
The 2006 United Nations Security Council election began on 16 October 2006 during the 61st session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2007.

The 2014 United Nations Security Council election was held on 16 October 2014 during the 69th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2015. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five available seats were allocated as follows:

The 2013 United Nations Security Council election was held on 17 October 2013 during the 68th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The Assembly elected Chad, Chile, Lithuania, Nigeria, and Saudi Arabia for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2014. The following day, Saudi Arabia announced that it was declining the seat, accusing UNSC of using "double standards" and being unable to resolve important issues in the Middle East. A second round of voting therefore took place on 6 December, in which Jordan was elected to the Council in lieu of Saudi Arabia.
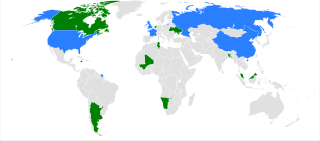
The 1999 United Nations Security Council election was held on 14 October 1999 during the Fifty-fourth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Bangladesh, Jamaica, Mali, Tunisia, and Ukraine, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2000.
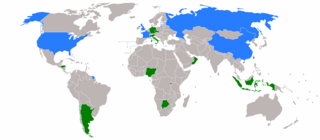
The 1994 United Nations Security Council election was held on 20 October 1994 during the Forty-ninth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Botswana, Germany, Honduras, Indonesia, and Italy, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1995.

The 1993 United Nations Security Council election was held on 29 October 1993 during the Forty-eighth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Argentina, the Czech Republic, Nigeria, Oman, and Rwanda, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1994.
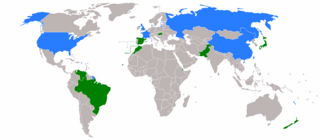
The 1992 United Nations Security Council election was held on 27 October 1992 during the Forty-seventh session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Brazil, Djibouti, New Zealand, Pakistan, and Spain, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1993.

The 1991 United Nations Security Council election was held on 16 October 1991 during the Forty-sixth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Cape Verde, Hungary, Japan, Morocco, and Venezuela, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1992.
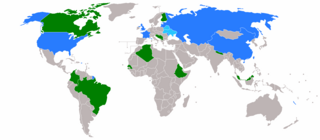
The 1988 United Nations Security Council election was held on 26 October 1988 during the Forty-third session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Canada, Colombia, Ethiopia, Finland, and Malaysia, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1989.

The 1987 United Nations Security Council election was held on 15 October 1987 during the Forty-second session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Algeria, Brazil, Nepal, Senegal, and Yugoslavia, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1988.

The 1986 United Nations Security Council election was held on 16 October 1986 during the Forty-first session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Argentina, Italy, Japan, West Germany, and Zambia, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1987.

The 1984 United Nations Security Council election was held from 22 October to 18 December 1984 during the Thirty-ninth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Australia, Denmark, Madagascar, Thailand, and Trinidad and Tobago, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1985.

The 1982 United Nations Security Council election was held on 19 October 1982 during the Thirty-seventh session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Malta, the Netherlands, Nicaragua, Pakistan, and Zimbabwe, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1983.

The 1977 United Nations Security Council election was held on 24 October 1977 during the Thirty-second session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Bolivia, Czechoslovakia, Gabon, Kuwait, and Nigeria, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1978.
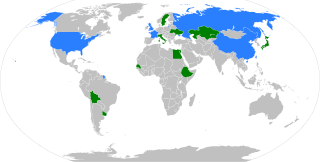
The 2016 United Nations Security Council election was held on 28 June during the 70th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2017. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five available seats were allocated as follows:

The 1975 United Nations Security Council election was held on between 20 October and 23 October 1975 during the Thirtieth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Dahomey, Libya, Pakistan, Panama, and Romania, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1976.
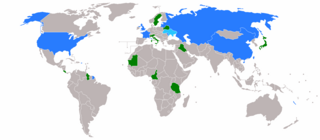
The 1974 United Nations Security Council election was held on 11 October 1974 during the Twenty-ninth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Guyana, Italy, Japan, Sweden, and Tanzania, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1975.

The 1969 United Nations Security Council election was held on 20 October 1969 during the Twenty-fourth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected the Burundi, Nicaragua, Poland, Sierra Leone, and Syria, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1970.
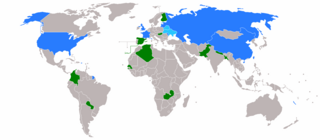
The 1968 United Nations Security Council election was held on 1 November 1968 during the Twenty-third session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Colombia, Finland, Nepal, Spain, and Zambia, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1969.
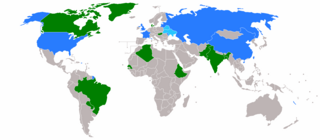
The 1967 United Nations Security Council election was held on 6 November 1967 during the Twenty-second session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Algeria, Hungary, Pakistan, Paraguay, and Senegal, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1968.





























