
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), charged with ensuring international peace and security, accepting new members to the United Nations and approving any changes to its charter. Its powers include the establishment of peacekeeping operations and international sanctions as well as the authorization of military actions through resolutions – it is the only body of the United Nations with the authority to issue binding resolutions to member states. The council held its first session on 17 January 1946.

The G4 nations comprising Brazil, Germany, India, and Japan are four countries which support each other’s bids for permanent seats on the United Nations Security Council. Unlike the G7, where the common denominator is the economy and long-term political motives, the G4's primary aim is the permanent member seats on the Security Council. Each of these four countries have figured among the elected non-permanent members of the council since the UN's establishment. Their economic and political influence has grown significantly in the last decades, reaching a scope comparable to the permanent members (P5). However, the G4's bids are often opposed by the Uniting for Consensus movement, and particularly their economic competitors or political rivals.

Reform of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) encompasses five key issues: categories of membership, the question of the veto held by the five permanent members, regional representation, the size of an enlarged Council and its working methods, and the Security Council-General Assembly relationship. Member States, regional groups and other Member State interest groupings developed different positions and proposals on how to move forward on this contested issue.

The 2006 United Nations Security Council election began on 16 October 2006 during the 61st session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2007.

The 2007 United Nations Security Council election was held on 16 October 2007 during the 62nd session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at UN Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2008.

The 2005 United Nations Security Council election was held on 10 October 2005 during the 60th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2006. The countries elected were the Republic of the Congo, Ghana, Peru, Qatar, and Slovakia.

The 2014 United Nations Security Council election was held on 16 October 2014 during the 69th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2015. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five available seats were allocated as follows:

The 2011 United Nations Security Council election was held on 21 and 24 October 2011 during the Sixty-sixth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Azerbaijan, Guatemala, Morocco, Pakistan, and Togo, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2012. Azerbaijan was elected after 17 rounds on 24 October, while the other four new members were chosen on 21 October.

The 2013 United Nations Security Council election was held on 17 October 2013 during the 68th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The Assembly elected Chad, Chile, Lithuania, Nigeria, and Saudi Arabia for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2014. The following day, Saudi Arabia announced that it was declining the seat, accusing UNSC of using "double standards" and being unable to resolve important issues in the Middle East. A second round of voting therefore took place on 6 December, in which Jordan was elected to the Council in lieu of Saudi Arabia.

The 2015 United Nations Security Council election was held on 15 October 2015 during the 70th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections are for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2016. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five available seats are allocated as follows:

The 1993 United Nations Security Council election was held on 29 October 1993 during the Forty-eighth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Argentina, the Czech Republic, Nigeria, Oman, and Rwanda, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1994.

The 1987 United Nations Security Council election was held on 15 October 1987 during the Forty-second session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Algeria, Brazil, Nepal, Senegal, and Yugoslavia, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1988.

The 1985 United Nations Security Council election was held on 17 October 1985 during the Fortieth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Bulgaria, Congo, Ghana, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1986.
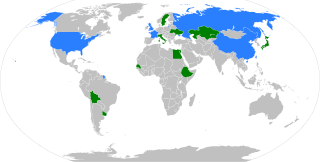
The 2016 United Nations Security Council election was held on 28 June during the 70th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2017. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five available seats were allocated as follows:

The 2017 United Nations Security Council election was held on 2 June 2017 during the 71st session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. In addition to the regular elections for five of the non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council, there was by-election for a sixth seat held by Italy who relinquished its seat at the end of the year as part of a term splitting agreement with the Netherlands. The regular elections are for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2018; the by-election is for the remainder of Italy's term. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five regularly available seats are allocated as follows:
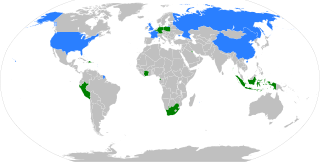
The 2018 United Nations Security Council election was held on 8 June during the 72nd session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2019.

The 1972 United Nations Security Council election was held on 20 October 1972 during the Twenty-seventh session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Australia, Austria, Indonesia, Kenya, and Peru, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1973.


























