
A subregion is a part of a larger region or continent. Cardinal directions are commonly used to define subregions. There are many criteria for creating systems of subregions; this article is focusing on the UN statistical geoscheme, which is a changing, constantly updated, UN tool based on specific political geography considerations relevant in UN statistics.

Geography of Asia reviews geographical concepts of classifying Asia, the central and eastern part of Eurasia, comprising 58 countries and territories.
The United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD), formerly the United Nations Statistical Office, serves under the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA) as the central mechanism within the Secretariat of the United Nations to supply the statistical needs and coordinating activities of the global statistical system. The Division is overseen by the United Nations Statistical Commission, established in 1947, as the apex entity of the global statistical system and highest decision making body for coordinating international statistical activities. It brings together the Chief Statisticians from member states from around the world.

The United Nations geoscheme is a system which divides 248 countries and territories in the world into six continental regions, 22 geographical subregions, and two intermediary regions. It was devised by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD) based on the M49 coding classification. The creators note that "the assignment of countries or areas to specific groupings is for statistical convenience and does not imply any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories".
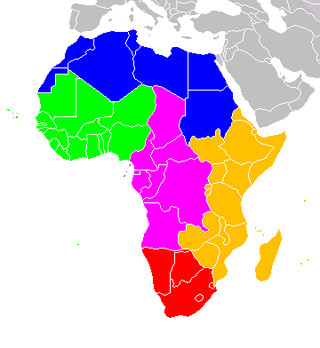
The following is an alphabetical list of subregions in the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, used by the United Nations and maintained by the UNSD department for statistical purposes.

The United Nations geoscheme for the Americas is an internal tool created and used by the UN's Statistics Division (UNSD) for the specific purpose of UN statistics.
UN M49 or the Standard Country or Area Codes for Statistical Use is a standard for area codes used by the United Nations for statistical purposes, developed and maintained by the United Nations Statistics Division. Each area code is a 3-digit number which can refer to a wide variety of geographical and political regions, like a continent and a country. Codes assigned in the system generally do not change when the country or area's name changes, but instead change when the territorial extent of the country or area changes significantly, although there have been exceptions to this rule.

The following is an alphabetical list of subregions in the United Nations geoscheme for Europe, created by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD). The scheme subdivides the continent into Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, Southern Europe, and Western Europe. The UNSD notes that "the assignment of countries or areas to specific groupings is for statistical convenience and does not imply any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories".

Determining the boundaries between the continents is generally a matter of geographical convention. Several slightly different conventions are in use. The number of continents is most commonly considered seven but may range as low as four when Afro-Eurasia and the Americas are both considered as single continents. An island can be considered to be associated with a given continent by either lying on the continent's adjacent continental shelf or being a part of a microcontinent on the same principal tectonic plate. An island can also be entirely oceanic while still being associated with a continent by geology or by common geopolitical convention. Another example is the grouping into Oceania of the Pacific Islands with Australia and Zealandia.

The United Nations geoscheme for Asia is an internal tool created and used by the United Nations, maintained by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD) for the specific purpose of UN statistics. The scheme's subregions are presented here in alphabetical order. Its subregions may not coincide with other geographic categorization schemes.
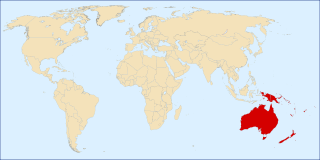
The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide to Oceania.
The decolonisation of Oceania occurred after World War II when nations in Oceania achieved independence by transitioning from European colonial rule to full independence.

Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania vary, with it being defined in various ways, often geopolitically or geographically. In the geopolitical conception used by the United Nations, International Olympic Committee, and many atlases, the Oceanic region includes Australia and the nations of the Pacific from Papua New Guinea east, but not the Malay Archipelago or Indonesian New Guinea. The term is sometimes used more specifically to denote Australasia as a geographic continent, or biogeographically as a synonym for either the Australasian realm or the Oceanian realm.

The term Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) is an English-language acronym referring to the Latin American and the Caribbean region. The term LAC covers an extensive region, extending from The Bahamas and Mexico to Argentina and Chile. The region has over 670,230,000 people as of 2016, and spanned for 21,951,000 square kilometres (8,475,000 sq mi).
Outlying Oceania is the name used in the Unicode Common Locale Data Repository for territories that are supplemented into the United Nations geoscheme for Oceania since they are not assigned to a subcontinent. The name has private-use region subtags assigned: alpha-2 QO, alpha-3 QOO and numeric 961.











