
Cymbidium, commonly known as boat orchids, is a genus of evergreen flowering plants in the orchid family Orchidaceae. Orchids in this genus are epiphytic, lithophytic, terrestrial or rarely leafless saprophytic herbs usually with pseudobulbs. There are usually between three and twelve leaves arranged in two ranks on each pseudobulb or shoot and lasting for several years. From one to a large number of flowers are arranged on an unbranched flowering stem arising from the base of the pseudobulb. The sepals and petals are all free from and similar to each other. The labellum is significantly different from the other petals and the sepals and has three lobes. There are about fifty-five species and sixteen further natural hybrids occurring in the wild from tropical and subtropical Asia to Australia. Cymbidiums are well known in horticulture and many cultivars have been developed.
Bulbophyllum acropogon is a species of orchid in the genus Bulbophyllum.
Bulbophyllum rhodoglossum is a species of orchid in the genus Bulbophyllum, first described by Rudolf Schlechter in 1913 in Repertorium Specierum Novarum Regni Vegetabilis. It is an epiphyte growing in Papua New Guinea on trees in mountain forests around 1000 metres in elevation. The flowers are white, and the labellum red with a yellow tip.

Calymmanthera is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It contains 5 species, native to Maluku, New Guinea, Fiji and the Solomon Islands.
- Calymmanthera filiformis(J.J.Sm.) Schltr. - New Guinea
- Calymmanthera majorSchltr. - New Guinea, Fiji and the Solomon Islands
- Calymmanthera montanaSchltr. - - New Guinea
- Calymmanthera paniculata(J.J.Sm.) Schltr. - New Guinea, Morotai
- Calymmanthera tenuisSchltr. - New Guinea
Goodyera yunnanensis is a species of orchid endemic to southern China. It has been reported only from the provinces of Yunnan and Sichuan, growing in forest scrub at elevations of 2,600–3,900 m (8,500–12,800 ft).

Habenaria ferdinandi, commonly known as the yellow rein orchid, is a species of orchid that is endemic to the Northern Territory. It usually has two leaves at its base and up to fifteen tiny yellowish green, strongly scented flowers.
Habenaria hymenophylla, commonly known as the coastal rein orchid, is a species of orchid that is endemic to northern Australia. It up to eight leaves scattered along the stem and up to thirty smelly green and white flowers.
Habenaria triplonema, commonly known as the twisted rein orchid, is a species of orchid that is endemic to northern Australia. It two or three leaves at its base and up to twenty five yellowish, strongly scented flowers.
Dendrobium litorale, commonly known as the coastal shaggy orchid, is an epiphytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae. It has a very short rhizome with crowded, slender stems with most of the leaves in the lower half. The leaves are flattened and pointed, the flowers small and pale greenish cream-coloured. It occurs on islands in the Torres Strait and in New Guinea.
Dendrobium maidenianum, commonly known as the coastal burr orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae and is endemic to tropical North Queensland, Australia. It has a single thin, dark green leaf on a thin stem and one or two small white flowers that self-pollinate. It grows on trees and rocks in shady rainforest.
Drymoanthus minutus, commonly known as green midget orchid, is a species of epiphytic or lithophytic orchid that forms small clumps with many thick roots emerging from a thin, erect stem. Between two and five dark green, leathery leaves are arranged along the stem and up to seven minute green to yellowish, star-shaped flowers are arranged on a stiff flowering stem. The sepals and petals are similar to each other and there is a fleshy white, unlobed labellum. This orchid occurs in northern Queensland where it grows in rainforest, usually at higher altitudes.

Robiquetia gracilistipes, commonly known as the large pouched orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid from the family Orchidaceae that forms large, hanging, straggly clumps. It has long, thick, roots, a single stem, many thick, leathery leaves and up to forty cream-coloured, pale green or brownish flowers with red spots and a three-lobed labellum. It grows on trees and rocks in rainforest, usually in bright light. It is found in Malesia including New Guinea, the Solomon Islands and tropical North Queensland, Australia.

Schoenorchis sarcophylla, commonly known as the fleshy flea orchid, is a small epiphytic orchid with many thin roots, between three and seven crowded, dark green leaves and up to thirty crowded, tube-shaped white flowers. It is found in New Guinea and tropical North Queensland.

Taeniophyllum malianum, commonly known as the tangled ribbonroot, is a species of leafless epiphytic or lithophytic orchid that forms tangled clumps. It has flattened green roots with irregular white spots and pressed against the substrate on which it is growing. There are up to fifteen fragrant yellow, short-lived flowers with up to three open at the same time. It only occurs in tropical North Queensland and in New Guinea.
Thrixspermum platystachys, commonly known as the starry hairseed, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid that forms untidy clumps with many tangled, wiry roots, up to ten stiff, leathery leaves and many star-shaped, cream-coloured flowers with an orange and white labellum. This orchid occurs from Papuasia to northern Queensland.

Trachoma speciosum, commonly known as the showy spectral orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid that forms clumps with many thick, cord-like roots, between four and eight thick, leathery leaves and many short-lived, cream-coloured flowers with an orange and white labellum. This orchid occurs in tropical North Queensland.

Trachoma stellatum, commonly known as the starry spectral orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic clump-forming orchid with many thick roots. It has between three and eight thick, leathery leaves and many short-lived, cream-coloured flowers with purple markings and a yellow-tipped labellum. This orchid occurs in tropical North Queensland.
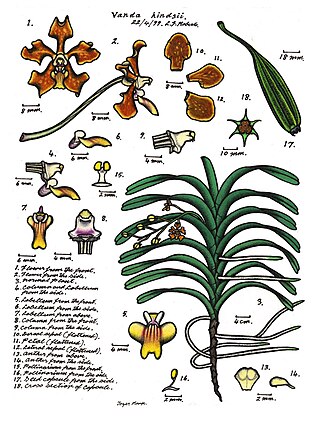
Vanda hindsii, commonly known as the native strap orchid or the Cape York vanda, is a large epiphytic or lithophytic clump-forming orchid. It has thick, white, cord-like roots, branching stems, many thick, leathery, strap-like leaves and between three and seven shiny brown flowers with greenish to yellow markings and a white labellum. This orchid occurs in New Guinea and tropical North Queensland.
Bryobium dischorense, commonly known as the spotted urchin orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic clump-forming orchid that has fleshy, oval pseudobulbs, each with a single thin leaf and between four and eight cup-shaped, cream-coloured or whitish flowers with red spots. This orchid occurs in New Guinea and Queensland.
Bryobium eriaeoides, commonly known as brittle urchin orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic clump-forming orchid that has fleshy, green pseudobulbs, each with two leaves and between three and twelve cup-shaped white to purplish flowers but that sometimes remain closed. This orchid occurs in New Guinea and Queensland.









