
The United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (UNMIBH) was a United Nations peacekeeping mission formed under the United Nations Security Council Resolution 1035 on 21 December 1995. It completed its mandate on 31 December 2002, when it was succeeded by the European Union Police Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
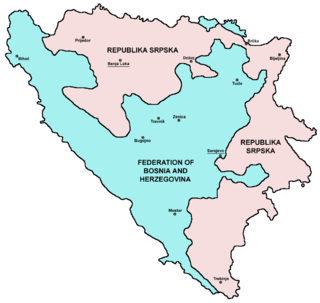
United Nations Security Council resolution 1035, adopted unanimously on 21 December 1995, after recalling Resolution 1031 (1995) and the Dayton Agreement, the Council authorised the establishment of a United Nations civilian police force, known as the International Police Task Force (IPTF) to carry out tasks in accordance with the agreement. It was part of the United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1088, adopted unanimously on 12 December 1996, after recalling all resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia and in particular resolutions 1031 (1995) and 1035 (1995), the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, authorised the creation of the Stabilisation Force (SFOR) in Bosnia and Herzegovina to replace the Implementation Force (IFOR).

United Nations Security Council resolution 1103, adopted unanimously on 31 March 1997, after recalling all resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia and in particular resolutions 1035 (1995) and 1088 (1996), the Council authorised an increase in the strength of the United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (UNMIBH) in Bosnia and Herzegovina.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1144, adopted unanimously on 19 December 1997, after recalling Resolution 1103 (1997) on the United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (UNMIBH) and United Nations International Police Task Force (UN-IPTF) in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Council extended the mandate of both until 21 June 1998.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1168, adopted unanimously on 21 May 1998, after recalling resolutions 1031 (1995), 1035 (1995), 1088 (1996), 1103 (1997), 1107 (1997) and 1144 (1997), the Council strengthened the International Police Task Force (IPTF) in Bosnia and Herzegovina by up to 30 posts to a total strength of 2,057.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1174, adopted unanimously on 15 June 1998, after recalling resolutions 1031 (1995), 1035 (1995), 1088 (1996), 1103 (1997), 1107 (1997), 1144 (1997) and 1168 (1998), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (UNMIBH) for a period terminating on 21 June 1999 and authorised states participating in the NATO led Stabilisation Force (SFOR) to continue to do so for a further twelve months.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1184, adopted unanimously on 16 July 1998, after recalling previous resolutions concerning the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, particularly resolutions 1168 (1998) and 1174 (1998), the council established a programme to monitor the court system in Bosnia and Herzegovina.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1247, adopted unanimously on 18 June 1999, after recalling resolutions 1031 (1995), 1035 (1995), 1088 (1996), 1103 (1997), 1107 (1997), 1144 (1997), 1168 (1998), 1174 (1998) and 1184 (1998), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (UNMIBH) for a period terminating on 21 June 2000 and authorised states participating in the NATO led Stabilisation Force (SFOR) to continue to do so for a further twelve months.
United Nations Security Council resolution 1305, adopted on 21 June 2000, after recalling resolutions 1031 (1995), 1035 (1995), 1088 (1996), 1103 (1997), 1107 (1997), 1144 (1997), 1168 (1998), 1174 (1998), 1184 (1998) and 1247 (1999), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (UNMIBH) for a period terminating on 19 June 2001 and authorised states participating in the NATO-led Stabilisation Force (SFOR) to continue to do so for a further twelve months.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1357, adopted unanimously on 21 June 2001, after recalling resolutions 1031 (1995), 1035 (1995), 1088 (1996), 1103 (1997), 1107 (1997), 1144 (1997), 1168 (1998), 1174 (1998), 1184 (1998), 1247 (1999) and 1305 (2000), the council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (UNMIBH) for a period until 21 June 2002 and authorised states participating in the NATO-led Stabilisation Force (SFOR) to continue to do so for a further twelve months.

In United Nations Security Council resolution 1396, adopted unanimously on 5 March 2002, after recalling resolutions 1031 (1995), 1088 (1996), 1112 (1997), 1256 (1999) and 1357 (2001) on the situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Council welcomed the acceptance by the Steering Board of the Peace Implementation Council on 28 February 2002 of the offer of the European Union to provide a European Union Police Mission (EUPM) to succeed the United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (UNMIBH) from 1 January 2003.
United Nations Security Council resolution 1420, adopted unanimously on 30 June 2002, after recalling all previous resolutions on the conflict in the former Yugoslavia, particularly resolutions 1357 (2001) and 1418 (2002), the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (UNMIBH) and authorised the continuation of the Stabilisation Force until 3 July 2002.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1421, adopted unanimously on 3 July 2002, after recalling all previous resolutions on the conflict in the former Yugoslavia, particularly resolutions 1357 (2001), 1418 (2002) and 1420 (2002), the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (UNMIBH) and authorised the continuation of the Stabilisation Force (SFOR) until 15 July 2002.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1423, adopted unanimously on 12 July 2002, after recalling resolutions 1031 (1995), 1035 (1995), 1088 (1996), 1103 (1997), 1107 (1997), 1144 (1997), 1168 (1998), 1174 (1998), 1184 (1998), 1247 (1999), 1305 (2000), 1357 (2001) and 1396 (2002), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Bosnia and Herzegovina (UNMIBH) for a period until on 31 December 2002 and authorised states participating in the NATO-led Stabilisation Force (SFOR) to continue to do so for a further twelve months.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1491, adopted unanimously on 11 July 2003, after recalling resolutions 1031 (1995), 1088 (1996) and 1423 (2002) on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, the Council extended the mandate of the Stabilisation Force (SFOR) in Bosnia and Herzegovina for a further period of twelve months.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1551, adopted unanimously on 9 July 2004, after recalling previous resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, including resolutions 1031 (1995), 1088 (1996), 1423 (2002) and 1491 (2003), the council extended the mandate of the Stabilisation Force (SFOR) in Bosnia and Herzegovina for a further period of six months and welcomed the deployment of EUFOR Althea at the end of the SFOR's mandate.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1575, adopted unanimously on 22 November 2004, after recalling previous resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, including resolutions 1031 (1995), 1088 (1996), 1423 (2002), 1491 (2003) and 1551 (2004), the council defined the role of EUFOR Althea in Bosnia and Herzegovina as a legal successor to the Stabilisation Force (SFOR).

United Nations Security Council resolution 1639, adopted unanimously on 21 November 2005, after recalling previous resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, including resolutions 1031 (1995), 1088 (1996), 1423 (2002), 1491 (2003), 1551 (2004) and 1575 (2004), the Council extended the mandate of EUFOR Althea in Bosnia and Herzegovina as a legal successor to the Stabilisation Force (SFOR) for a further twelve months.
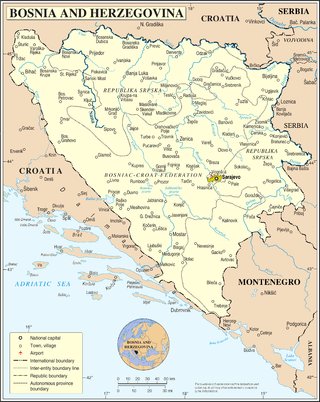
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1722, adopted unanimously on November 21, 2006, after recalling previous resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, including resolutions 1031 (1995), 1088 (1996), 1423 (2002), 1491 (2003), 1551 (2004), 1575 (2004) and 1639 (2005), the Council extended the mandate of EUFOR Althea in Bosnia and Herzegovina as a legal successor to the Stabilisation Force (SFOR) for a further twelve months.


















