
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.
The Suzuki reaction or Suzuki coupling is an organic reaction that uses a palladium complex catalyst to cross-couple a boronic acid to an organohalide. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, and he shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Richard F. Heck and Ei-ichi Negishi for their contribution to the discovery and development of noble metal catalysis in organic synthesis. This reaction is sometimes telescoped with the related Miyaura borylation; the combination is the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. It is widely used to synthesize polyolefins, styrenes, and substituted biphenyls.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of n, the material is either a dense brown solid or a soluble reddish salt. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis, notably for the industrial production of acetic acid and hydroformylation.

Metal carbonyls are coordination complexes of transition metals with carbon monoxide ligands. Metal carbonyls are useful in organic synthesis and as catalysts or catalyst precursors in homogeneous catalysis, such as hydroformylation and Reppe chemistry. In the Mond process, nickel tetracarbonyl is used to produce pure nickel. In organometallic chemistry, metal carbonyls serve as precursors for the preparation of other organometallic complexes.
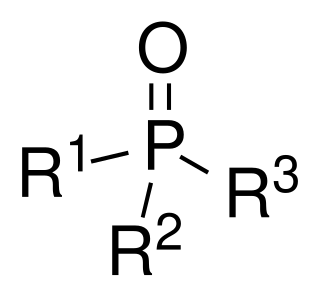
Phosphine oxides are phosphorus compounds with the formula OPX3. When X = alkyl or aryl, these are organophosphine oxides. Triphenylphosphine oxide is an example. An inorganic phosphine oxide is phosphoryl chloride (POCl3). The parent phosphine oxide (H3PO) remains rare and obscure.

Chloro(triphenylphosphine)gold(I) or triphenylphosphinegold(I) chloride is a coordination complex with the formula (Ph3P)AuCl. This colorless solid is a common reagent for research on gold compounds.

Organoactinide chemistry is the science exploring the properties, structure, and reactivity of organoactinide compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to actinide chemical bond.

Trimethylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(CH3)3, commonly abbreviated as PMe3. This colorless liquid has a strongly unpleasant odor, characteristic of alkylphosphines. The compound is a common ligand in coordination chemistry.

Organoaluminium chemistry is the study of compounds containing bonds between carbon and aluminium. It is one of the major themes within organometallic chemistry. Illustrative organoaluminium compounds are the dimer trimethylaluminium, the monomer triisobutylaluminium, and the titanium-aluminium compound called Tebbe's reagent. The behavior of organoaluminium compounds can be understood in terms of the polarity of the C−Al bond and the high Lewis acidity of the three-coordinated species. Industrially, these compounds are mainly used for the production of polyolefins.
Organophosphines are organophosphorus compounds with the formula PRnH3−n, where R is an organic substituent. These compounds can be classified according to the value of n: primary phosphines (n = 1), secondary phosphines (n = 2), tertiary phosphines (n = 3). All adopt pyramidal structures. Organophosphines are generally colorless, lipophilic liquids or solids. The parent of the organophosphines is phosphine (PH3).
Martin Arthur Bennett FRS is an Australian inorganic chemist. He gained recognition for studies on the co-ordination chemistry of tertiary phosphines, olefins, and acetylenes, and the relationship of their behaviour to homogeneous catalysis.
Organoarsenic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing a chemical bond between arsenic and carbon. A few organoarsenic compounds, also called "organoarsenicals," are produced industrially with uses as insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides. In general these applications are declining in step with growing concerns about their impact on the environment and human health. The parent compounds are arsane and arsenic acid. Despite their toxicity, organoarsenic biomolecules are well known.

Tributylphosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula P(CH2CH2CH2CH3)3, often abbreviated as PBu3. It is a tertiary phosphine. It is an oily liquid at room temperature, with a nauseating odor. It reacts slowly with atmospheric oxygen, and rapidly with other oxidizing agents, to give the corresponding phosphine oxide. It is usually handled using air-free techniques.
Transition metal hydrides are chemical compounds containing a transition metal bonded to hydrogen. Most transition metals form hydride complexes and some are significant in various catalytic and synthetic reactions. The term "hydride" is used loosely: some of them are acidic (e.g., H2Fe(CO)4), whereas some others are hydridic, having H−-like character (e.g., ZnH2).
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.
Organoplatinum chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to platinum chemical bond, and the study of platinum as a catalyst in organic reactions. Organoplatinum compounds exist in oxidation state 0 to IV, with oxidation state II most abundant. The general order in bond strength is Pt-C (sp) > Pt-O > Pt-N > Pt-C (sp3). Organoplatinum and organopalladium chemistry are similar, but organoplatinum compounds are more stable and therefore less useful as catalysts.

A metal-phosphine complex is a coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0).
A transition metal phosphido complex is a coordination complex containing a phosphido ligand (R2P, where R = H, organic substituent). With two lone pairs on phosphorus, the phosphido anion (R2P−) is comparable to an amido anion (R2N−), except that the M-P distances are longer and the phosphorus atom is more sterically accessible. For these reasons, phosphido is often a bridging ligand. The -PH2 ion or ligand is also called phosphanide or phosphido ligand.

Organoberyllium chemistry involves the synthesis and properties of organometallic compounds featuring the group 2 alkaline earth metal beryllium (Be). The area remains understudied, relative to the chemistry of other main-group elements, because although metallic beryllium is relatively unreactive, its dust causes berylliosis and compounds are toxic. Organoberyllium compounds are typically prepared by transmetallation or alkylation of beryllium chloride.
















