The majority of Indonesia's railways are on Java, used for both passenger and freight transport. There are three noncontinuous railway networks in Sumatra while two new networks are being developed in Kalimantan and Sulawesi. Indonesia has finalized its plan for a national railway network recently. According to the plan, 3,200 km of train tracks will crisscross the islands of Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan, and Sulawesi. It has been touted as the most extensive railway project in Indonesia since its independence from the Dutch in 1945. Indonesia targets to extend the national railway network to 10,524 kilometres by 2030. As of September 2022, the network spans 7,032 km.

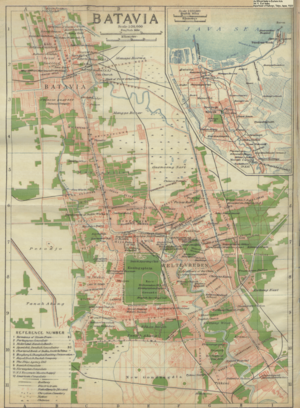
Menteng is a district in the administrative city of Central Jakarta, Indonesia. Menteng is surrounded by the districts of Senen and Matraman to the east, Tebet and Setiabudi to the south, Tanah Abang to the west, and Gambir to the north. Menteng is bound by the West Flood Canal to the west, Ciliwung River to the south and east, and Kebon Sirih Road to the north. Menteng is the district seat of the Central Jakarta government.

Jakarta Kota Station is a railway station, located in the old city core of Kota, Jakarta, Indonesia.

Gambir Station is a major railway station in Gambir, Gambir, Central Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia. The station is located on the eastern side of Merdeka Square and the western side of the Pramuka Movement headquarters and Immanuel Church. It is operated by the KAI.
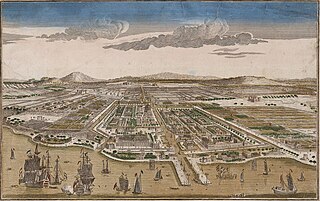
Jakarta is Indonesia's capital and largest city. Located on an estuary of the Ciliwung River, on the northwestern part of Java, the area has long sustained human settlement. Historical evidence from Jakarta dates back to the 4th century CE, when it was a Hindu settlement and port. The city has been sequentially claimed by the Indianized kingdom of Tarumanegara, the Hindu Kingdom of Sunda, the Muslim Sultanate of Banten, and by Dutch, Japanese and Indonesian administrations. The Dutch East Indies built up the area before it was taken during World War II by the Empire of Japan and finally became independent as part of Indonesia.

Trams in Ballarat were first used for public transport in 1887. They ceased to operate as a means of public transport in 1971, but a section continues to be operated today as a tourist attraction.

Colonial buildings and structures in Jakarta include those that were constructed during the Dutch colonial period of Indonesia. The period succeeded the earlier period when Jakarta, governed by the Sultanate of Banten, were completely eradicated and replaced with a walled city of Batavia. The dominant styles of the colonial period can be divided into three periods: the Dutch Golden Age, the transitional style period, and Dutch modernism. Dutch colonial architecture in Jakarta is apparent in buildings such as houses or villas, churches, civic buildings, and offices, mostly concentrated in the administrative city of Central Jakarta and West Jakarta.

The Rotterdam tramway network is a key element of the overall public transport arrangements in Rotterdam, Netherlands.

Depok Station (DP) is a railway station located in Pancoran Mas, Pancoran Mas, Depok, West Java. This station is commonly known as Depok Lama, to distinguish with Depok Baru Station. The station is one of the oldest station in Jakarta metropolitan area. At present it serves as a station of Jakarta Commuter Rail. Depok EMU depot is located to the southwest of the station.

Bogor Station (BOO), formerly Buitenzorg Station, is a railway station located in the city of Bogor, West Java. This station serves as the terminus for the Red Line service of KRL Commuterline. The station has five island platforms and two side platforms. The station is located +246 meters above sea level.

Bekasi Station (BKS) is a railway station located in Marga Mulya, North Bekasi, Bekasi, West Java. The station is at an altitude of +19 meters above sea level. This station serves the KRL Commuterline and inter-city trains.

Pieter Adriaan Jacobus "Piet" Moojen was a Netherlands-Indies architect, painter and writer. He studied architecture and painting in Antwerp. He lived and worked in the Dutch East Indies from 1903 to 1929. He was one of the first architects to implement Modernism in the Dutch East Indies. Moojen became widely known for his work on the Dutch entry at the Paris Colonial Exposition in 1931. He was active as an architect between 1909 and 1931.
Most railway lines in Indonesia were constructed during the Dutch colonial rule. After independence in 1945, many lines were abandoned. The current national rail operator, PT Kereta Api Indonesia (Persero), was founded on 28 September 1945.

N.V. Nederlandsch-Indische Spoorweg Maatschappij, abbreviated to NIS, NISM or N.V. NISM was a private-owned railways company in charge of rail transport in Java, Dutch East Indies. The company's headquarters were in Semarang, Central Java. The company started its maiden route from Semarang to the Vorstenlanden and in 1873 they also built their line to the Willem I Railway Station of Ambarawa–Kedungjati and Batavia–Buitenzorg lines. Later the network expanded to Bandung and Surabaya. It was absorbed into the present Kereta Api Indonesia after Indonesian independence in 1949. It was the main competitor to Staatsspoorwegen as state-owned railway company and established on April 6, 1875.

Jalan Gajah Mada and Jalan Hayam Wuruk, formerly Molenvliet West and Molenvliet Oost respectively, is a major thoroughfare located in Jakarta, Indonesia. The two streets with its canal, the Batang Hari, connect Glodok and Kota Tua Jakarta to the north with Harmoni Junction to the south. Completed in late 1640s, the canal-street Gajah Mada and Hayam Wuruk is Jakarta's oldest major thoroughfare.

Perusahaan Umum Pengangkutan Penumpang Djakarta was an Indonesian statutory corporation that moves in the transportation sector, specifically land transportation in Jakarta and areas around. It is known that Perum PPD operates approximately 494 single buses and 59 articulated buses for TransJakarta. Perum PPD is also known to operate JA Connexion, JR Connexion and Transjabodetabek routes serving Jakarta's suburban area and Trans Sarbagita in Denpasar, Bali.

Cikampek Station (CKP) is a large class type B railway station located in Cikampek Kota, Cikampek, Karawang Regency. The station, which is located at an altitude of +46 meters, is the station that is located in the easternmost part of the Operational Area I Jakarta and Karawang Regency, and is the largest railway station in Karawang Regency.

There was a tram system in Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia from 1889 to 1978. The tramway was operated by a private company Oost-Java Stoomtram Maatschappij, and later by Kereta Api Indonesia (KAI), and was the only OJS-owned rail system survived in post-independence Indonesia. The tramway linked Ujung with Wonokromo and continued towards Krian in Sidoarjo. All land assets of the tramway is currently owned by Operational Area VII Surabaya of the KAI.

Oost-Java Stoomtram Maatschappij (OJS) is the name of a private railway company which once operated in Surabaya, Dutch East Indies. The network had 46 stops with a total of near 66 miles (107 km) track; prior to its demise, it operated between the cities of Surabaya and Sidoarjo, Mojokerto Regency and Jombang Regency, on a mixture of former railway lines and urban on-street running.