
A nebula is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the "Pillars of Creation" in the Eagle Nebula. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter and eventually become dense enough to form stars. The remaining material is then thought to form planets and other planetary system objects.

A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses (M☉), possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes, neutron stars are the smallest and densest known class of stellar objects. Neutron stars have a radius on the order of 10 kilometers (6 mi) and a mass of about 1.4 M☉. They result from the supernova explosion of a massive star, combined with gravitational collapse, that compresses the core past white dwarf star density to that of atomic nuclei.

Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can range from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the current age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are formed from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star.

A supernova remnant (SNR) is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar material it sweeps up and shocks along the way.
Timeline of neutron stars, pulsars, supernovae, and white dwarfs

The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus. The common name comes from a drawing of the object produced by William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, in 1842 or 1843 using a 36-inch (91 cm) telescope that somewhat resembled a crab with arms. The nebula was discovered by English astronomer John Bevis in 1731. It corresponds with a bright supernova recorded by Chinese astronomers in 1054 as a guest star. The nebula was the first astronomical object identified that corresponds with a historically-observed supernova explosion.
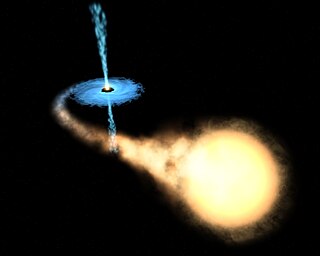
X-ray binaries are a class of binary stars that are luminous in X-rays. The X-rays are produced by matter falling from one component, called the donor, to the other component, called the accretor, which is either a neutron star or black hole. The infalling matter releases gravitational potential energy, up to 30 percent of its rest mass, as X-rays. The lifetime and the mass-transfer rate in an X-ray binary depends on the evolutionary status of the donor star, the mass ratio between the stellar components, and their orbital separation.

A pulsar wind nebula, sometimes called a plerion, is a type of nebula sometimes found inside the shell of a supernova remnant (SNR), powered by winds generated by a central pulsar. These nebulae were proposed as a class in 1976 as enhancements at radio wavelengths inside supernova remnants. They have since been found to be infrared, optical, millimetre, X-ray and gamma ray sources.

A pulsar is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Earth, and is responsible for the pulsed appearance of emission. Neutron stars are very dense and have short, regular rotational periods. This produces a very precise interval between pulses that ranges from milliseconds to seconds for an individual pulsar. Pulsars are one of the candidates for the source of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays.

The Crab Pulsar is a relatively young neutron star. The star is the central star in the Crab Nebula, a remnant of the supernova SN 1054, which was widely observed on Earth in the year 1054. Discovered in 1968, the pulsar was the first to be connected with a supernova remnant.

First observed between August 4 and August 6, 1181, Chinese and Japanese astronomers recorded the supernova now known as SN 1181 in eight separate texts. One of only five supernovae in the Milky Way confidently identified in pre-telescopic records, it appeared in the constellation Cassiopeia and was visible and motionless against the fixed stars for 185 days. F. R. Stephenson first recognized that the 1181 AD "guest star" must be a supernova, because such a bright transient that lasts for 185 days and does not move in the sky can only be a galactic supernova.

The Cygnus Loop is a large supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cygnus, an emission nebula measuring nearly 3° across. Some arcs of the loop, known collectively as the Veil Nebula or Cirrus Nebula, emit in the visible electromagnetic range. Radio, infrared, and X-ray images reveal the complete loop.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to astronomy:
A pulsar kick is the name of the phenomenon that often causes a neutron star to move with a different, usually substantially greater, velocity than its progenitor star. The cause of pulsar kicks is unknown, but many astrophysicists believe that it must be due to an asymmetry in the way a supernova explodes. If true, this would give information about the supernova mechanism.

IC 443 is a galactic supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Gemini. On the plane of the sky, it is located near the star Eta Geminorum. Its distance is roughly 5,000 light years from Earth.

Gamma-ray burst progenitors are the types of celestial objects that can emit gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). GRBs show an extraordinary degree of diversity. They can last anywhere from a fraction of a second to many minutes. Bursts could have a single profile or oscillate wildly up and down in intensity, and their spectra are highly variable unlike other objects in space. The near complete lack of observational constraint led to a profusion of theories, including evaporating black holes, magnetic flares on white dwarfs, accretion of matter onto neutron stars, antimatter accretion, supernovae, hypernovae, and rapid extraction of rotational energy from supermassive black holes, among others.

Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays.

Victoria Michelle Kaspi is a Canadian astrophysicist and a professor at McGill University. Her research primarily concerns neutron stars and pulsars.

IGR J11014−6103, also called the Lighthouse Nebula, is a pulsar wind nebula trailing the neutron star which has the longest relativistic jet observed in the Milky Way.

PSR J0002+6216, also dubbed the Cannonball Pulsar, is a pulsar discovered by the Einstein@Home project in 2017. It is one of the fastest moving pulsars known, and has moved 53 ly (5.0×1014 km; 3.1×1014 mi) away from the location of its formation supernova, where the remaining supernova nebula, CTB 1 (Abell 85), is. Due to its speed in traversing the interstellar medium, at 1,127 km/s (700 mi/s), it is leaving a 13 ly (1.2×1014 km; 7.6×1013 mi) long wake tail and is traveling fast enough to leave the Milky Way galaxy. The pulsar is currently 6,500 ly (6.1×1016 km; 3.8×1016 mi) away in the Cassiopeia constellation. The star rotates at a rate of 8.7 times a second. There is bow-shock pulsar wind nebula (PWN) associated with PSR J0002+6216.

















