| Irritant contact dermatitis | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Irritant contact dermatitis is a form of contact dermatitis that can be divided into forms caused by chemical irritants and those caused by physical irritants.
| Irritant contact dermatitis | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Irritant contact dermatitis is a form of contact dermatitis that can be divided into forms caused by chemical irritants and those caused by physical irritants.
Chemical irritant contact dermatitis is either acute or chronic, which is usually associated with strong and weak irritants respectively. [1] The following definition is provided by Mathias and Maibach (1978): [2] The mechanism of action varies. Detergents, surfactants, extremes of pH, and organic solvents all directly affect the barrier properties of the epidermis. These effects include removing fat emulsion, defatting of dermal lipids, inflicting cellular damage on the epithelium, and increasing the transepidermal water loss by damaging the horny layer water-binding mechanisms and damaging the DNA, which causes the layer to thin. Concentrated irritants have an acute effect, but this is not as common as the accumulative, chronic effect of irritants whose deleterious effects build up with subsequent doses (ESCD 2006).
Chemical irritants are often strong alkalis as found in drain cleaners and soap with lye residues. Many other chemical compounds can also cause contact dermatitis.
Physical irritant contact dermatitis is a less-researched form of irritant contact dermatitis [3] due to its various mechanisms of action and a lack of a test for its diagnosis.
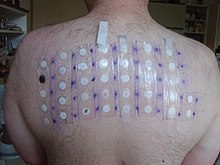
A complete patient history combined with negative allergic patch testing is usually necessary to reach a correct diagnosis. [4] The simplest form of physical irritant contact dermatitis results from prolonged rubbing, although the diversity of implicated irritants is far wider. [5] Examples include paper friction, fiberglass, and scratchy clothing.
Low humidity from air conditioning was found to be the most common cause of physical irritant contact dermatitis. [3] To the lay person a definition of low humidity being a physical irritant can be confusing because low humidity is a deficit (or absence) of an elemental substance, whereas all other irritants implicated in contact dermatitis are in concentrations of relative abundance. So the irritant is actually a lack of water vapour. This confusion is further compounded with the use of the term contact implying 'touching' (as is the case with all other forms of physical irritant contact dermatitis) whereas in the case of low humidity physical irritant contact dermatitis there is an absence of contact with water vapour.
Many plants cause irritant contact dermatitis through their spines or irritant hairs. Some plants such as the buttercup, spurge, and daisy act by chemical means. The sap of these plants contains a number of alkaloids, glycosides, saponins, anthraquinones, and (in the case of plant bulbs) irritant calcium oxalate crystals – all of which can cause crystal irritant contact dermatitis.[ citation needed ]
Butternut squash and acorn squash have been known to cause an allergic reaction in many individuals, especially in food preparation where the squash skin is cut and exposed to the epidermis.[ citation needed ] Food handlers and kitchen workers often take precautions to wear rubber or latex gloves when peeling butternut and acorn squash to avoid temporary butternut squash (Cucurbita moschata) dermatitis [6] A contact dermatitis reaction to butternut or acorn squash may result in orange and cracked skin, a sensation of "tightness", "roughness" or "rawness".
Some species of insects and spiders possess urticating hairs, including the caterpillars of the hickory tussock moth, the saddleback moth, the buck moth, and most species of tarantula from North and South America. [7] These hairs produce irritant contact dermatitis in a similar way to the way that plant hairs do.
A humidifier can be used to prevent low indoor humidity during winter (especially with indoor heating), and dry season.

Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can vary from small to covering the entire body. Dermatitis is also called eczema but the same term is often used for the most common type of skin inflammation, atopic dermatitis.

Cucurbita is a genus of herbaceous fruits in the gourd family, Cucurbitaceae, native to the Andes and Mesoamerica. Five edible species are grown and consumed for their flesh and seeds. They are variously known as squash, pumpkin, or gourd, depending on species, variety, and local parlance. Other kinds of gourd, also called bottle-gourds, are native to Africa and belong to the genus Lagenaria, which is in the same family and subfamily as Cucurbita, but in a different tribe, their young fruits are eaten much like those of the Cucurbita species.

Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are not contagious or life-threatening, but can be very uncomfortable.

Urticating hairs or urticating bristles are one of the primary defense mechanisms used by numerous plants, almost all New World tarantulas, and various lepidopteran caterpillars. Urtica is Latin for "nettle", and bristles that urticate are characteristic of this type of plant, and many other plants in several families. This term also refers to certain types of barbed bristles that cover the dorsal and posterior surface of a tarantula's or caterpillar's abdomen. Many tarantula species eject bristles from their abdomens, directing them toward potential attackers. These bristles can embed themselves in the other animal's skin or eyes, causing physical irritation, usually to great discomfort. The term "hairs" is technically a misnomer, as only mammals possess true hairs. The scientific term for plant hairs is trichomes.

A moisturizer, or emollient, is a cosmetic preparation used for protecting, moisturizing, and lubricating the skin. These functions are normally performed by sebum produced by healthy skin. The word "emollient" is derived from the Latin verb mollire, to soften.
An occupational disease or industrial disease is any chronic ailment that occurs as a result of work or occupational activity. It is an aspect of occupational safety and health. An occupational disease is typically identified when it is shown that it is more prevalent in a given body of workers than in the general population, or in other worker populations. The first such disease to be recognised, squamous-cell carcinoma of the scrotum, was identified in chimney sweep boys by Sir Percival Pott in 1775. Occupational hazards that are of a traumatic nature are not considered to be occupational diseases.

The oak processionary (OPM) is a moth whose caterpillars can be found in oak forests, where they feed on oak leaves, causing significant damage. They travel in nose-to-tail processions, often arrow-headed, with a leader followed by rows of several caterpillars abreast. They are a human irritant because of their venomous setae, which can cause skin irritation and asthma. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.

A patch test is a diagnostic method used to determine which specific substances cause allergic inflammation of a patient's skin.

Butternut squash, known in Australia and New Zealand as butternut pumpkin or gramma, is a type of winter squash that grows on a vine. It has a sweet, nutty taste similar to that of a pumpkin. It has tan-yellow skin and orange fleshy pulp with a compartment of seeds in the blossom end. When ripening, the flesh turns increasingly deep orange due to its rich content of beta-carotene, a provitamin A compound.
Cocamidopropyl betaine (CAPB) is a mixture of closely related organic compounds derived from coconut oil and dimethylaminopropylamine. CAPB is available as a viscous pale yellow solution and it is used as a surfactant in personal care products and animal husbandry. The name reflects that the major part of the molecule, the lauric acid group, is derived from coconut oil. Cocamidopropyl betaine to a significant degree has replaced cocamide DEA.

Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a form of contact dermatitis that is the manifestation of an allergic response caused by contact with a substance; the other type being irritant contact dermatitis (ICD).

Winter squash is an annual fruit representing several squash species within the genus Cucurbita. Late-growing, less symmetrical, odd-shaped, rough or warty varieties, small to medium in size, but with long-keeping qualities and hard rinds, are usually called winter squash. They differ from summer squash in that they are harvested and eaten in the mature stage when their seeds within have matured fully and their skin has hardened into a tough rind. At this stage, most varieties of this vegetable can be stored for use during the winter. Winter squash is generally cooked before being eaten, and the skin or rind is not usually eaten as it is with summer squash.
Eyelid dermatitis is commonly related to atopic dermatitis or allergic contact dermatitis. Volatile substances, tosylamide/formaldehyde resin, epoxy hardeners, insect repellent sprays, and lemon peel oil may be implicated, with many cases of eyelid contact dermatitis being caused by substances transferred by the hands to the eyelids.
Id reactions are types of acute dermatitis developing after days or weeks at skin locations distant from the initial inflammatory or infectious site. They can be localised or generalised. This is also known as an autoeczematous response and there must be an identifiable initial inflammatory or infectious skin problem which leads to the generalised eczema. Often intensely itchy, the red papules and pustules can also be associated with blisters and scales and are always remote from the primary lesion. It is most commonly a blistering rash with itchy vesicles on the sides of fingers and feet as a reaction to fungal infection on the feet, athlete's foot. Stasis dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, acute irritant contact eczema and infective dermatitis have been documented as possible triggers, but the exact cause and mechanism is not fully understood. Several other types of id reactions exist including erythema nodosum, erythema multiforme, Sweet's syndrome and urticaria.
A barrier cream is a topical formulation used in industrial applications and as a cosmetic to place a physical barrier between the skin and contaminants that may irritate the skin. There are many other terms for creams designed to protect skin from harmful substances, including skin protective creams, pre-work creams, antisolvent gels, protective ointments, and shielding lotions. Three classes of barrier creams are used: water repellent creams, water-soluble creams, and creams designed for special applications. Barrier creams may contain substances such as zinc oxide, talc or kaolin to layer over the skin. For hand care they are designed to protect against the harm from detergents and other irritants.

Defatting is the chemical dissolving of dermal lipids, from the skin, on contact with defatting agents. This can result in water loss from the affected area and cause the whitening and drying of the skin which may result in cracking, secondary infection and chemical irritant contact dermatitis.

Garlic allergy or allergic contact dermatitis to garlic is a common inflammatory skin condition caused by contact with garlic oil or dust. It mostly affects people who cut and handle fresh garlic, such as chefs, and presents on the tips of the thumb, index and middle fingers of the non-dominant hand. The affected fingertips show an asymmetrical pattern of fissure as well as thickening and shedding of the outer skin layers, which may progress to second- or third-degree burn of injured skin.

Irritant folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicle. It characteristically presents with small red bumps in the skin at sites of occlusion, pressure, friction, or hair removal; typically around the beard area in males, pubic area and lower legs of females, or generally the inner thighs and bottom. An associated itch may or may not be present. Pseudofolliculitis barbae is a type of irritant folliculitis in the beard area.
Occupational skin diseases are ranked among the top five occupational diseases in many countries.
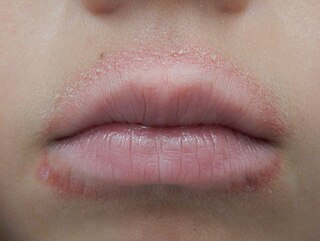
Lip licker's dermatitis is a type of skin inflammation around the lips due to damage by saliva from repetitive lip licking and is classified as a subtype of irritant contact cheilitis. The resulting scaling, redness, chapping, and crusting makes a well-defined ring around the lips. The rash may extend as far as the tongue can reach and usually does not occur at the corners of the mouth. It commonly occurs during winter months but some people can have it year-round if lip licking is a chronic habit.