Related Research Articles

Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are not contagious or life-threatening, but can be very uncomfortable.

Nummular dermatitis is one of the many forms of dermatitis. It is characterized by round or oval-shaped itchy lesions. The name comes from the Latin word "nummus," which means "coin."
Stasis dermatitis refers to the skin changes that occur in the leg as a result of "stasis" or blood pooling from insufficient venous return; the alternative name of varicose eczema comes from a common cause of this being varicose veins.

Erythroderma is an inflammatory skin disease with redness and scaling that affects nearly the entire cutaneous surface. This term applies when 90% or more of the skin is affected.

Tinea manuum is a fungal infection of the hand, mostly a type of dermatophytosis, often part of two feet-one hand syndrome. There is diffuse scaling on the palms or back of usually one hand and the palmer creases appear more prominent. When both hands are affected, the rash looks different on each hand, with palmer creases appearing whitish if the infection has been present for a long time. It can be itchy and look slightly raised. Nails may also be affected.

Tetrazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative with anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, muscle relaxant and slightly hypnotic properties. It was formerly used mainly in Austria, France, Belgium, Germany and Spain to treat muscle spasm, anxiety disorders such as panic attacks, or more rarely to treat depression, premenstrual syndrome or agoraphobia. Tetrazepam has relatively little sedative effect at low doses while still producing useful muscle relaxation and anxiety relief. The Co-ordination Group for Mutual Recognition and Decentralised Procedures-Human endorsed the Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) recommendation to suspend the marketing authorisations of tetrazepam-containing medicines across the European Union (EU) in April 2013. The European Commission has confirmed the suspension of the marketing authorisations for Tetrazepam in Europe because of cutaneous toxicity, effective from the 1 August 2013.
Id reactions are types of acute dermatitis developing after days or weeks at skin locations distant from the initial inflammatory or infectious site. They can be localised or generalised. This is also known as an 'autoeczematous response' and there must be an identifiable initial inflammatory or infectious skin problem which leads to the generalised eczema. Often intensely itchy, the red papules and pustules can also be associated with blisters and scales and are always remote from the primary lesion. It is most commonly a blistering rash with itchy vesicles on the sides of fingers and feet as a reaction to fungal infection on the feet, athlete's foot. Stasis dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, acute irritant contact eczema and infective dermatitis have been documented as possible triggers, but the exact cause and mechanism is not fully understood. Several other types of id reactions exist including erythema nodosum, erythema multiforme, Sweet's syndrome and urticaria.
Plummer's nail is a clinical sign in which there is onycholysis, or separation of the nail from the nail bed, particularly affecting the ring and little fingers. It occurs in patients with thyrotoxicosis. About 5% of hyperthyroid patients display abnormal nail changes. Plummer's nail is also associated with psoriasis, traumatic injury, and allergic contact dermatitis.
Sea anemone dermatitis is a cutaneous condition similar to jellyfish and hydroid dermatitis, caused by contact with certain sea anemones.
Blister beetle dermatitis is a cutaneous condition that occurs after contact with any of several types of beetles, including those from the Meloidae and Oedemeridae families. Blister beetles secrete an irritant called cantharidin, a vesicant that can get onto humans if they touch the beetles.
Airbag dermatitis is skin irritation secondary to the deployment of airbags.
Lacquer dermatitis is a cutaneous condition characterized by a contact dermatitis to various lacquers.

Abietic acid dermatitis is a contact dermatitis often seen in association with musical instruments.
African blackwood dermatitis is a condition characterized by an allergic contact dermatitis associated with a musical instrument made of a particular type of wood.
Uranium dermatosis is a cutaneous condition characterized by an irritant contact dermatitis and skin burns due to exposure to uranium.
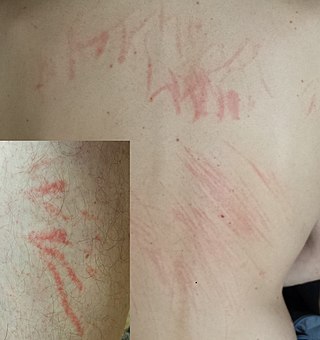
Shiitake mushroom dermatitis is an intensely itchy dermatitis characterized by disseminated 1mm erythematous micropapules seen in a linear grouped arrangement secondary to Koebnerization due to patient scratching. It is caused by the ingestion of shiitake mushrooms and was first described in 1977 by Nakamura. Although it is rarely seen outside China and Japan due to a lower incidence of shiitake consumption outside these regions, there is a well-established association between flagellate dermatitis and shiitake mushroom ingestion. Bleomycin ingestion may also cause similar findings. On physical exam, one key difference between the two is that post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation changes are usually seen with bleomycin-induced flagellate dermatitis and are not typically present with shiitake mushroom induced flagellate dermatitis. The median time of onset from ingestion of shiitake mushrooms is typically 24 hours, ranging from 12 hours to 5 days. Most patients completely recover by 3 weeks, with or without treatment. Although the pathogenesis of shiitake induced flagellate dermatitis is not clear, the theory most argued for is a toxic reaction to lentinan, a polysaccharide isolated from shiitake mushrooms. However, Type I and Type IV allergic hypersensitivities have also been supported by the 24-hour median time of onset, clearance in 3–21 days, severe pruritus, benefit of steroids and antihistamines, and lack of grouped outbreaks in people exposed to shared meals containing shiitake mushrooms. Most cases reported shortly after its discovery were due to consumption of raw shiitake mushrooms, but several cases have since been reported after consumption of fully cooked mushrooms.
Protein contact dermatitis is a cutaneous condition, and was a term originally used to describe an eczematous reaction to protein-containing material in food handlers.

Garlic allergy or allergic contact dermatitis to garlic is a common inflammatory skin condition caused by contact with garlic oil or dust. It mostly affects people who cut and handle fresh garlic, such as chefs, and presents on the tips of the thumb, index and middle fingers of the non-dominant hand. The affected fingertips show an asymmetrical pattern of fissure as well as thickening and shedding of the outer skin layers, which may progress to second- or third-degree burn of injured skin.
Baker's itch is a cutaneous reaction caused by bites of Acarus siro, the flour mite.
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 258. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.