Related Research Articles
In physics, an electronvolt is the measure of an amount of kinetic energy gained by a single electron accelerating from rest through an electric potential difference of one volt in vacuum. When used as a unit of energy, the numerical value of 1 eV in joules is equivalent to the numerical value of the charge of an electron in coulombs. Under the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, this sets 1 eV equal to the exact value 1.602176634×10−19 J.
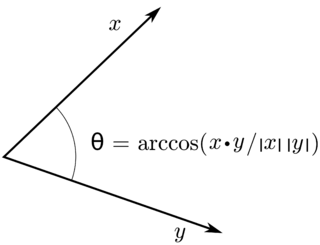
In mathematics, an inner product space is a real vector space or a complex vector space with an operation called an inner product. The inner product of two vectors in the space is a scalar, often denoted with angle brackets such as in . Inner products allow formal definitions of intuitive geometric notions, such as lengths, angles, and orthogonality of vectors. Inner product spaces generalize Euclidean vector spaces, in which the inner product is the dot product or scalar product of Cartesian coordinates. Inner product spaces of infinite dimension are widely used in functional analysis. Inner product spaces over the field of complex numbers are sometimes referred to as unitary spaces. The first usage of the concept of a vector space with an inner product is due to Giuseppe Peano, in 1898.

In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes. The same amount of work is done by the body when decelerating from its current speed to a state of rest. Formally, a kinetic energy is any term in a system's Lagrangian which includes a derivative with respect to time.
In physics, power is the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the watt, equal to one joule per second. In older works, power is sometimes called activity. Power is a scalar quantity.

A thermocouple, also known as a "thermoelectrical thermometer", is an electrical device consisting of two dissimilar electrical conductors forming an electrical junction. A thermocouple produces a temperature-dependent voltage as a result of the Seebeck effect, and this voltage can be interpreted to measure temperature. Thermocouples are widely used as temperature sensors.

A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching.
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filter design. The filter is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble-cut filter in audio applications. A low-pass filter is the complement of a high-pass filter.
The molar gas constant is denoted by the symbol R or R. It is the molar equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, expressed in units of energy per temperature increment per amount of substance, i.e. the pressure–volume product, rather than energy per temperature increment per particle. The constant is also a combination of the constants from Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. It is a physical constant that is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law, the Arrhenius equation, and the Nernst equation.
The Black–Scholes or Black–Scholes–Merton model is a mathematical model for the dynamics of a financial market containing derivative investment instruments. From the parabolic partial differential equation in the model, known as the Black–Scholes equation, one can deduce the Black–Scholes formula, which gives a theoretical estimate of the price of European-style options and shows that the option has a unique price given the risk of the security and its expected return. The equation and model are named after economists Fischer Black and Myron Scholes; Robert C. Merton, who first wrote an academic paper on the subject, is sometimes also credited.

In physics, work is the energy transferred to or from an object via the application of force along a displacement. In its simplest form, for a constant force aligned with the direction of motion, the work equals the product of the force strength and the distance traveled. A force is said to do positive work if when applied it has a component in the direction of the displacement of the point of application. A force does negative work if it has a component opposite to the direction of the displacement at the point of application of the force.

A composite material is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions.

In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of work that may be performed by a thermodynamically closed system at constant temperature and pressure. It also provides a necessary condition for processes such as chemical reactions that may occur under these conditions.

In biochemistry, Michaelis–Menten kinetics is one of the best-known models of enzyme kinetics. It is named after German biochemist Leonor Michaelis and Canadian physician Maud Menten. The model takes the form of an equation describing the rate of enzymatic reactions, by relating reaction rate to , the concentration of a substrate S. Its formula is given by

In physics and relativity, time dilation is the difference in the elapsed time as measured by two clocks. It is either due to a relative velocity between them or to a difference in gravitational potential between their locations. When unspecified, "time dilation" usually refers to the effect due to velocity.
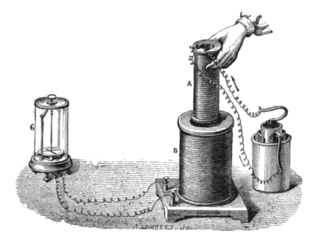
Faraday's law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism predicting how a magnetic field will interact with an electric circuit to produce an electromotive force (emf)—a phenomenon known as electromagnetic induction. It is the fundamental operating principle of transformers, inductors, and many types of electrical motors, generators and solenoids.

Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions.
In fluid dynamics, drag is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers or between a fluid and a solid surface. Unlike other resistive forces, such as dry friction, which are nearly independent of velocity, the drag force depends on velocity.
In linear algebra, an eigenvector or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a scalar factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often denoted by , is the factor by which the eigenvector is scaled.

Joachim-Yehoyachin Stutschewsky, was a Ukraine-born Austrian and Israeli cellist, composer, musicologist.

A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
References
- 1 2 Sepkoski, Jack (2002). "A compendium of fossil marine animal genera". Bulletins of American Paleontology. 364: 560. Retrieved 2009-02-27.
- ↑ "Gasterosteiformes". Paleobiology Database. Retrieved November 11, 2012.