
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the chest cavity. They serve to protect the lungs, heart, and other internal organs of the thorax. In some animals, especially snakes, ribs may provide support and protection for the entire body.

In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck.

The rib cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrate animals that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels. The circumferential enclosure formed by left and right rib cages, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi-rigid bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the shoulder girdles to form the core part of the axial skeleton.

The sacrum, in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1–S5) between ages 18 and 30.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

In anatomy, the axis or epistropheus is the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine, immediately inferior to the atlas, upon which the head rests.
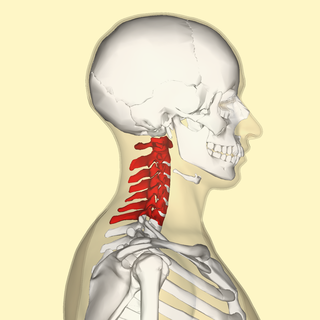
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae lie caudal of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine.
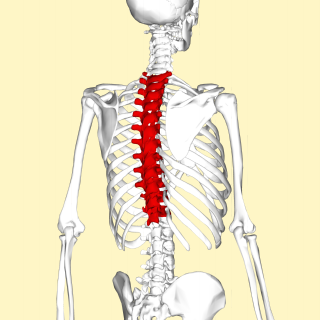
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae, with the lower ones being much larger than the upper. They are distinguished by the presence of facets on the sides of the bodies for articulation with the heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region.
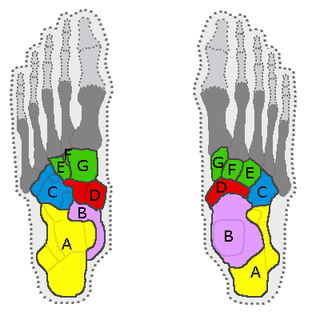
In the human body, the tarsus is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot and hindfoot.

The talus, talus bone, astragalus, or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.
The intermetacarpal joints are in the hand formed between the metacarpal bones. The bases of the second, third, fourth and fifth metacarpal bones articulate with one another by small surfaces covered with cartilage. The metacarpal bones are connected together by dorsal, palmar, and interosseous ligaments.
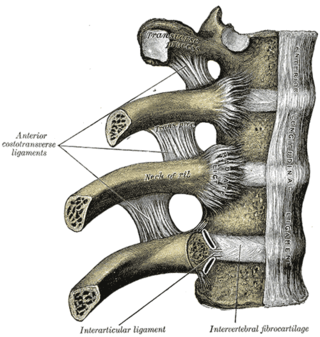
The articulations of the heads of the ribs constitute a series of gliding or arthrodial joints, and are formed by the articulation of the heads of the typical ribs with the costal facets on the contiguous margins of the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae and with the intervertebral discs between them; the first, eleventh and twelfth ribs each articulate with a single vertebra.

The inferior costal facet is a site where a rib forms a joint with the inferior aspect of the body of a thoracic vertebra.

The superior costal facet is a site where a rib forms a joint with the top of a vertebra.
A costal facet is a site of connection between a rib and a vertebra. The costal facets are located on the vertebrae that the rib articulates with. They are the superior costal facet, the inferior costal facet, and the transverse costal facet. Rib 1 only articulates with a transverse costal facet.

The fourth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is smaller in size than the third metatarsal bone and is the third longest of the five metatarsal bones. The fourth metatarsal is analogous to the fourth metacarpal bone in the hand
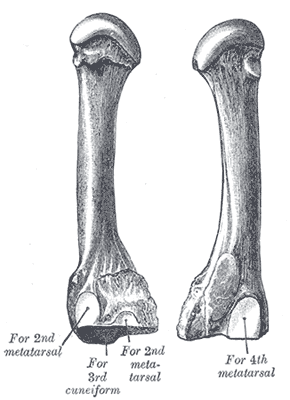
The third metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is the second longest metatarsal. The longest being the second metatarsal. The third metatarsal is analogous to the third metacarpal bone in the hand
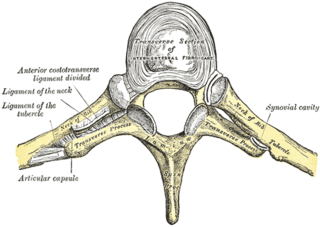
The costotransverse joint is the joint formed between the facet of the tubercle of the rib and the adjacent transverse process of a thoracic vertebra. The costotransverse joint is a plane type of synovial joint which, under physiological conditions, allows only gliding movement.

The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word sternum originates from Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon) 'chest'.

Each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species.


















