
Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl4. It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. TiCl4 is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4", as a phonetic representation of the symbols of its molecular formula.

Triphenylmethane or triphenyl methane (sometimes also known as Tritan), is the hydrocarbon with the formula (C6H5)3CH. This colorless solid is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents and not in water. Triphenylmethane is the basic skeleton of many synthetic dyes called triarylmethane dyes, many of them are pH indicators, and some display fluorescence. A trityl group in organic chemistry is a triphenylmethyl group Ph3C, e.g. triphenylmethyl chloride (trityl chloride) and the triphenylmethyl radical (trityl radical).

Copper(I) chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl. The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Impure samples appear green due to the presence of copper(II) chloride (CuCl2).

Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides/oxychlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive solid, although commercial samples can be yellowish and contaminated with hydrogen chloride.

Phosphorus trichloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PCl3. A colorless liquid when pure, it is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of phosphites and other organophosphorus compounds. It is toxic and reacts readily with water to release hydrogen chloride.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic red-brown solids. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is the usual compound of commerce. It is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis.

1,1'-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) is an organic compound with the molecular formula (C3H3N2)2CO. It is a white crystalline solid. It is often used for the coupling of amino acids for peptide synthesis and as a reagent in organic synthesis.

Thiophenol is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SH, sometimes abbreviated as PhSH. This foul-smelling colorless liquid is the simplest aromatic thiol. The chemical structures of thiophenol and its derivatives are analogous to phenols. An exception is the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the aromatic ring is replaced by a sulfur atom. The prefix thio- implies a sulfur-containing compound and when used before a root word name for a compound which would normally contain an oxygen atom, in the case of 'thiol' that the alcohol oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom.

Triflic acid, the short name for trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, TFMS, TFSA, HOTf or TfOH, is a sulfonic acid with the chemical formula CF3SO3H. It is one of the strongest known acids. Triflic acid is mainly used in research as a catalyst for esterification. It is a hygroscopic, colorless, slightly viscous liquid and is soluble in polar solvents.
Organophosphorus chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organophosphorus compounds, which are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents.

Tungsten hexachloride is an inorganic chemical compound of tungsten and chlorine with the chemical formula WCl6. This dark violet-blue compound exists as volatile crystals under standard conditions. It is an important starting reagent in the preparation of tungsten compounds. Other examples of charge-neutral hexachlorides are rhenium(VI) chloride and molybdenum(VI) chloride. The highly volatile tungsten hexafluoride is also known.

Platinum(II) chloride is the chemical compound PtCl2. It is an important precursor used in the preparation of other platinum compounds. It exists in two crystalline forms, but the main properties are somewhat similar: dark brown, insoluble in water, diamagnetic, and odorless.
Organogermanium chemistry is the science of chemical species containing one or more C–Ge bonds. Germanium shares group 14 in the periodic table with carbon, silicon, tin and lead. Historically, organogermanes are considered as nucleophiles and the reactivity of them is between that of organosilicon and organotin compounds. Some organogermanes have enhanced reactivity compared with their organosilicon and organoboron analogues in some cross-coupling reactions.

Gold compounds are compounds by the element gold (Au). Although gold is the most noble of the noble metals, it still forms many diverse compounds. The oxidation state of gold in its compounds ranges from −1 to +5, but Au(I) and Au(III) dominate its chemistry. Au(I), referred to as the aurous ion, is the most common oxidation state with soft ligands such as thioethers, thiolates, and organophosphines. Au(I) compounds are typically linear. A good example is Au(CN)−2, which is the soluble form of gold encountered in mining. The binary gold halides, such as AuCl, form zigzag polymeric chains, again featuring linear coordination at Au. Most drugs based on gold are Au(I) derivatives.
Organoarsenic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing a chemical bond between arsenic and carbon. A few organoarsenic compounds, also called "organoarsenicals," are produced industrially with uses as insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides. In general these applications are declining in step with growing concerns about their impact on the environment and human health. The parent compounds are arsane and arsenic acid. Despite their toxicity, organoarsenic biomolecules are well known.
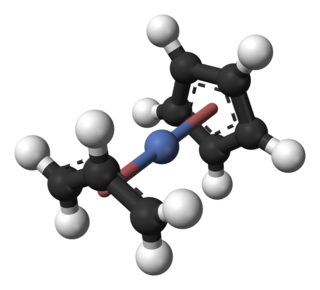
Cyclopentadienyl allyl palladium is an organopalladium compound with formula (C5H5)Pd(C3H5). This reddish solid is volatile with an unpleasant odor. It is soluble in common organic solvents. The molecule consists of a Pd centre sandwiched between a Cp and allyl ligands.
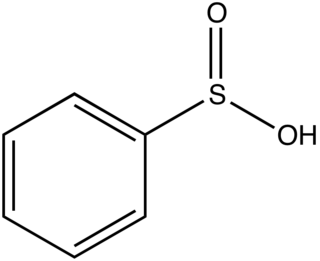
Phenylsulfinic acid is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SO2H. It is a colorless or white crystalline solid that is usually stored in the form of its sodium salt. In aqueous solution it is strongly acidic and is easily oxidized in air. Phenylsulfinic acid and its esters are chiral.

In organosulfur chemistry, sulfenamides are a class of organosulfur compounds characterized by the general formula R−S−N(−R)2, where the R groups are hydrogen, alkyl, or aryl. Sulfenamides have been used extensively in the vulcanization of rubber using sulfur. They are related to the oxidized compounds known as sulfinamides and sulfonamides.
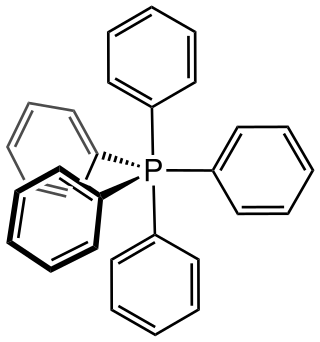
Pentaphenylphosphorus is an organic phosphorane containing five phenyl groups connected to a central phosphorus atom. The phosphorus atom is considered to be in the +5 oxidation state. The chemical formula could be written as P(C6H5)5 or Ph5P, where Ph represents the phenyl group. It was discovered and reported in 1949 by Georg Wittig.


















