Chhattisgarh is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Pradesh to the northwest, Maharashtra to the southwest, Jharkhand to the northeast, Odisha to the east, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh to the south. Formerly a part of Madhya Pradesh, it was granted statehood on 1 November 2000 with Raipur as the designated state capital.
Regional science is a field of the social sciences concerned with analytical approaches to problems that are specifically urban, rural, or regional. Topics in regional science include, but are not limited to location theory or spatial economics, location modeling, transportation, migration analysis, land use and urban development, interindustry analysis, environmental and ecological analysis, resource management, urban and regional policy analysis, geographical information systems, and spatial data analysis. In the broadest sense, any social science analysis that has a spatial dimension is embraced by regional scientists.

Raipur ( ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. Raipur is also the administrative headquarters of Raipur district and Raipur division, and the largest city of the state. It was a part of Madhya Pradesh before the state of Chhattisgarh was formed on 1 November 2000. It is a major commercial hub for trade and commerce in the region. It has exponential industrial growth and has become a major business hub in Central India. It has been ranked as India's 6th cleanest city as per the Swachh Survekshan for the year 2021. Raipur is ranked 7th in the Ease of Living Index 2019 and 7th in the Municipal Performance Index 2020, both by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).

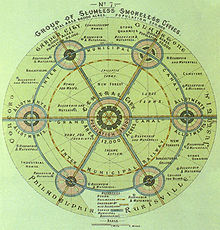
Central place theory is an urban geographical theory that seeks to explain the number, size and range of market services in a commercial system or human settlements in a residential system. It was introduced in 1933 to explain the spatial distribution of cities across the landscape. The theory was first analyzed by German geographer Walter Christaller, who asserted that settlements simply functioned as 'central places' providing economic services to surrounding areas. Christaller explained that a large number of small settlements will be situated relatively close to one another for efficiency, and because people don’t want to travel far for everyday needs, like getting bread from a bakery. But people would travel further for more expensive and infrequent purchases or specialized goods and services which would be located in larger settlements that are farther apart.

Ambikapur is a city and headquarters of Surguja district in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. It is one of the oldest cities in the state, in east-central India. Ambikapur is also the divisional headquarters of Surguja Division which consists of the six districts of Surguja, Korea, Manendragarh, Balrampur, Surajpur and Jashpur.

Bilaspur, also known as "The City of Festivals", is a city located in Bilaspur District in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. Bilaspur is the Administrative headquarters of the Bilaspur District and Bilaspur Division. The Chhattisgarh High Court, located at Bodri, District Bilaspur has privileged it with the title Nyayadhani of the State. This city is the commercial center and business hub of North East Chhattisgarh region. It is also an important city for the Indian Railways, as it is the headquarters for South East Central Railway Zone (SECR) and the Bilaspur Railway Division. Bilaspur is also the headquarters of South Eastern Coalfields Limited. Chhattisgarh biggest power plant operated by NTPC is in Sipat. PowerGrid in Sipat pools electricity from other power plants in region and transmits electricity to Delhi via one of longest HVDC line.

Bilaspur district is a district of the Chhattisgarh state of India. Bilaspur city is the headquarters of the district. As of 2011, it is the second most populous district of Chhattisgarh, after Raipur.
Urban planning in Singapore is the direction of infrastructure development in Singapore. It is done through a three-tiered planning framework, consisting of a long-term plan to plot out Singapore's development over at least 50 years, a Master Plan for the medium term, and short-term plans, the first two of which are prepared by the Urban Redevelopment Authority (URA) and the last by multiple agencies.

Durg is a city in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh, east of the Shivnath River and is part of the Durg-Bhilai urban agglomeration. With an urban population of 1,064,077, Durg-Bhilai is the second largest urban area in Chhattisgarh after Raipur. It is the headquarters of Durg District.

Kapsi is a large marketplace village in the Kanker district of Chhattisgarh, India. It holds significance as a model village under two ambitious schemes of the Government of India, namely the Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana and the Shyama Prasad Mukherjee National Rurban Mission. It is also the headquarters of the Kapsi forest range, the East Kapsi forest subdivision and the Kapsi water resource subdivision. Owing to its sizeable tribal population, it is defined as a Scheduled Area under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India.
Provision of Urban Amenities to Rural Areas (PURA) is a strategy for rural development in India. This concept was given by former president Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam and discussed in his book Target 3 Billion which he co-authored with Srijan Pal Singh. The genesis of PURA can be traced to the work done by Nimbkar Agricultural Research Institute in the early 1990s on Taluka energy self-sufficiency. It was shown in the study that energy self-sufficient talukas can be a new development model for rural India in terms of creation of jobs and better amenities to its population.

A settlement hierarchy is a way of arranging settlements into a hierarchy based upon their population or some other criteria. The term is used by landscape historians and in the National Curriculum for England. The term is also used in the planning system for the UK and for some other countries such as Ireland, India, and Switzerland. The term was used without comment by the geographer Brian Roberts in 1972.

Naya Raipur, officially known as Atal Nagar-Nava Raipur, is a planned city and fully Greenfield city in Indian state of Chhattisgarh. It is planned to replace Raipur as the capital city of Chhattisgarh. The Government of Chhattisgarh, the state's administrative body is situated here. The city is located between National Highway 53 and National Highway 30, about 17 km south-east of the capital city Raipur. Swami Vivekananda Airport separates Raipur and Nava Raipur.
An urban planner is a professional who practices in the field of town planning, urban planning or city planning.

Bhilai is a city in Durg district of the Indian state of Chhattisgarh, in eastern central India. Along with its twin-city Durg, the urban agglomeration of Durg-Bhilainagar has a population of more than a million, making it the second-largest urban area in Chhattisgarh after Raipur. Bhilai is a major industrial city as well as an education hub of central India. The Bhilai metropolis contains three municipal corporations: Bhilai Municipal Corporation, Bhilai-Charoda Municipal Corporation and Risali Municipal Corporation.

Settlement geography is a branch of human geography that investigates the earth's surface's part settled by humans. According to the United Nations' Vancouver Declaration on Human Settlements (1976), "human settlements means the totality of the human community – whether city, town or village – with all the social, material, organizational, spiritual and cultural elements that sustain it."

Urban planning, also known as town planning, city planning, regional planning, or rural planning, is a technical and political process that is focused on the development and design of land use and the built environment, including air, water, and the infrastructure passing into and out of urban areas, such as transportation, communications, and distribution networks and their accessibility. Many professional practitioners of urban planning, especially practitioners with the title "urban planner" study urban planning education, while some paraprofessional practitioners are educated in urban studies; others study and work in urban policy - the aspect of public policy used in the public administration subfield of political science that is most aligned with urban planning. Traditionally, urban planning followed a top-down approach in master planning the physical layout of human settlements. The primary concern was the public welfare, which included considerations of efficiency, sanitation, protection and use of the environment, as well as effects of the master plans on the social and economic activities. Over time, urban planning has adopted a focus on the social and environmental bottom-lines that focus on planning as a tool to improve the health and well-being of people while maintaining sustainability standards. Sustainable development was added as one of the main goals of all planning endeavors in the late 20th century when the detrimental economic and the environmental impacts of the previous models of planning had become apparent. Similarly, in the early 21st century, Jane Jacobs's writings on legal and political perspectives to emphasize the interests of residents, businesses and communities effectively influenced urban planners to take into broader consideration of resident experiences and needs while planning.

Ambikapur, station code ABKP, is a railway station that connects the city of Ambikapur, Chhattisgarh to the Indian Railway network. It is the connecting point of Surguja district and Surajpur district and falls within the South East Central Railway zone of the Indian Railways.

Indian Institute of Technology Bhilai is a public technical and research university located in Bhilai, Chhattisgarh, India. It is one of the six young IITs established by the Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India, located in Chhattisgarh state. Classified as an Institute of National Importance, IITBH formally came into existence in July 2016 with the influx of the first batch of students on 25 July 2016.
Smart Village is a concept adopted by national, state and local governments of India, as an initiative focused on holistic rural development, derived from Mahatma Gandhi's vision of Adarsh Gram and Swaraj. Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojana (SAGY) or SAANJHI) on 2 October 2014, Gandhi's birthday, in addition to Smart Cities and Digital India, as a development programme for India. The Parliamentarian's Model Village Scheme main goal is for each Member of Parliament and Minister to adopt a rural village and develop it into a model by 2019 under the SAGY guidelines. The vision of SAGY is an integrated village development plan, encompassing Personal, Human, Social, and Economic dimensions.