
The Inaccessible Island rail is a small bird of the rail family, Rallidae. Endemic to Inaccessible Island in the Tristan Archipelago in the isolated south Atlantic, it is the smallest extant flightless bird in the world. The species was described by physician Percy Lowe in 1923 but had first come to the attention of scientists 50 years earlier. The Inaccessible Island rail's affinities and origin were a long-standing mystery; in 2018 its closest relative was identified as the South American dot-winged crake, and it was proposed that both species should be nested within the genus Laterallus.

Atyidae is a family of shrimp, present in all tropical and most temperate waters of the world. Adults of this family are almost always confined to fresh water. This is the only family in the superfamily Atyoidea.

The Himalayan swiftlet is a small swift. It is a common colonial breeder in the Himalayas and Southeast Asia. Some populations are migratory.
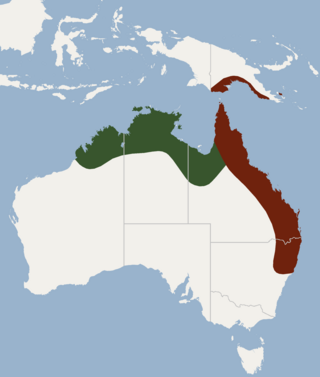
The hoary wattled bat is a species of vesper bat found in northern Australia and Papua New Guinea. Two subspecies are currently recognised:
Hoplophryne rogersi, also known as the Tanzania banana frog, Usambara banana frog, Usambara blue-bellied frog, and Roger's three-fingered frog, is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to north-eastern Tanzania and known from the Usambara, Magrotto, and Nguru Mountains of Tanga Region. The specific name rogersi honours F. W. Rogers, the custodian of the Amani Research Institute at the time of the describers' visit to Usambara.
Typhlatya iliffei is a species of basket shrimp in the family Atyidae, and was first described in 1981 by C.W. Hart Junior & Raymond B. Manning. It is found in the Caribbean.

Typhlatya is a genus of shrimp in the family Atyidae. These are small, stygobitic shrimp found in the West Mediterranean region, Caribbean region, Ascension Island and the Galápagos, although the individual species often have very small ranges. Species in this genus are found in salt, brackish and fresh waters, mostly in anchialine habitats and none in the open sea.
Typhlatya monae is a species of basket shrimp in the family Atyidae. It is found in the Caribbean and Africa.
Kinkonychelys is an extinct genus of side-necked turtle which existed in Madagascar during the Late Cretaceous period. It contains the single species Kinkonychelys rogersi, named in honor of its discoverer, Raymond R. Rogers. The genus and species are based on UA 9748, a nearly complete skull, which represents the first turtle skull described from the pre-Holocene era in Madagascar. A number of isolated skull and jaw bones have also been assigned to K. rogersi. These specimens were found in rocks of the Maastrichtian-age Maevarano Formation in the Mahajanga Basin of northwestern Madagascar. Another specimen, FMNH PR 2446, is speculated to represent another species, currently known as Kinkonychelys sp., but consensus on its distinction from K. rogersi remains unclear.
Raymond Brendan Manning was an American carcinologist, specialising in alpha taxonomy and mantis shrimp.
Fenner Albert Chace Jr. was an American carcinologist.
Colotis rogersi, the Rogers' orange tip, is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. It is found in northern Kenya, southern Ethiopia and south-eastern Sudan. The habitat consists of very dry savanna.

Acraea rogersi, the Rogers' large acraea, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae which is native to the African tropics and northern subtropics.
Eicochrysops rogersi, the Rogers' blue, is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. It is found in central and southern Kenya and possibly Tanzania. The habitat consists of savanna.
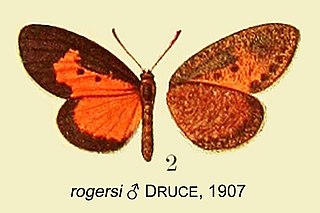
Pentila rogersi, or Rogers' pentila, is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. The species was first described by Hamilton Herbert Druce in 1907. It is found in Kenya and Tanzania. The habitat consists of coastal forests and lowland forests at altitudes ranging from sea level to 900 metres.

Abisara rogersi, the light banded Judy, is a butterfly in the family Riodinidae. The species was first described by Herbert Druce in 1878. It is found in Nigeria, Cameroon, Angola, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, Tanzania and Zambia. The habitat consists of shady areas in forests and open areas in submontane forests.
Kedestes rogersi is a butterfly in the family Hesperiidae. It is found in southern Sudan, Uganda, Kenya and northern Tanzania. The habitat consists of dry thornbush and Acacia country.
Eucereon rogersi is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Herbert Druce in 1884. It is found in Costa Rica, Panama, as well as on Guadeloupe and Saint Kitts.
Virbia rogersi is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Herbert Druce in 1885. It is found in Costa Rica.







