
United Nations Security Council resolution 1244, adopted on 10 June 1999, after recalling resolutions 1160 (1998), 1199 (1998), 1203 (1998) and 1239 (1999), authorised an international civil and military presence in the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and established the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK). It followed an agreement by Yugoslav President Slobodan Milošević to terms proposed by President of Finland Martti Ahtisaari and former Prime Minister of Russia Viktor Chernomyrdin on 8 June, involving withdrawal of all Yugoslav state forces from Kosovo.

United Nations Security Council resolution 859, adopted unanimously on 24 August 1993, after recalling all resolutions on the situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the council noted that, despite all previous security council resolutions since Resolution 713 (1991), the region was still a scene of hostilities and there was little compliance with previous resolutions, particularly by the Bosnian Serb party.
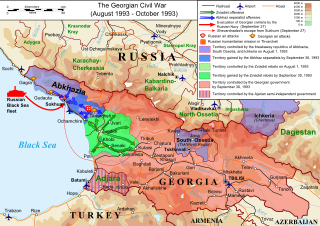
United Nations Security Council resolution 876, adopted unanimously on 19 October 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 849 (1993), 854 (1993) and 858 (1993) concerning the Georgian–Abkhazian war, the council determined that the situation continued to constitute a threat to international peace and security.
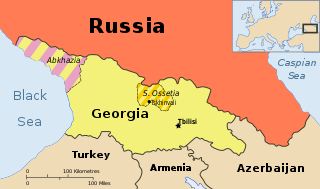
United Nations Security Council resolution 896, adopted unanimously on 31 January 1994, after reaffirming resolutions 849 (1993), 854 (1993), 858 (1993), 876 (1993), 881 (1993) and 892 (1993) on the Georgian–Abkhazian war and Resolution 868 (1993) concerning the safety of United Nations peacekeepers, the Council considered the possible establishment of peacekeeping force in Abkhazia and Georgia, and discussed the peace process.

United Nations Security Council resolution 937, adopted on 21 July 1994, after reaffirming resolutions 849 (1993), 854 (1993), 858 (1993), 876 (1993), 881 (1993), 892 (1993), 896 (1994), 901 (1994), 906 (1994) and 934 (1994), the Council expanded the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) to include co-operation with the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and extended its mandate until 13 January 1995.

United Nations Security Council resolution 997, adopted unanimously on 9 June 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Rwanda, particularly resolutions 872 (1993), 912 (1994), 918 (1994), 925 (1994), 955 (1994) and 965 (1994), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Assistance Mission for Rwanda (UNAMIR) until 8 December 1995 and adjusted its operations from peacekeeping to confidence-building.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1004, adopted unanimously on 12 July 1995, after recalling all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, demanded that Bosnian Serb forces withdraw from the safe area of Srebrenica in Bosnia and Herzegovina and respect the safety of personnel from the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR). The resolution was passed during the Srebrenica massacre.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1065, adopted unanimously on 12 July 1996, after reaffirming all resolutions on Georgia, particularly 1036 (1996), the Council discussed efforts for a political settlement between Georgia and Abkhazia and extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 January 1997.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1076, adopted unanimously on 22 October 1996, after considering the situation in Afghanistan, resolutions by the General Assembly and the Joint Declaration made on 4 October 1996 by the leaders of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan on developments in the country, the Council discussed the deteriorating political, military and humanitarian situation in Afghanistan.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1078, adopted unanimously on 9 November 1996, after expressing concern at the situation in the African Great Lakes region, the Council discussed proposals for a regional conference on security and a multinational humanitarian force in eastern Zaire.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1080, adopted unanimously on 15 November 1996, after reaffirming Resolution 1078 (1996) on the situation in the African Great Lakes region, the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, established a multinational humanitarian force in eastern Zaire.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1234, adopted unanimously on 9 April 1999, after expressing concern at the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Council demanded an immediate halt to hostilities in the region, a withdrawal of foreign forces and the re-establishment of the government's authority.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1304, adopted unanimously on 16 June 2000, after recalling resolutions 1234 (1999), 1258 (1999), 1273 (1999), 1279 (1999), 1291 (1999) and 1296 (2000) on situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Council demanded the immediate withdrawal of Ugandan, Rwandan, Congolese opposition and other armed groups from Kisangani in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
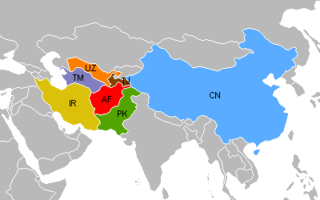
United Nations Security Council resolution 1453, adopted unanimously on 24 December 2002, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Afghanistan, the Council endorsed the "Kabul Declaration on Good-Neighbourly Relations" signed by the Afghan government and six neighbouring countries on 22 December 2002.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1565, adopted unanimously on 1 October 2004 after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until 31 March 2005 and authorised an additional deployment of 5,900 troops and police. It reaffirmed the commitment to respect the “sovereignty, territorial integrity and political independence [sic]” of Congo and States in the region.
Organisation of the Islamic Conference Resolution 10/11, titled "The aggression of the Republic of Armenia against the Republic of Azerbaijan", is an Organisation of the Islamic Conference Resolution on Nagorno-Karabakh conflict adopted by its member states on March 13–14, 2008 during the OIC summit in Dakar, Senegal. The resolution, titled "Aggression by the Republic of Armenia against the Republic of Azerbaijan," aims to express concern over Armenia's aggression against Azerbaijan and to provide comprehensive support for the territorial integrity of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The Dakar conference is considered a "successful step" towards supporting Azerbaijan's just cause. It was during this session that the new Charter of the Islamic Cooperation Organization was adopted, and in the section on the purposes and objectives of this international organization, it was stipulated that the member states support the right of states under occupation to restore their territorial integrity.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1653, adopted unanimously on January 27, 2006, after recalling previous resolutions concerning the situations in the African Great Lakes region, Democratic Republic of the Congo and Burundi, particularly resolutions 1625 (2005), 1631 (2005), 1649 (2005) and 1650 (2005), the Council addressed the stability of the Great Lakes region in Africa.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1666, adopted unanimously on March 31, 2006, after reaffirming all resolutions on Abkhazia and Georgia, particularly Resolution 1615 (2005), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until October 15, 2006.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1716, adopted unanimously on October 13, 2006, after reaffirming all resolutions on Abkhazia and Georgia, particularly Resolution 1666 (2006), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until April 15, 2007.
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 48/144 of 20 December 1993 is a resolution in which the General Assembly expressed its concern at the ongoing degradation of the humanitarian situation in Azerbaijan because of the displacement of considerable number of citizens due to Nagorno Karabakh conflict and supporting "emergency international assistance to refugees and displaced persons in Azerbaijan". The resolution is titled “48/114. Emergency international assistance to refugees and displaced persons in Azerbaijan”. It became the fifth United Nations document concerning Nagorno-Karabakh and the first United Nations General Assembly document on humanitarian aid to those affected by this conflict. This resolution was the first international document affirming the number of refugees and displaced persons in Azerbaijan exceeded one million. The document does not make any specific reference to previous UN resolutions on the ongoing conflict, but "its relevant resolutions regarding humanitarian assistance to refugees and displaced persons". The resolution was adopted by consensus without voting.

















