
D, or d, is the fourth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is dee, plural dees.

A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor, called the proto-language of that family. The term family is a metaphor borrowed from biology, with the tree model used in historical linguistics analogous to a family tree, or to phylogenetic trees of taxa used in evolutionary taxonomy. Linguists thus describe the daughter languages within a language family as being genetically related. The divergence of a proto-language into daughter languages typically occurs through geographical separation, with different regional dialects of the proto-language undergoing different language changes and thus becoming distinct languages over time.

A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. They work across a wide range of research fields, spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena.

Mistletoe is the common name for obligate hemiparasitic plants in the order Santalales. They are attached to their host tree or shrub by a structure called the haustorium, through which they extract water and nutrients from the host plant.

Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods that are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, medical, and criminal justice contexts. In some cases, criminal or anti-social behavior occurs when the person is under the influence of a drug, and long-term personality changes in individuals may also occur. In addition to possible physical, social, and psychological harm, the use of some drugs may also lead to criminal penalties, although these vary widely depending on the local jurisdiction.

Loranthaceae, commonly known as the showy mistletoes, is a family of flowering plants. It consists of about 75 genera and 1,000 species of woody plants, many of them hemiparasites. The three terrestrial species are Nuytsia floribunda, Atkinsonia ligustrina, and Gaiadendron punctatum Loranthaceae are primarily xylem parasites, but their haustoria may sometimes tap the phloem, while Tristerix aphyllus is almost holoparasitic. For a more complete description of the Australian Loranthaceae, see Flora of Australia onlineArchived 2018-04-01 at the Wayback Machine., for the Malesian Loranthaceae see Flora of Malesia.

Killed in action (KIA) is a casualty classification generally used by militaries to describe the deaths of their own personnel at the hands of enemy or hostile forces at the moment of action. The United States Department of Defense, for example, says that those declared KIA did not need to have fired their weapons, but only to have been killed due to hostile attack. KIAs include those killed by friendly fire in the midst of combat, but not from incidents such as accidental vehicle crashes, murder or other non-hostile events or terrorism. KIA can be applied both to front-line combat troops and to naval, air and support troops.
A cousin is a relative that is the child of a parent's sibling; this is more specifically referred to as a first cousin.

Scorpio (♏︎) is the eighth astrological sign in the zodiac, originating from the constellation of Scorpius. It spans 210–240° ecliptic longitude. Under the tropical zodiac, the Sun transits this sign on average from October 23 to November 21. Depending on which zodiac system one uses, someone born under the influence of Scorpio may be called a Scorpio or a Scorpionic.

The great sapphirewing is a species of hummingbird in the "brilliants", tribe Heliantheini in subfamily Lesbiinae. It is found in Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru.

The crag chilia or crag earthcreeper is a species of bird in the Furnariinae subfamily of the ovenbird family Furnariidae. It is endemic to Chile.
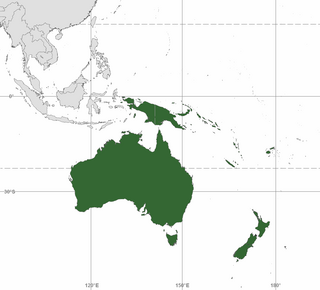
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand, and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands. The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different but related regions.

Leucostele chiloensis is a species of cactus native to South America; genus members are known as hedgehog cacti, sea-urchin cactus or Easter lily cactus.

Arjona is a genus of flowering plants in the family Schoepfiaceae. They are hemiparasites.
Romina Vidal-Russell is an Argentinean botanist who works in the areas of phytogeography, phylogeny, and parasitic plants, and on which she has written extensively. Her papers on the phylogeny of parasitic plants are cited on the APG website, and elsewhere and her collaborations are international. She currently works at the National University of Comahue in Argentina. She earned a Ph.D. at SIUC with Daniel L. Nickrent as supervisor.

Tristerix corymbosus, commonly named quintral, cutral, and quitral in Spanish, is a species of Tristerix found in Chile at elevations of 0 to 2075 meters. is a species of Tristerix found in Chile at elevations of 0 to 2075 meters. It is a preferred source of fruit for the monito del monte.

Tristerix verticillatus is a species of Tristerix found in Argentina, Bolivia, and Chile.















