
The lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system in many terrestrial animals, including all tetrapod vertebrates and a small number of amphibious fish, pulmonate gastropods, and some arachnids. Their function is to conduct gas exchange by extracting oxygen from the air into the bloodstream via diffusion directly across the humidified airway epithelia, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream out into the atmosphere, a process also known as respiration. This article is primarily concerned with the lungs of tetrapods, which are paired and located on either side of the heart, occupying most of the volume of the thoracic cavity, and are homologous to the swim bladders in ray-finned fish.

A lobotomy or leucotomy is a discredited form of neurosurgical treatment for psychiatric disorder or neurological disorder that involves severing connections in the brain's prefrontal cortex. The surgery causes most of the connections to and from the prefrontal cortex, the anterior part of the frontal lobes of the brain, to be severed.

The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The human pituitary gland is oval shaped, about 1 cm in diameter, 0.5–1 gram (0.018–0.035 oz) in weight on average, and about the size of a kidney bean.

The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is the part of the brain responsible for cognition.

A camshaft is a shaft that contains a row of pointed cams in order to convert rotational motion to reciprocating motion. Camshafts are used in piston engines, mechanically controlled ignition systems and early electric motor speed controllers.

Sarcopterygii — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii — is a clade of vertebrate animals which includes a group of bony fish commonly referred to as lobe-finned fish. These vertebrates are characterised by prominent muscular limb buds (lobes) within their fins, which are supported by articulated appendicular skeletons. This is in contrast to the other clade of bony fish, the Actinopterygii, which have only skin-covered bony spines supporting the fins.

A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. These are the widest bronchi, and enter the right lung, and the left lung at each hilum. The main bronchi branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as 4th order, 5th order, and 6th order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi, when too narrow to be supported by cartilage, are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi.

The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.

The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.

The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere. It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove between tissues called the central sulcus and from the temporal lobe by a deeper groove called the lateral sulcus. The most anterior rounded part of the frontal lobe is known as the frontal pole, one of the three poles of the cerebrum.

The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ob, 'behind', and caput, 'head'.

The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the dorsal telencephalon, or pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric left and right cerebral hemispheres.
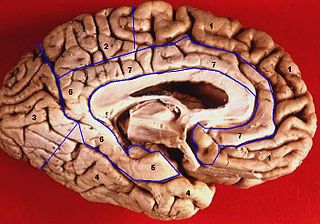
The limbic lobe is an arc-shaped cortical region of the limbic system, on the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere of the mammalian brain, consisting of parts of the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes. The term is ambiguous, with some authors including the paraterminal gyrus, the subcallosal area, the cingulate gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus, the dentate gyrus, the hippocampus and the subiculum; while the Terminologia Anatomica includes the cingulate sulcus, the cingulate gyrus, the isthmus of cingulate gyrus, the fasciolar gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus, the parahippocampal sulcus, the dentate gyrus, the fimbrodentate sulcus, the fimbria of hippocampus, the collateral sulcus, and the rhinal sulcus, and omits the hippocampus.
Focal seizures are seizures that affect initially only one hemisphere of the brain. The brain is divided into two hemispheres, each consisting of four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes. A focal seizure is generated in and affects just one part of the brain – a whole hemisphere or part of a lobe. Symptoms will vary according to where the seizure occurs. When seizures occur in the frontal lobe, the patient may experience a wave-like sensation in the head. When seizures occur in the temporal lobe, a feeling of déjà vu may be experienced. When seizures are localized to the parietal lobe, a numbness or tingling may occur. With seizures occurring in the occipital lobe, visual disturbances or hallucinations have been reported.

In the field of neurology, temporal lobe epilepsy is an enduring brain disorder that causes unprovoked seizures from the temporal lobe. Temporal lobe epilepsy is the most common type of focal onset epilepsy among adults. Seizure symptoms and behavior distinguish seizures arising from the medial temporal lobe from seizures arising from the lateral (neocortical) temporal lobe. Memory and psychiatric comorbidities may occur. Diagnosis relies on electroencephalographic (EEG) and neuroimaging studies. Anticonvulsant medications, epilepsy surgery and dietary treatments may improve seizure control.
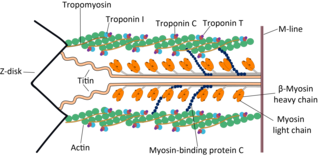
Troponin C is a protein which is part of the troponin complex. It contains four calcium-binding EF hands, although different isoforms may have fewer than four functional calcium-binding subdomains. It is a component of thin filaments, along with actin and tropomyosin. It contains an N lobe and a C lobe. The C lobe serves a structural purpose and binds to the N domain of troponin I (TnI). The C lobe can bind either Ca2+ or Mg2+. The N lobe, which binds only Ca2+, is the regulatory lobe and binds to the C domain of troponin I after calcium binding.
Tornoceratidae is a family of goniatitid ammonoids from the middle and upper Devonian. The family is included in the suborder Tornoceratina and the superfamily Tornoceratoidea.

The liver is a major metabolic organ exclusively found in vertebrate animals, which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and various other biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells.
The neuroanatomy of memory encompasses a wide variety of anatomical structures in the brain.

Emphysema is any air-filled enlargement in the body's tissues. Most commonly emphysema refers to the permanent enlargement of air spaces (alveoli) in the lungs, and is also known as pulmonary emphysema.











