United Nations Security Council resolution 896, adopted unanimously on 31 January 1994, after reaffirming resolutions 849 (1993), 854 (1993), 858 (1993), 876 (1993), 881 (1993) and 892 (1993) on the Georgian–Abkhazian war and Resolution 868 (1993) concerning the safety of United Nations peacekeepers, the Council considered the possible establishment of peacekeeping force in Abkhazia and Georgia, and discussed the peace process.

United Nations Security Council resolution 937, adopted on 21 July 1994, after reaffirming resolutions 849 (1993), 854 (1993), 858 (1993), 876 (1993), 881 (1993), 892 (1993), 896 (1994), 901 (1994), 906 (1994) and 934 (1994), the Council expanded the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) to include co-operation with the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and extended its mandate until 13 January 1995.

United Nations Security Council resolution 993, adopted unanimously on 12 May 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on Georgia, particularly 971 (1995), the Council discussed efforts for a political settlement between Georgia and Abkhazia and extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 12 January 1996.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1036, adopted unanimously on 12 January 1996, after reaffirming all resolutions on Georgia, particularly 993 (1995), the Council discussed efforts for a political settlement between Georgia and Abkhazia and extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) for another six months until 12 July 1996.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1065, adopted unanimously on 12 July 1996, after reaffirming all resolutions on Georgia, particularly 1036 (1996), the Council discussed efforts for a political settlement between Georgia and Abkhazia and extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 January 1997.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1096, adopted unanimously on 30 January 1997, after reaffirming all resolutions on Georgia, particularly Resolution 1065 (1996), the Council addressed the current situation extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 July 1997.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1124, adopted unanimously on 31 July 1997, after reaffirming all resolutions on Georgia, particularly Resolution 1096 (1997), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 January 1998.

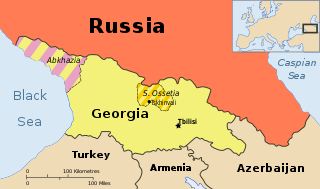
United Nations Security Council resolution 1150, adopted unanimously on 30 January 1998, after reaffirming all resolutions on Georgia, particularly Resolution 1124 (1997), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 July 1998.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1187, adopted unanimously on 30 July 1998, after reaffirming all resolutions on Georgia, particularly Resolution 1150 (1998), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 January 1999, and discussed recent hostilities in the country.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1225, adopted unanimously on 28 January 1999, after reaffirming all resolutions on Georgia, particularly Resolution 1187 (1998), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 July 1999, and expressed an intention to review its mandate.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1339, adopted unanimously on 31 January 2001, after reaffirming all resolutions on Abkhazia and Georgia, particularly Resolution 1311 (2000), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 July 2001.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1364, adopted unanimously on 31 July 2001, after reaffirming all resolutions on Abkhazia and Georgia, particularly Resolution 1339 (2001), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 January 2002.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1393, adopted unanimously on 31 January 2002, after reaffirming all resolutions on Abkhazia and Georgia, particularly Resolution 1364 (2001), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 July 2002.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1427, adopted unanimously on 29 July 2002, after reaffirming all resolutions on Abkhazia and Georgia, particularly Resolution 1393 (2002), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 January 2003.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1462, adopted unanimously on 30 January 2003, after reaffirming all resolutions on Abkhazia and Georgia, particularly Resolution 1427 (2002), the council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 July 2003.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1494, adopted unanimously on 30 July 2003, after reaffirming all resolutions on Abkhazia and Georgia, particularly Resolution 1462 (2003), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 January 2004 and endorsed the establishment of a police component.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1524, adopted unanimously on 30 January 2004, after reaffirming all resolutions on Abkhazia and Georgia, particularly Resolution 1494 (2003), the council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 July 2004.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1554, adopted unanimously on 29 July 2004, after reaffirming all resolutions on Abkhazia and Georgia, particularly Resolution 1524 (2004), the council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 January 2005.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1582, adopted unanimously on 28 January 2005, after reaffirming all resolutions on Abkhazia and Georgia, particularly Resolution 1554 (2004), the council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 July 2005.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1666, adopted unanimously on March 31, 2006, after reaffirming all resolutions on Abkhazia and Georgia, particularly Resolution 1615 (2005), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until October 15, 2006.


















