Related Research Articles

Perspiration, also known as sweat, is the fluid secreted by sweat glands in the skin of mammals.

Allergic rhinitis, of which the seasonal type is called hay fever, is a type of inflammation in the nose that occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the air. Signs and symptoms include a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, red, itchy, and watery eyes, and swelling around the eyes. The fluid from the nose is usually clear. Symptom onset is often within minutes following allergen exposure, and can affect sleep and the ability to work or study. Some people may develop symptoms only during specific times of the year, often as a result of pollen exposure. Many people with allergic rhinitis also have asthma, allergic conjunctivitis, or atopic dermatitis.
A food allergy is an abnormal immune response to food. The symptoms of the allergic reaction may range from mild to severe. They may include itchiness, swelling of the tongue, vomiting, diarrhea, hives, trouble breathing, or low blood pressure. This typically occurs within minutes to several hours of exposure. When the symptoms are severe, it is known as anaphylaxis. A food intolerance and food poisoning are separate conditions, not due to an immune response.

Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are not contagious or life-threatening, but can be very uncomfortable.

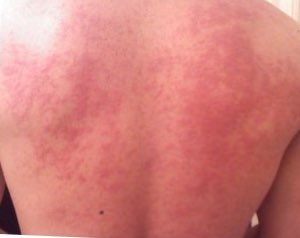
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and does not leave any long-lasting skin change. Fewer than 5% of cases last for more than six weeks. The condition frequently recurs.

Cold urticaria is a disorder in which large red welts called hives (urticaria) form on the skin after exposure to a cold stimulus. The hives are usually itchy and often the hands and feet will become itchy and swollen as well. Hives vary in size from about 7 mm in diameter to as big as about 27 mm or larger.

Physical urticaria is a distinct subgroup of urticaria (hives) that are induced by an exogenous physical stimulus rather than occurring spontaneously. There are seven subcategories that are recognized as independent diseases. Physical urticaria is known to be painful, itchy and physically unappealing; it can recur for months to years.
Allergies to cats are one of the most common allergies among human individuals. Among the eight known cat allergens, the most prominent allergen is secretoglobin Fel d 1, which is produced in the anal glands, salivary glands, and, mainly, in sebaceous glands of cats, and is ubiquitous in the United States, even in households without cats.

Milk allergy is an adverse immune reaction to one or more proteins in cow's milk. Symptoms may take hours to days to manifest, with symptoms including atopic dermatitis, inflammation of the esophagus, enteropathy involving the small intestine and proctocolitis involving the rectum and colon. However, rapid anaphylaxis is possible, a potentially life-threatening condition that requires treatment with epinephrine, among other measures.

Wheat allergy is an allergy to wheat which typically presents itself as a food allergy, but can also be a contact allergy resulting from occupational exposure. Like all allergies, wheat allergy involves immunoglobulin E and mast cell response. Typically the allergy is limited to the seed storage proteins of wheat. Some reactions are restricted to wheat proteins, while others can react across many varieties of seeds and other plant tissues. Wheat allergy is rare. Prevalence in adults was found to be 0.21% in a 2012 study in Japan.
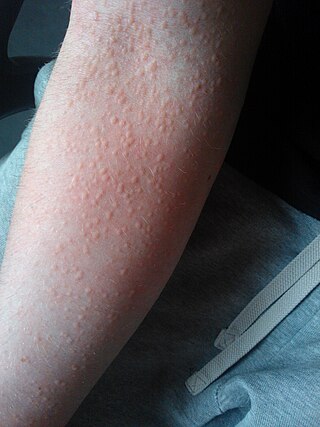
Cholinergic urticaria is a type of hives (urticaria) that is triggered by an increase in body temperature, such as during exercise, sweating, or exposure to heat. It is also sometimes called exercise-induced urticaria or heat hives. The condition is caused by an overreaction of the immune system to the release of histamine and other chemicals in response to the increase in body temperature. This results in the characteristic red, itchy, and sometimes raised bumps or welts on the skin that are associated with hives.

Solar urticaria (SU) is a rare condition in which exposure to ultraviolet or UV radiation, or sometimes even visible light, induces a case of urticaria or hives that can appear in both covered and uncovered areas of the skin. It is classified as a type of physical urticaria. The classification of disease types is somewhat controversial. One classification system distinguished various types of SU based on the wavelength of the radiation that causes the breakout; another classification system is based on the type of allergen that initiates a breakout.

Prostaglandin D2 receptor 2 (DP2 or CRTH2) is a human protein encoded by the PTGDR2 gene and GPR44. DP2 has also been designated as CD294 (cluster of differentiation 294). It is a member of the class of prostaglandin receptors which bind with and respond to various prostaglandins. DP2 along with Prostaglandin DP1 receptor are receptors for prostaglandin D2 (PGD2). Activation of DP2 by PGD2 or other cognate receptor ligands has been associated with certain physiological and pathological responses, particularly those associated with allergy and inflammation, in animal models and certain human diseases.
Aquagenic urticaria, also known as water allergy and water urticaria, is a rare form of physical urticaria in which hives develop on the skin after contact with water, regardless of its temperature. The condition typically results from contact with water of any type, temperature or additive.
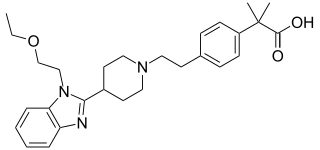
Bilastine is an antihistamine medication used to treat hives (urticaria), allergic rhinitis and itchy inflamed eyes (allergic conjunctivitis) caused by an allergy. It is a second-generation antihistamine and takes effect by selectively inhibiting the histamine H1 receptor, preventing these allergic reactions. Bilastine has an effectiveness similar to cetirizine, fexofenadine, and desloratadine.
Idiopathic pure sudomotor failure (IPSF) is the most common cause of a rare disorder known as acquired idiopathic generalized anhidrosis (AIGA), a clinical syndrome characterized by generalized decrease or absence of sweating without other autonomic and somatic nervous dysfunctions and without persistent organic cutaneous lesions.
Exercise-induced anaphylaxis is a rare condition in which anaphylaxis, a serious or life-threatening allergic response, is brought on by physical activity. Approximately 5–15% of all reported cases of anaphylaxis are thought to be exercise-induced.

Shellfish allergy is among the most common food allergies. "Shellfish" is a colloquial and fisheries term for aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs such as clams, mussels, oysters and scallops, crustaceans such as shrimp, lobsters and crabs, and cephalopods such as squid and octopus. Shellfish allergy is an immune hypersensitivity to proteins found in shellfish. Symptoms can be either rapid or gradual in onset. The latter can take hours to days to appear. The former may include anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition which requires treatment with epinephrine. Other presentations may include atopic dermatitis or inflammation of the esophagus. Shellfish is one of the eight common food allergens, responsible for 90% of allergic reactions to foods: cow's milk, eggs, wheat, shellfish, peanuts, tree nuts, fish, and soy beans.
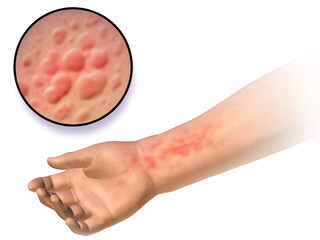
Autoimmune urticaria, also known as chronic autoimmune urticaria, is a type of chronic urticaria characterized by the presence of autoantibodies in the patient's immune system that target the body's own mast cells, leading to episodes of hives (urticaria). This immunologically distinct type of urticaria is considered autoimmune because the immune system, which normally protects the body from foreign organisms, mistakenly attacks the body's own cells, causing inflammation and other symptoms.
References
- ↑ Kan T, Hiragun T, Ishii K, Hiragun M, Yanase Y, Tanaka A, Hide M (July 2015). "Evaluation of recombinant MGL_1304 produced by Pichia pastoris for clinical application to sweat allergy". Allergology International. 64 (3): 266–271. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2015.03.003 . PMID 26117259.
- 1 2 Hiragun T, Hiragun M, Ishii K, Kan T, Hide M (July 2017). "Sweat allergy: Extrinsic or intrinsic?". Journal of Dermatological Science. 87 (1): 3–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2017.03.002 . PMID 28416076.
- ↑ Hiragun T, Hide M (2016). "Sweat Allergy". Current Problems in Dermatology. Karger Publishers. 51: 101–108. doi:10.1159/000446788. ISBN 978-3-318-05904-5. PMID 27584969.
- ↑ Yokozeki H (2016). Perspiration research. Basel New York: Karger. p. 52. ISBN 9783318059052.
- ↑ Moore-Robinson M, Warin RP (December 1968). "Some clinical aspects of cholinergic urticaria". The British Journal of Dermatology. 80 (12): 794–799. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1968.tb11948.x. PMID 5706797. S2CID 58415911.
- ↑ Hirschmann JV, Lawlor F, English JS, Louback JB, Winkelmann RK, Greaves MW (April 1987). "Cholinergic urticaria. A clinical and histologic study". Archives of Dermatology. 123 (4): 462–467. doi:10.1001/archderm.1987.01660280064024. PMID 3827277.
- ↑ Nakamizo S, Egawa G, Miyachi Y, Kabashima K (January 2012). "Cholinergic urticaria: pathogenesis-based categorization and its treatment options". Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 26 (1): 114–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04017.x . PMID 21371134. S2CID 35802279.
- ↑ Bito T, Sawada Y, Tokura Y (December 2012). "Pathogenesis of cholinergic urticaria in relation to sweating". Allergology International. 61 (4): 539–544. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.12-RAI-0485 . PMID 23093795.