in India.

Karna, also known as Vasusena, Anga-Raja, Sutaputra and Radheya, is one of the major characters in the Hindu epic Mahābhārata. He is the son of Surya and princess Kunti. Kunti was granted the boon to bear a child with desired divine qualities from the gods and without much knowledge, Kunti invoked the sun god to confirm it if it was true indeed. Karna was secretly born to an unmarried Kunti in her teenage years, and fearing outrage and backlash from society over her premarital pregnancy, Kunti had to abandon the newly born Karna adrift in a basket on the Ganges. The basket is discovered floating on the Ganges River. He is adopted and raised by foster Suta parents named Radha and Adhiratha Nandana of the charioteer and poet profession working for king Dhritarashtra. Karna grows up to be an accomplished warrior of extraordinary abilities, a gifted speaker and becomes a loyal friend of Duryodhana. He is appointed the king of Anga (Bihar-Bengal) by Duryodhana. Karna joins the losing Duryodhana side of the Mahabharata war. He is a key antagonist who aims to kill Arjuna but dies in a battle with him during the Kurushetra war.

The history of Hinduism covers a wide variety of related religious traditions native to the Indian subcontinent. It overlaps or coincides with the development of religion in the Indian subcontinent since the Iron Age, with some of its traditions tracing back to prehistoric religions such as those of the Bronze Age Indus Valley Civilisation. Hinduism has been called the "oldest religion" in the world, but scholars regard Hinduism as a relatively recent synthesis of various Indian cultures and traditions, with diverse roots and no single founder, which emerged around the beginning of the Common Era.

The Smartatradition, also called Smartism, is a movement in Hinduism that developed and expanded with the Puranas genre of literature. It reflects a synthesis of four philosophical strands, namely Uttara Mīmāṃsā, Advaita, Yoga, and theism. The Smarta tradition rejects theistic sectarianism, and is notable for the domestic worship of five shrines with five deities, all treated as equal – Ganesha, Shiva, Shakti, Vishnu and Surya. The Smarta tradition contrasted with the older Shrauta tradition, which was based on elaborate rituals and rites. There has been a considerable overlap in the ideas and practices of the Smarta tradition with other significant historic movements within Hinduism, namely Shaivism, Brahmanism, Vaishnavism, and Shaktism.

Kuru was a Vedic Indo-Aryan tribal union in northern Iron Age India of the Bharata and Puru tribes. The Kuru kingdom appeared in the Middle Vedic period, encompassing parts of the modern-day states of Haryana, Delhi, and some North parts of Western Uttar Pradesh. The Kuru Kingdom was the first recorded state-level society in the Indian subcontinent.

Iravan also known as Iravat and Iravant, is a minor character from the Hindu epic Mahabharata. The son of Pandava prince Arjuna and the Naga princess Ulupi, Iravan is the central deity of the cult of Kuttantavar (Kuttandavar) which is also the name commonly given to him in that tradition—and plays a major role in the sect of Draupadi. Both these sects are of Tamil origin, from a region of the country where he is worshipped as a village deity and is known as Aravan. He is also a patron god of well-known transgender communities called Alis.
The Battle of the Ten Kings was first alluded to in the 7th Mandala of the Rigveda (RV) and took place between a king of the Bharatas named King Sudas versus a confederation of tribes. It resulted in a decisive victory for the Bharatas and subsequent formation of the Kuru polity. The Battle of the Ten Kings, mentioned in the Rigveda may have "formed the 'nucleus' of story" of the Kurukshetra War in the Mahabharata.

The Vanniyar, also spelled Vanniya, formerly known as the Palli, are a Dravidian community or jāti found in the northern part of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu.
Alha was a legendary general of the Chandel king Paramardideva, who fought Prithviraj Chauhan in 1182 CE. He is one of the main characters of the Alha-Khand ballad.
Konar is Hindu caste found in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. They are traditionally a pastoral community involved in cattle herding and cultivation. They are a part of the Yadav community. They also known as Ayar and Idaiyar, and appear in the ancient Sangam literature as occupants of the Mullai.

The Vedic period, or the Vedic age, is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas, was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the end of the urban Indus Valley Civilisation and a second urbanisation, which began in the central Indo-Gangetic Plain c. 600 BCE. The Vedas are liturgical texts which formed the basis of the influential Brahmanical ideology, which developed in the Kuru Kingdom, a tribal union of several Indo-Aryan tribes. The Vedas contain details of life during this period that have been interpreted to be historical and constitute the primary sources for understanding the period. These documents, alongside the corresponding archaeological record, allow for the evolution of the Indo-Aryan and Vedic culture to be traced and inferred.

The early Dravidian religion constituted a non-Vedic, pre-Indo-Aryan, indigenous religion practiced by Dravidian peoples in the Indian subcontinent that they were either historically or are at present Āgamic. The Agamas are non-Vedic in origin, and have been dated either as post-Vedic texts, or as pre-Vedic compositions. The Agamas are a collection of Tamil and Sanskrit scriptures chiefly constituting the methods of temple construction and creation of murti, worship means of deities, philosophical doctrines, meditative practices, attainment of sixfold desires and four kinds of yoga. The worship of tutelary deities and sacred flora and fauna in Hinduism is also recognized as a survival of the pre-Vedic Dravidian religion. Dravidian linguistic influence on early Vedic religion is evident; many of these features are already present in the oldest known Indo-Aryan language, the language of the Rigveda, which also includes over a dozen words borrowed from Dravidian. The linguistic evidence for Dravidian impact grows increasingly strong as one moves from the Samhitas down through the later Vedic works and into the classical post-Vedic literature. This represents an early religious and cultural fusion or synthesis between ancient Dravidians and Indo-Aryans that went on to influence Indian civilisation.

The Pashupati seal, is a steatite seal which was uncovered in Mohenjo-daro, now in modern day Pakistan, a major urban site of the Indus Valley civilisation ("IVC"), during excavations in 1928–29, when the region was under British rule. The excavations were carried out by the Archaeological Survey of India, the official body responsible for preservation and excavation. The seal depicts a seated figure that is possibly tricephalic. The seated figure has been thought to be ithyphallic, an interpretation that has been questioned by many, but was still held by the IVC specialist Jonathan Mark Kenoyer in a publication of 2003. The man has a horned headdress and is surrounded by animals. He may represent a horned deity.
Alfred John Hiltebeitel was Columbian Professor of Religion, History, and Human Sciences at George Washington University in Washington, D.C., US. His academic specialism was in ancient Sanskrit epics such as the Mahabharata and Ramayana, together with Indian religious tradition and folklore.

The religion and belief system of the Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC) people have received considerable attention, with many writers concerned with identifying precursors to the religious practices and deities of much later Indian religions. However, due to the sparsity of evidence, which is open to varying interpretations, and the fact that the Indus script remains undeciphered, the conclusions are partly speculative and many are largely based on a retrospective view from a much later Hindu perspective.