
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. A silvery-coloured metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, the so-called "tin cry" can be heard as a result of twinning in tin crystals; this trait is shared by indium, cadmium, zinc, and mercury in its solid state.
The Stille reaction is a chemical reaction widely used in organic synthesis. The reaction involves the coupling of two organic groups, one of which is carried as an organotin compound (also known as organostannanes). A variety of organic electrophiles provide the other coupling partner. The Stille reaction is one of many palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions.
Tin(IV) chloride, also known as tin tetrachloride or stannic chloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula SnCl4. It is a colorless hygroscopic liquid, which fumes on contact with air. It is used as a precursor to other tin compounds. It was first discovered by Andreas Libavius (1550–1616) and was known as spiritus fumans libavii.

Organotin chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organotin compounds or stannanes, which are organometallic compounds containing tin carbon bonds. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide, discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory.

A trimethylsilyl group (abbreviated TMS) is a functional group in organic chemistry. This group consists of three methyl groups bonded to a silicon atom [−Si(CH3)3], which is in turn bonded to the rest of a molecule. This structural group is characterized by chemical inertness and a large molecular volume, which makes it useful in a number of applications.

n-Butyllithium C4H9Li (abbreviated n-BuLi) is an organolithium reagent. It is widely used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS). Also, it is broadly employed as a strong base (superbase) in the synthesis of organic compounds as in the pharmaceutical industry.

Tributyltin oxide (TBTO) is an organotin compound chiefly used as a biocide (fungicide and molluscicide), especially a wood preservative. Its chemical formula is [(C4H9)3Sn]2O. It is a colorless viscous liquid. It is poorly soluble in water (20 ppm) but highly soluble in organic solvents. It is a potent skin irritant.

Tetrabutyltin is the organotin compound with the molecular formula Sn(CH2CH2CH2CH3)4 or SnBu4, where Bu is butyl −CH2CH2CH2CH3. Sometimes abbreviated TTBT, it is a colorless, lipophilic oil.
Boron trichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula BCl3. This colorless gas is a reagent in organic synthesis. It is highly reactive toward water.

Tributyltin (TBT) is an umbrella term for a class of organotin compounds which contain the (C4H9)3Sn group, with a prominent example being tributyltin oxide. For 40 years TBT was used as a biocide in anti-fouling paint, commonly known as bottom paint, applied to the hulls of oceangoing vessels. Bottom paint improves ship performance and durability as it reduces the rate of biofouling, the growth of organisms on the ship's hull. The TBT slowly leaches out into the marine environment where it is highly toxic toward nontarget organisms. TBT toxicity can lead to biomagnification or bioaccumulation within such nontarget organisms like invertebrates, vertebrates, and a variety of mammals. TBT is also an obesogen. After it led to collapse of local populations of organisms, TBT was banned.

Triphenyltin hydride is the organotin compound with the formula (C6H5)3SnH. It is a white distillable oil that is soluble in organic solvents. It is often used as a source of "H·" to generate radicals or cleave carbon-oxygen bonds.
Tributyltin hydride is an organotin compound with the formula (C4H9)3SnH. It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents. The compound is used as a source of hydrogen atoms in organic synthesis.

Trimethyltin chloride is an organotin compound with the formula (CH3)3SnCl. It is a white solid that is highly toxic and malodorous. It is susceptible to hydrolysis.

Tetramethyltin is an organometallic compound with the formula (CH3)4Sn. This liquid, one of the simplest organotin compounds, is useful for transition-metal mediated conversion of acid chlorides to methyl ketones and aryl halides to aryl methyl ketones. It is volatile and toxic, so care should be taken when using it in the laboratory.
Triphenyltin compounds are organotin compounds with the general formula (C6H5)3SnX. They contain the triphenyltin group, (C6H5)3Sn, or Ph3Sn, which consists of an atom of tin bonded to three phenyl groups. Examples of triphenyltins include:

Tributyltin azide is an organotin compound with the formula (C4H9)3SnN3. It is a colorless solid although older samples can appear as yellow oils. The compound is used as a reagent in organic synthesis.

Dibutylchloromethyltin chloride (DBCT) is a toxic organotin compound. It's a potent and irreversible ATP synthase inhibitor. DBCT is a volatile liquid with powerful vesicant effects.
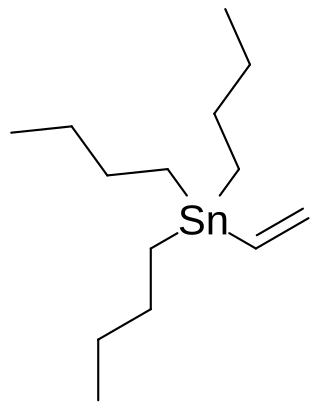
Vinyl tributyltin is an organotin compound with the formula Bu3SnCH=CH2 (Bu = butyl). It is a white, air-stable solid. It is used as a source of vinyl anion equivalent in Stille coupling reactions. As a source of vinyltin reagents, early work used vinyl trimethyltin, but trimethyltin compounds are avoided nowadays owing to their toxicity.
Niobium(III) chloride also known as niobium trichloride is a compound of niobium and chlorine. The binary phase NbCl3 is not well characterized but many adducts are known.
Germanium dichloride dioxane is a chemical compound with the formula GeCl2(C4H8O2), where C4H8O2 is 1,4-dioxane. It is a white solid. The compound is notable as a source of Ge(II), which contrasts with the pervasiveness of Ge(IV) compounds. This dioxane complex represents a well-behaved form of germanium dichloride.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
















