Hydrolase is a class of enzymes that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases.
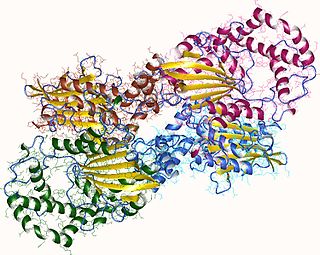
Acid phosphatase is an enzyme that frees attached phosphoryl groups from other molecules during digestion. It can be further classified as a phosphomonoesterase. It is stored in lysosomes and functions when these fuse with endosomes, which are acidified while they function; therefore, it has an acid pH optimum. This enzyme is present in many animal and plant species.
In enzymology, a meso-tartrate dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.1.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tartrate epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an adenosylmethionine hydrolase (EC 3.3.1.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alkenylglycerophosphocholine hydrolase (EC 3.3.2.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alkenylglycerophosphoethanolamine hydrolase (EC 3.3.2.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an isochorismatase (EC 3.3.2.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
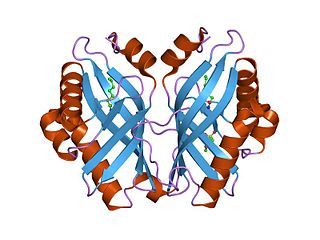
In enzymology, a limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase (EC 3.3.2.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an adenylylsulfatase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.6, systematic name = S-(2-hydroxyacyl)glutathione hydrolase) catalyzes the following reaction:
The enzyme 11-cis-retinyl-palmitate hydrolase (EC 3.1.1.63) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase (EC 3.1.1.47) catalyzes the reaction

The enzyme 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.4) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme alkylacetylglycerophosphatase (EC 3.1.3.59) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme alkylglycerophosphoethanolamine phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.39) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme retinoid isomerohydrolase (EC 3.1.1.64, all-trans-retinyl-palmitate hydrolase) catalyzes the reaction

In enzymology, a bisphosphoglycerate phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a glucosylceramidase (EC 3.2.1.45) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a riboflavinase (EC 3.5.99.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction





