| Abietic acid dermatitis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Various types of rosin for violins, violas and cellos | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Abietic acid dermatitis is a contact dermatitis often seen in association with musical instruments. [1]
| Abietic acid dermatitis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Various types of rosin for violins, violas and cellos | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Abietic acid dermatitis is a contact dermatitis often seen in association with musical instruments. [1]
The main cause is a type-I hypersensitivity reaction to products containing abietic acid, such as the rosin/colophony, which is commonly used as a friction-increasing agent. Players of bowed string instruments (violin, viola, cello, double bass) rub cakes or blocks of rosin on their bow so it can grip the strings. Ballet and flamenco dancers sometimes rub their shoes in powdered rosin to reduce slippage before going on stage. Gymnasts, baseball pitchers and ten pin bowlers use rosin to improve grip. Common locations of this contact dermatitis are hands, face and neck. [2] : 1374
It has also occurred as a result of dehydroabietic acid in an over-the-counter hydrocolloid dressing. [3]

Cutaneous disorders in musicians include frictional injury ("fiddler's neck"), hyperhidrosis, acne mechanica and vascular compromise. Other agents of irritant and allergic contact dermatitis may be rosewood, Makassar ebony, cocobolo wood, African blackwood, nickel, reed, propolis (bee glue), chromium and paraphenylenediamine. Patch testing can be performed for identification of the cause.
Treatment may include corticoids, astringents, and keratolytics. Dermatoses tend to be recurrent unless the use or contact can be avoided. Discontinuation of the instrument is curative in almost all cases, but usually impractical.

Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can vary from small to covering the entire body. Dermatitis is also called eczema but the same term is often used for the most common type of skin inflammation, atopic dermatitis.

Rosin, also known as colophony or Greek pitch, is a solid form of resin obtained from pine trees and other plants, mostly conifers, primarily through heating fresh liquid resin to vaporize the volatile liquid terpene components. Used widely in various industries and arts, rosin appears as a semi-transparent, brittle substance that ranges in color from yellow to black and melts at stove-top temperatures. Rosin consists mainly of resin acids, especially abietic acid, and is soluble in alcohol, ether, benzene and chloroform.

Abietic acid is a mild organic acid found in coniferous trees.
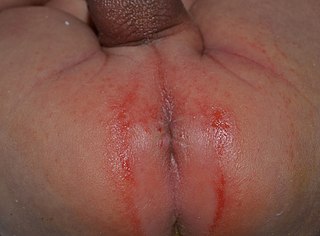
Irritant diaper dermatitis is a generic term applied to skin rash in the diaper area that are caused by various skin disorders and/or irritants.

Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are not contagious or life-threatening, but can be very uncomfortable.
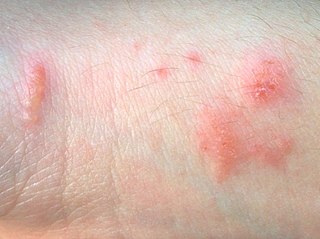
Urushiol-induced contact dermatitis is a type of allergic contact dermatitis caused by the oil urushiol found in various plants, most notably sumac family species of the genus Toxicodendron: poison ivy, poison oak, poison sumac, and the Chinese lacquer tree. The name is derived from the Japanese word for the sap of the Chinese lacquer tree, urushi. Other plants in the sumac family also contain urushiol, as do unrelated plants such as Ginkgo biloba.

Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a form of contact dermatitis that is the manifestation of an allergic response caused by contact with a substance; the other type being irritant contact dermatitis (ICD).
Irritant contact dermatitis is a form of contact dermatitis that can be divided into forms caused by chemical irritants and those caused by physical irritants.

Cheilitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the lips. The inflammation may include the perioral skin, the vermilion border, or the labial mucosa. The skin and the vermilion border are more commonly involved, as the mucosa is less affected by inflammatory and allergic reactions.
Keratolysis exfoliativa is a sometimes harmless, sometimes painful skin condition that can affect the focal surface of the fingers and/or the palm or soles of the feet. It is often misdiagnosed as chronic contact dermatitis or psoriasis. It is characterized by dry skin and superficial, air-filled blisters. These blisters can be peeled off very easily and will leave reddish, tender areas. The loss of this corneal layer of the skin, which protects the underlying layers, leaves the skin more vulnerable to dryness and cracking.
Id reactions are types of acute dermatitis developing after days or weeks at skin locations distant from the initial inflammatory or infectious site. They can be localised or generalised. This is also known as an autoeczematous response and there must be an identifiable initial inflammatory or infectious skin problem which leads to the generalised eczema. Often intensely itchy, the red papules and pustules can also be associated with blisters and scales and are always remote from the primary lesion. It is most commonly a blistering rash with itchy vesicles on the sides of fingers and feet as a reaction to fungal infection on the feet, athlete's foot. Stasis dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, acute irritant contact eczema and infective dermatitis have been documented as possible triggers, but the exact cause and mechanism is not fully understood. Several other types of id reactions exist including erythema nodosum, erythema multiforme, Sweet's syndrome and urticaria.

Airbag dermatitis is skin irritation secondary to the deployment of airbags. The diagnosis of "air bag dermatitis" is relatively recent; the first case was reported in 1994.
Contact stomatitis is inflammation or pain of the oral mucosa caused by external stimuli. It is characterized by cutaneous lesions that may be located where the offending agent contacts the mucosa for a prolonged time. Oftentimes it presents in the mouth after contact with hot food or from ill-fitted dentures or other irritant. Consequently, patients may seek resolve from their dentist rather than a dermatologist. Unlike with allergic contact stomatitis, the skin requires no previous exposure to a stimulant before crafting an immune reaction.

Paederus dermatitis, medically known as dermatitis linearis, is a skin irritation resulting from contact with the hemolymph of certain rove beetles, a group that belongs to the insect order Coleoptera and the genus Paederus. Other local names given to Paederus dermatitis include spider-lick, whiplash dermatitis, and Nairobi fly dermatitis.
Tulip fingers are a cutaneous condition, a combined allergic and irritant contact dermatitis caused by contact with tulip bulbs.
Protein contact dermatitis is a cutaneous condition, and was a term originally used to describe an eczematous reaction to protein-containing material in food handlers. Usually affecting the hands or forearms, it manifests clinically as a subacute or chronic dermatitis that recurs frequently over time. Niels Hjorth and Jytte Roed-Petersen coined the phrase "protein contact dermatitis" in 1976.
Acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus is a cutaneous condition characterized by a bilateral malar rash and lesions that tend to be transient, and that follow sun exposure. The acute form is distinct from chronic and subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus, which may have different types of skin lesions. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus is associated with both lupus erythematosus-specific lesions and cutaneous manifestations that are not specific to lupus erythematosus, such as oral ulcers and urticaria. Because of the diagnostic criteria used to diagnose systemic lupus erythematosus, a patient with only cutaneous manifestations may be diagnosed with the systemic form of the disease.
Fiddler's neck is an occupational disease that affects violin and viola players.

Nickel allergy is any of several allergic conditions provoked by exposure to the chemical element nickel. Nickel allergy often takes the form of nickel allergic contact dermatitis (Ni-ACD), a form of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD). Ni-ACD typically causes a rash that is red and itchy and that may be bumpy or scaly. The main treatment for it is avoiding contact with nickel-releasing metals, such as inexpensive jewelry. Another form of nickel allergy is a systemic form: systemic nickel allergy syndrome (SNAS) can mimic some of the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and also has a dermatologic component.
The intense contact between a musical instrument and skin may exaggerate existing skin conditions or cause new skin conditions. Skin conditions like hyperhidrosis, lichen planus, psoriasis, eczema, and urticaria may be caused in instrumental musicians due to occupational exposure and stress. Allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis are the most common skin conditions seen in string musicians.