| Tobacco ringspot virus | |
|---|---|
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Pisuviricota |
| Class: | Pisoniviricetes |
| Order: | Picornavirales |
| Family: | Secoviridae |
| Genus: | Nepovirus |
| Species: | Nepovirus nicotianae |
Tobacco ringspot virus (TRSV) is a plant pathogenic virus in the plant virus family Secoviridae . It is the type species of the genus Nepovirus . Nepoviruses are transmitted between plants by nematodes, thrips, mites, grasshoppers, and flea beetles. [1] TRSV is also easily transmitted by sap inoculation and transmission in seeds has been reported. [2] In recent cases it has also been shown to appear in bees, but no transmission to plants from bees has been noted. [3]
Contents
TRSV was observed for the first time in tobacco fields in Virginia and described in 1927. [4] It is an isometric particle [5] with a bipartite RNA genome. The virus has a wide host range [6] that includes field grown crops, ornamentals and weeds. Its name comes from its most common symptom being chlorotic ringspots on the leaves of infected plants. [7] In some areas this virus has caused growers to stop growing affected crops. [8]
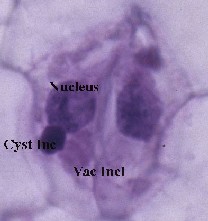
Symptoms and virus inclusions of Tobacco ringspot nepovirus in the host Zamia furfuracea, the Cardboard Cycad. [9] A. The first symptoms seen were chlorotic ringspots. With time they become necrotic. B. There are two types of inclusions found in leaf strips stained with Azure A (nucleic acid stain), [10] one is vacuolate (Vac Inc) and the other more crystalloid (Cyst Inc - darker spots). C. Vacuolate inclusions only.