
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that lasted from 28 February 1998 until 11 June 1999. It was fought between the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY), which controlled Kosovo before the war, and the Kosovo Albanian separatist militia known as the Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA). The conflict ended when the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) intervened by beginning air strikes in March 1999 which resulted in Yugoslav forces withdrawing from Kosovo.

The United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo is the officially mandated mission of the United Nations in Kosovo. The UNMIK describes its mandate as being to "help the United Nations Security Council achieve an overall objective, namely, to ensure conditions for a peaceful and normal life for all inhabitants of Kosovo and advance regional stability in the Western Balkans."

The Kosovo Liberation Army was an ethnic Albanian separatist militia that sought the separation of Kosovo, the vast majority of which is inhabited by Albanians, from the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY) and Serbia during the 1990s. Albanian nationalism was a central tenet of the KLA and many in its ranks supported the creation of a Greater Albania, which would encompass all Albanians in the Balkans, stressing Albanian culture, ethnicity and nation.
The legitimacy under international law of the 1999 NATO bombing of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia has been questioned. The UN Charter is the foundational legal document of the United Nations (UN) and is the cornerstone of the public international law governing the use of force between States. NATO members are also subject to the North Atlantic Treaty.

The Kosovo Force (KFOR) is a NATO-led international peacekeeping force and military of Kosovo. KFOR is the third security responder, after the Kosovo Police and the EU Rule of Law (EULEX) mission, respectively, with whom NATO peacekeeping forces work in close coordination. Its operations are gradually reducing until the Kosovo Security Force, established in 2009, becomes self-sufficient.

The Kosovo Protection Corps was a civilian emergency services organization in Kosovo active from 1999 until 2009.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1244, adopted on 10 June 1999, after recalling resolutions 1160 (1998), 1199 (1998), 1203 (1998) and 1239 (1999), authorised an international civil and military presence in the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and established the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK). It followed an agreement by Yugoslav President Slobodan Milošević to terms proposed by President of Finland Martti Ahtisaari and former Prime Minister of Russia Viktor Chernomyrdin on 8 June, involving withdrawal of all Yugoslav state forces from Kosovo.
The Podujevo bus bombing was an attack on a bus carrying Serb civilians near the town of Podujevë in Kosovo on 16 February 2001. The bombing killed twelve Serb civilians who were travelling to Gračanica and injured dozens more. Albanian extremists are suspected of being responsible for the attack. Gračanica is a predominantly Serb-populated town in central Kosovo, near the regional capital Pristina, in a predominantly Albanian-populated area. Following the Kosovo War in 1999 it became an enclave within Albanian-controlled territory. Relations between the two communities were tense and occasionally violent.

On 17–18 March 2004, violence erupted in Kosovo, leaving hundreds wounded and at least 19 people dead. The unrest was precipitated by unsubstantiated reports in the Kosovo Albanian media which claimed that three Kosovo Albanian boys had drowned after being chased into the Ibar River by a group of Kosovo Serbs. UN peacekeepers and NATO troops scrambled to contain a gun battle between Serbs and Albanians in the partitioned town of Mitrovica, Kosovo before the violence spread to other parts of Kosovo. Kosovo Serb communities and cultural heritage were attacked by crowds of Albanians. Serbs call the event the March Pogrom, while the Albanians call it the March Unrest.
The political status of Kosovo, also known as the Kosovo question, is the subject of a long-running political and territorial dispute between the Serbian government and the Government of Kosovo, stemming from the breakup of Yugoslavia (1991–92) and the ensuing Kosovo War (1998–99). In 1999, the administration of the Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija was handed on an interim basis to the United Nations under the terms of UNSCR 1244 which ended the Kosovo conflict of that year. That resolution reaffirmed the territorial integrity of Serbia over Kosovo but required the UN administration to promote the establishment of 'substantial autonomy and self-government' for Kosovo pending a 'final settlement' for negotiation between the parties.
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of armed conflicts on the territory of the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY) that took place between 1991 and 2001. This article is a timeline of relevant events preceding, during, and after the wars.

The insurgency in the Preševo Valley was an approximately two year-long armed conflict between 1999 and 2001, between the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the ethnic Albanian separatists of the Liberation Army of Preševo, Medveđa and Bujanovac (UÇPMB). There were instances during the conflict in which the Yugoslav government requested KFOR support in suppressing UÇPMB attacks since they could only use lightly armed military forces as part of the Kumanovo Treaty that ended the Kosovo War, which created a buffer zone between FR Yugoslavia and Kosovo.
The 2008 Kosovo declaration of independence, which proclaimed the Republic of Kosovo to be an independent and sovereign state, was adopted at a meeting held on 17 February 2008 by 109 out of the 120 members of the Assembly of Kosovo, including the Prime Minister of Kosovo, Hashim Thaçi, and by the President of Kosovo, Fatmir Sejdiu. It was the second declaration of independence by Kosovo's Albanian-majority political institutions; the first was proclaimed on 7 September 1990.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1160, adopted on 31 March 1998, after noting the situation in Kosovo, the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, imposed an arms embargo and economic sanctions on the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, hoping to end the use of excessive force by the government.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1199, adopted on 23 September 1998, after recalling Resolution 1160 (1998), the Council demanded that the Albanian and Yugoslav parties in Kosovo end hostilities and observe a ceasefire.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1203, adopted on 24 October 1998, after recalling resolutions 1160 (1998) and 1199 (1998) on Kosovo, the Council demanded that the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia comply with previous Security Council resolutions and co-operate with the NATO and Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) verification missions in Kosovo.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1371, adopted unanimously on 26 September 2001, after reaffirming resolutions 1244 (1999) and 1345 (2001) on the situation in the former Yugoslavia including Macedonia, the Council called for the full implementation of its Resolution 1345 concerning violence and terrorist activities in Macedonia and southern Serbia.

The 2000 unrest in Kosovo was the result of the United Nations Interim Administration adopting Resolution 1244 on 10 June 1999. The unrest was fought between the Kosovo Force (KFOR), Kosovar Albanians, and Kosovar Serbs. It lasted somewhere from February 16, 2000 – June 6, 2000. An unknown number of Kosovar Albanians and Kosovar Serbs died along with an unknown number injured, while 1 Russian KFOR soldier died from shot wounds and UNMIK vehicles were burned during the unrest.
This article includes information on actions described as terrorist acts in the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Serbia and Montenegro (2003–2006) and Serbia.
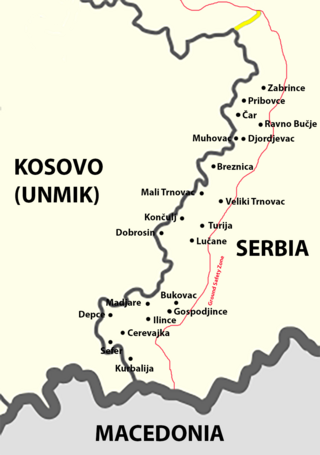
The Ground Safety Zone was a 5-kilometre-wide demilitarized zone (DMZ) established in June 1999 after the signing of the Kumanovo agreement which ended the Kosovo War. It bordered the area between the Yugoslavia and Kosovo.














