
Placodermi is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyletic, consisting of several distinct outgroups or sister taxa to all living jawed vertebrates, which originated among their ranks. This is illustrated by a 419-million-year-old fossil, Entelognathus, from China, which is the only known placoderm with a type of bony jaw like that found in modern bony fishes, including a dentary bone, which is found in humans and other tetrapods. The jaws in other placoderms were simplified and consisted of a single bone. Placoderms were also the first fish to develop pelvic fins, the precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods, as well as true teeth. Paraphyletic groupings are problematic, as one can not talk precisely about their phylogenic relationships, characteristic traits, and complete extinction. 380-million-year-old fossils of three other genera, Incisoscutum, Materpiscis and Austroptyctodus, represent the oldest known examples of live birth. In contrast, one 2016 analysis concluded that placodermi are likely monophyletic, though these analyses have been further dismissed with more transitional taxa between placoderms and modern gnathosthomes solidying their paraphyletic status.

Gustaf Lindström was a Swedish paleontologist.

Chytra kirki is a species of tropical freshwater snail with an operculum, aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Paludomidae.

Stagnicola utahensis, common name the thickshell pondsnail, is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Lymnaeidae, the pond snails. This species is endemic to Utah Lake in the United States. The last living snails were found in the 1930s.

Tiphobia horei is a species of freshwater snail with an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Paludomidae.

Sphaerexochus is a genus of trilobite from the Middle Ordovician to Late Silurian of Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America.

Marstonia scalariformis, previously known as Pyrgulopsis scalariformis, common name the moss pyrg, is a species of freshwater snail with a gill and an operculum, aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Hydrobiidae.

Tryblidium is a paleozoic genus of Ordovician and Silurian monoplacophorans.

Pilina unguis is an extinct species of Paleozoic Silurian monoplacophoran. It was first named as Tryblidium unguis and described by Gustaf Lindström in Latin from the Silurian deposits of Gotland in Sweden, in 1880.

Pilina is an extinct genus of paleozoic monoplacophorans in the family Tryblidiidae.

Helcionopsis radiatum is an extinct species of paleozoic monoplacophoran in the family Tryblidiidae.

Helcionopsis is an extinct genus of paleozoic monoplacophoran in the family Tryblidiidae.
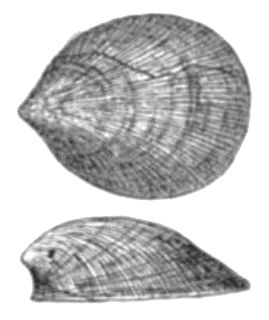
Helcionopsis striata is an extinct species of paleozoic monoplacophoran in the family Tryblidiidae.
Helcionopsis subcarinata is an extinct species of paleozoic monoplacophoran in the family Tryblidiidae.

Pilina solarium is an extinct species of a paleozoic Silurian monoplacophoran. It was first named as Palaeacmaea solarium and described by Gustaf Lindström from Silurian of Gotland in Sweden in 1884.

Conus ebraeus, common name the black-and-white cone, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Conidae, the cone snails and their allies.

Edentulina moreleti is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Streptaxidae.
Similodonta is an extinct genus of early bivalve in the extinct family Praenuculidae. The genus is one of eleven genera in the subfamily Praenuculinae. Similodonta is known from Middle Ordovician through Middle Silurian fossils found in Europe and North America. The genus currently contains eight accepted species, Similodonta ceryx, Similodonta collina, Similodonta djupvikensis, Similodonta magna, Similodonta recurva, Similodonta spjeldnaesi, Similodonta wahli and the type species Similodonta similis.

Cyrtospirifer is an extinct genus of brachiopods. The fossils are present in the Middle and Upper Devonian.
Frodospira cochleata is a species of extinct sea snail in the family Lophospiridae. Fossil specimens from 422.9 and 421.3 million years ago have been found in Sweden at Grogarnsberget, Hemse, and Sandarve kulle, in a hill about a kilometer north of Fardhem Church. A species of epifaunal filter feeder, it had a slender, turriculate shell consisting of twelve to thirteen whorls.
















