In vertebrate anatomy, ribs are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the thoracic cavity, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the thoracic cavity. They serve to protect the lungs, heart, and other vital organs of the thorax. In some animals, especially snakes, ribs may provide support and protection for the entire body.

In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck.

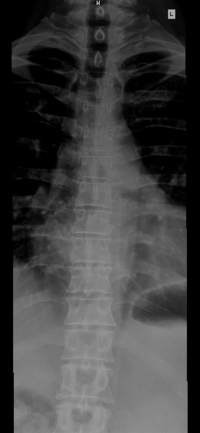
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels and support the shoulder girdle to form the core part of the axial skeleton.

The sacrum, in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1–S5) between ages 18 and 30.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

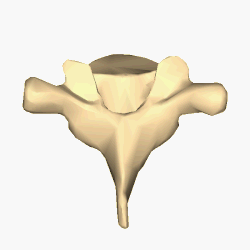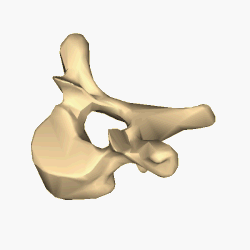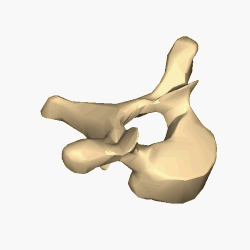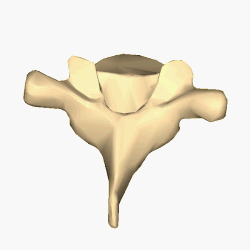
The lumbar vertebrae are located between the thoracic vertebrae and pelvis. They form the lower part of the human back in humans, and the tail end of the back in quadrupeds. In humans, there are five lumbar vertebrae. The term is used to describe the anatomy of humans and quadrupeds, such as horses, pigs, or cattle. These bones are found in particular cuts of meat, including tenderloin or sirloin steak.

In anatomy, the axis is the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine, immediately inferior to the atlas, upon which the head rests. The spinal cord passes through the axis.

Spondylosis is the degeneration of the vertebral column from any cause. In the more narrow sense it refers to spinal osteoarthritis, the age-related degeneration of the spinal column, which is the most common cause of spondylosis. The degenerative process in osteoarthritis chiefly affects the vertebral bodies, the neural foramina and the facet joints. If severe, it may cause pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots with subsequent sensory or motor disturbances, such as pain, paresthesia, imbalance, and muscle weakness in the limbs.
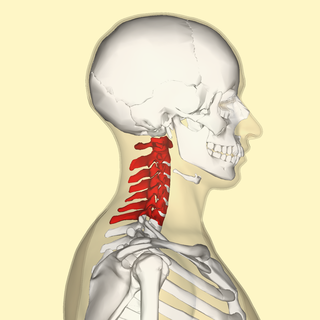
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae lie caudal of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine.

The intertransversarii are small muscles placed between the transverse processes of the vertebrae.
Congenital vertebral anomalies are a collection of malformations of the spine. Most, around 85%, are not clinically significant, but they can cause compression of the spinal cord by deforming the vertebral canal or causing instability. This condition occurs in the womb. Congenital vertebral anomalies include alterations of the shape and number of vertebrae.
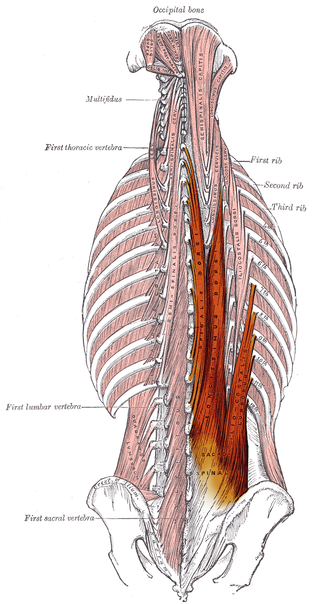
The erector spinae or spinal erectors is a set of muscles that straighten and rotate the back. The spinal erectors work together with the glutes to maintain stable posture standing or sitting.

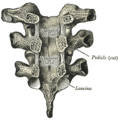
The ligamenta flava are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. They help to preserve upright posture, preventing hyperflexion, and ensuring that the vertebral column straightens after flexion. Hypertrophy can cause spinal stenosis.

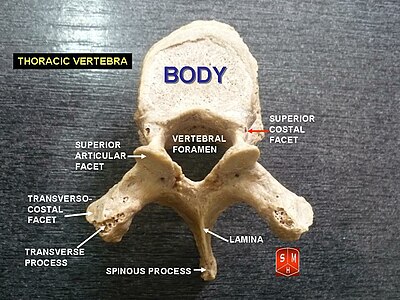
The articular process or zygapophysis of a vertebra is a projection of the vertebra that serves the purpose of fitting with an adjacent vertebra. The actual region of contact is called the articular facet.

The intervertebral foramen is an opening between two pedicles of adjacent vertebra in the articulated spine. Each intervertebral foramen gives passage to a spinal nerve and spinal blood vessels, and lodges a posterior (dorsal) root ganglion. Cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae all have intervertebral foramina.
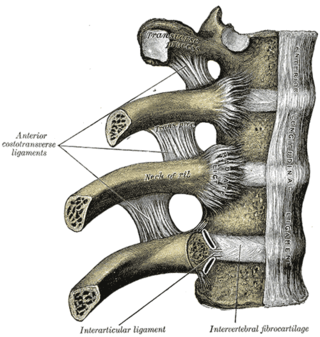
The articulations of the heads of the ribs constitute a series of gliding or arthrodial joints, and are formed by the articulation of the heads of the typical ribs with the costal facets on the contiguous margins of the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae and with the intervertebral discs between them; the first, eleventh and twelfth ribs each articulate with a single vertebra.
A laminotomy is an orthopaedic neurosurgical procedure that removes part of the lamina of a vertebral arch in order to relieve pressure in the vertebral canal. A laminotomy is less invasive than conventional vertebral column surgery techniques, such as laminectomy because it leaves more ligaments and muscles attached to the spinous process intact and it requires removing less bone from the vertebra. As a result, laminotomies typically have a faster recovery time and result in fewer postoperative complications. Nevertheless, possible risks can occur during or after the procedure like infection, hematomas, and dural tears. Laminotomies are commonly performed as treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis and herniated disks. MRI and CT scans are often used pre- and post surgery to determine if the procedure was successful.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The vertebral column, also known as the spinal column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrate animals. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate endoskeleton, where the notochord found in all chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of mineralized irregular bones called vertebrae, separated by fibrocartilaginous intervertebral discs. The dorsal portion of the vertebral column houses the spinal canal, an elongated cavity formed by alignment of the vertebral neural arches that encloses and protects the spinal cord, with spinal nerves exiting via the intervertebral foramina to innervate each body segments.

Each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species.