
Reform of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) encompasses five key issues: categories of membership, the question of the veto held by the five permanent members, regional representation, the size of an enlarged Council and its working methods, and the Security Council-General Assembly relationship. Member States, regional groups and other Member State interest groupings developed different positions and proposals on how to move forward on this contested issue.

The 2006 United Nations Security Council election began on 16 October 2006 during the 61st session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2007.

The 2009 United Nations Security Council election was held on 15 October 2009 during the 64th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The election was for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council to serve two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2010.

The 2014 United Nations Security Council election was held on 16 October 2014 during the 69th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2015. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five available seats were allocated as follows:

The 2012 United Nations Security Council election was held on 18 October 2012 during the 67th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2013 to replace the five countries whose terms expired. The countries elected were Argentina, Australia, Luxembourg, the Republic of Korea, and Rwanda.

The 2011 United Nations Security Council election was held on 21 and 24 October 2011 during the Sixty-sixth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Azerbaijan, Guatemala, Morocco, Pakistan, and Togo, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2012. Azerbaijan was elected after 17 rounds on 24 October, while the other four new members were chosen on 21 October.

The 2015 United Nations Security Council election was held on 15 October 2015 during the 70th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections are for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2016. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five available seats are allocated as follows:
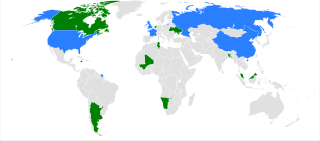
The 1999 United Nations Security Council election was held on 14 October 1999 during the Fifty-fourth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Bangladesh, Jamaica, Mali, Tunisia, and Ukraine, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2000.

The 1993 United Nations Security Council election was held on 29 October 1993 during the Forty-eighth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Argentina, the Czech Republic, Nigeria, Oman, and Rwanda, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1994.

The Sixty-seventh session of the United Nations General Assembly opened on 18 September 2012 and having its last scheduled meeting on 11 September 2013. The President of the United Nations General Assembly was chosen from the EEG with Serbia's then foreign minister Vuk Jeremić beating out Lithuania's Dalius Čekuolis in an election. Notably, the session led to United Nations General Assembly resolution 67/19 which granted Palestine non-member observer state status.

The 1987 United Nations Security Council election was held on 15 October 1987 during the Forty-second session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Algeria, Brazil, Nepal, Senegal, and Yugoslavia, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1988.

The 1985 United Nations Security Council election was held on 17 October 1985 during the Fortieth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Bulgaria, Congo, Ghana, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1986.

The 1977 United Nations Security Council election was held on 24 October 1977 during the Thirty-second session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Bolivia, Czechoslovakia, Gabon, Kuwait, and Nigeria, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1978.
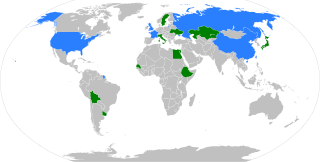
The 2016 United Nations Security Council election was held on 28 June during the 70th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2017. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five available seats were allocated as follows:

The 2017 United Nations Security Council election was held on 2 June 2017 during the 71st session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. In addition to the regular elections for five of the non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council, there was by-election for a sixth seat held by Italy who relinquished its seat at the end of the year as part of a term splitting agreement with the Netherlands. The regular elections are for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2018; the by-election is for the remainder of Italy's term. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five regularly available seats are allocated as follows:
The 2021 United Nations Security Council election will be held in mid-2021 during the 75th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections are for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2022. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five available seats are allocated as follows:

The 1973 United Nations Security Council election was held on 15 October 1973 during the Twenty-eighth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected the Byelorussian SSR, Cameroon, Costa Rica, Iraq, and Mauritania, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1974.
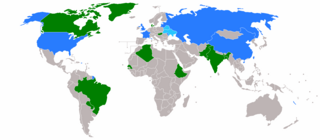
The 1967 United Nations Security Council election was held on 6 November 1967 during the Twenty-second session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Algeria, Hungary, Pakistan, Paraguay, and Senegal, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1968.

The Seventieth Session of the United Nations General Assembly opened on 15 September 2015. The President of the United Nations General Assembly is from the Western European and Others Group.





























