
The Ruhr is a river in western Germany, a right tributary (east-side) of the Rhine.

The Sauerland is a rural, hilly area spreading across most of the south-eastern part of North Rhine-Westphalia, in parts heavily forested and, apart from the major valleys, sparsely inhabited.

Meschede is a town in the Hochsauerland district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the capital of the district Hochsauerlandkreis.

Olsberg is a town in the Hochsauerland district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.
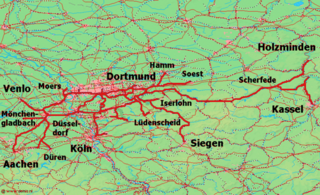
The Bergisch-Markisch Railway Company, also referred to as the Berg-Mark Railway Company or, more rarely, as the Bergisch-Markische Railway Company, was a German railway company that together with the Cologne-Minden Railway and the Rhenish Railway Company was one of the three (nominally) private railway companies that in the mid-19th century built the first railways in the Ruhr and large parts of today's North Rhine-Westphalia. Its name refers to Bergisches Land and the County of Mark.

The DBAG Class 612 is a two car, tilting, diesel multiple unit operated by the Deutsche Bahn for fast regional rail services on unelectrified lines.
The Hagen–Hamm railway is a continuous two-track, electrified main line in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, connecting Hagen via Schwerte, Holzwickede and Unna to Hamm.

The Ruhr Valley Railway is a partly abandoned railway line in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, running from Düsseldorf-Rath via Old Kupferdreh station, Bochum-Dahlhausen, Witten-Herbede, Hagen-Vorhalle and Schwerte to Warburg. It was built between 1872 and 1876 by the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company, one of the three major private railway companies in the Ruhr area. The railway tracks that were built along the Ruhr river had a relatively uniform grade that was suitable for railway operations at the time.

Hofgeismar is a railway station located in Hofgeismar, Germany. The station is located on the Kassel–Warburg railway. The train services are operated by Deutsche Bahn, abellio Deutschland and RegioTram Gesellschaft.

Schwerte station is a through station in the town of Schwerte in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The station was opened with the section of the Hagen–Hamm railway between Hagen and Holzwickede, opened by the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company on 1 April 1867. It has six platform tracks and it is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 4 station.

The Arnsberg (Westfalen) station is a station on the Upper Ruhr Valley Railway in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It was opened in Arnsberg with the construction of the line in 1870/71. The station building was built in 1869 in the Renaissance Revival style. The station building is still used for passenger traffic. Some of the space in the building is used by various social groups and institutions.

The Brilon Wald station is a station on the Upper Ruhr Valley Railway in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It was opened 5.5 km south of Brilon in the forest (Wald) with the construction of the line on 10 February 1873, as it was impractical to build the railway through Brilon. The station was called Brilon-Corbach until 1880, when the current name was adopted. The Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company created the small town of Brilon Wald at the same time. The station is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 5 station.

The Letmathe–Fröndenberg railway is a two-track, partially electrified and partially disused branch line in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. For over 100 years it ran from Letmathe via Iserlohn, Hemer and Menden to Fröndenberg. The section between Hemer and Iserlohn and the branch line from Hemer to Sundwig have been closed and dismantled.
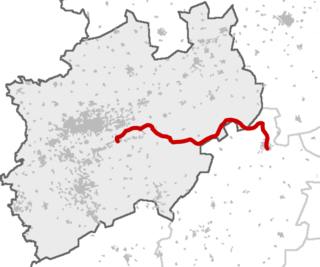
The Sauerland-ExpressRE 17 is a Regional-Express service in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, running from Hagen to Warburg (Westf). It is managed by the Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Ruhr, the Verkehrsgemeinschaft Ruhr-Lippe, the Nahverkehrsverbund Paderborn-Höxter and the Nordhessischer Verkehrsverbund. It is operated by DB Regio NRW with Pesa Link electric multiple units.
The Sauerland Net is a group of railway services in the western Sauerland and the eastern Ruhr of the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and consists of four Regionalbahn services, RB 43 (Dortmund–Dorsten), RB 52 (Dortmund–Hagen–Lüdenscheid), RB 53 (Dortmund–Schwerte–Iserlohn) and RB 54 (Unna–Fröndenberg–Menden–Neuenrade), and the Regional-Express service RE 57. The RB 43 also carries the brand name of the Emschertal-Bahn, the RB 52 is called the Volmetal-Bahn, the RB 53 is called the Ardey-Bahn, the RB 54 is called the Hönnetal-Bahn and the RE 57 is called the Dortmund Sauerland-Express. In December 2004, DB Regio NRW took over or retained operations of these services. Previously the RB 53, RB 54 and RE 57 had been operated by DB Regio NRW and RB 52 had been operated by the Dortmund-Märkische Eisenbahn (DME).
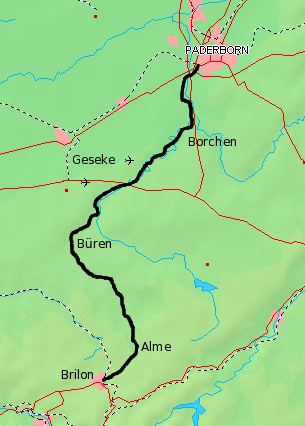
The Alme Valley Railway was an approximately 60 km long, mostly single-track branch line from Paderborn via Buren to Brilon in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is named after the Alme river and runs through its valley in a north–south direction. The line is disused and dismantled between Paderborn and Büren-Weiberg, but it has not been formally closed. The remaining line between Büren-Weiberg and Brilon Wald (forest) was for a long time only used for freight and museum trains, but the section between Brilon Stadt (town) and Brilon Wald has been back in use by regional services since 2011.

Brilon Stadt (town) station is one of four passenger stations that are still in service in the town of Brilon in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is located near the centre of Brilon. The former goods shed of the station is a listed building.

The Warburg–Sarnau railway is a 100.9 kilometre-long, single-track, partially disused secondary railway line in North Rhine-Westphalia and North Hesse. The middle section, Korbach–Frankenberg, is called the Untere Edertalbahn or the Nationalparkbahn and the southern section, Frankenberg–Sarnau(–Marburg), is called the Burgwaldbahn.

The Wabern–Brilon Wald railway is a 86.7 kilometre-long, single-track, partially disused secondary railway line from Wabern in North Hesse to Brilon-Wald in North Rhine-Westphalia.

The Dortmund-Märkische Eisenbahn GmbH (DME) was a German train operating company, that operated the Dortmund–Hagen–Lüdenscheid train service from 30 May 1999 to 11 December 2004. It was a subsidiary of the Dortmunder Stadtwerke (74%) and the Märkische Verkehrsgesellschaft (26%), the municipal public transport operators of Dortmund and Märkischer Kreis.





















