| |||
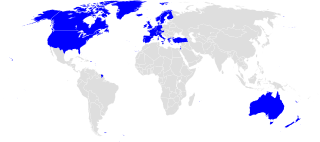
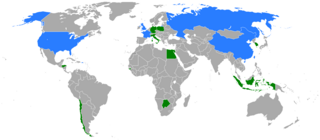
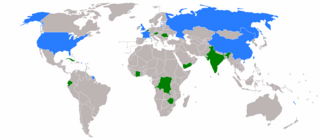
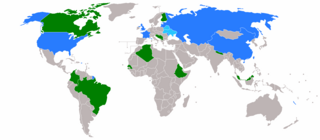
5 (of 10) non-permanent seats on the United Nations Security Council | |||
| |||
| Unsuccessful candidates |
The 1998 United Nations Security Council election was held on 8 October 1998 at United Nations Headquarters in New York City during the 53rd session of the United Nations General Assembly. The General Assembly elected five non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year terms commencing on 1 January 1999.

The City of New York, usually called either New York City (NYC) or simply New York (NY), is the most populous city in the United States and in the U.S. state of New York. With an estimated 2017 population of 8,622,698 distributed over a land area of about 302.6 square miles (784 km2), New York is also the most densely populated major city in the United States. Located at the southern tip of the state of New York, the city is the center of the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban landmass and one of the world's most populous megacities, with an estimated 20,320,876 people in its 2017 Metropolitan Statistical Area and 23,876,155 residents in its Combined Statistical Area. A global power city, New York City has been described as the cultural, financial, and media capital of the world, and exerts a significant impact upon commerce, entertainment, research, technology, education, politics, tourism, art, fashion, and sports. The city's fast pace has inspired the term New York minute. Home to the headquarters of the United Nations, New York is an important center for international diplomacy.

The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization that was tasked to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international co-operation and be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. The headquarters of the UN is in Manhattan, New York City, and is subject to extraterritoriality. Further main offices are situated in Geneva, Nairobi, and Vienna. The organization is financed by assessed and voluntary contributions from its member states. Its objectives include maintaining international peace and security, protecting human rights, delivering humanitarian aid, promoting sustainable development and upholding international law. The UN is the largest, most familiar, most internationally represented and most powerful intergovernmental organization in the world. In 24 October 1945, at the end of World War II, the organization was established with the aim of preventing future wars. At its founding, the UN had 51 member states; there are now 193. The UN is the successor of the ineffective League of Nations.

The United Nations General Assembly is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), the only one in which all member nations have equal representation, and the main deliberative, policy-making, and representative organ of the UN. Its powers are to oversee the budget of the UN, appoint the non-permanent members to the Security Council, appoint the Secretary-General of the United Nations, receive reports from other parts of the UN, and make recommendations in the form of General Assembly Resolutions. It has also established numerous subsidiary organs.
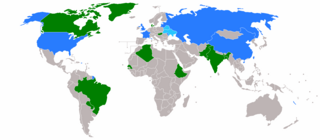
The five candidates elected were Argentina, Canada, Malaysia, Namibia, and the Netherlands.

Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country located mostly in the southern half of South America. Sharing the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, the country is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. With a mainland area of 2,780,400 km2 (1,073,500 sq mi), Argentina is the eighth-largest country in the world, the fourth largest in the Americas, and the largest Spanish-speaking nation. The sovereign state is subdivided into twenty-three provinces and one autonomous city, Buenos Aires, which is the federal capital of the nation as decided by Congress. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over part of Antarctica, the Falkland Islands, and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands.

Canada is a country in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres, making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Canada's southern border with the United States is the world's longest bi-national land border. Its capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. As a whole, Canada is sparsely populated, the majority of its land area being dominated by forest and tundra. Consequently, its population is highly urbanized, with over 80 percent of its inhabitants concentrated in large and medium-sized cities, many near the southern border. Canada's climate varies widely across its vast area, ranging from arctic weather in the north, to hot summers in the southern regions, with four distinct seasons.

Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. The federal constitutional monarchy consists of 13 states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two similarly sized regions, Peninsular Malaysia and East Malaysia. Peninsular Malaysia shares a land and maritime border with Thailand in the north and maritime borders with Singapore in the south, Vietnam in the northeast, and Indonesia in the west. East Malaysia shares land and maritime borders with Brunei and Indonesia and a maritime border with the Philippines and Vietnam. Kuala Lumpur is the national capital and largest city while Putrajaya is the seat of federal government. With a population of over 30 million, Malaysia is the world's 44th most populous country. The southernmost point of continental Eurasia, Tanjung Piai, is in Malaysia. In the tropics, Malaysia is one of 17 megadiverse countries, with large numbers of endemic species.