
Alappuzha district, is one of the 14 districts in the Indian state of Kerala. It was formed as Alleppey district on 17 August 1957, the name of the district being changed to Alappuzha in 1990. Alappuzha is the smallest district of Kerala. Alleppey town, the district headquarters, was renamed Alappuzha in 2012.

A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck is hung below suspension cables on vertical suspenders. The first modern examples of this type of bridge were built in the early 1800s. Simple suspension bridges, which lack vertical suspenders, have a long history in many mountainous parts of the world.

A through arch bridge, also known as a through-type arch bridge, is a bridge that is made from materials such as steel or reinforced concrete, in which the base of an arch structure is below the deck but the top rises above it. It can either be lower bearing or mid-bearing. Thus, the deck is within the arch, and cables or beams that are in tension suspend the central part of the deck from the arch.

Vembanad is the longest lake in India, as well as the largest in the state of Kerala. The lake has an area of 230 square kilometers and a maximum length of 96.5 km.

Ashtamudi Lake, in the Kollam District of the Indian state of Kerala is a unique wetland ecosystem and a large palm-shaped water body. It is second only in size to the Vembanad estuary ecosystem of the state. Ashtamudi means 'eight hills or peaks' in the local Malayalam language. The name is indicative of the lake's topography with its multiple branches. The lake is also called the gateway to the backwaters of Kerala and is well known for its houseboat and backwater resorts. Ashtamudi Wetland was included in the list of wetlands of international importance, as defined by the Ramsar Convention for the conservation and sustainable utilization of wetlands. Ashtamudi Estuary is the deepest among all the estuaries in Kerala, with a maximum depth of 6.4 meters at the confluence zone.

The Nordhordland Bridge is a combined cable-stayed and pontoon bridge which crosses Salhusfjorden between Klauvaneset and the island of Flatøy in Vestland county, Norway. It is 1,614 meters (5,295 ft) long, of which the pontoon section is 1,246 meters (4,088 ft) long. The cable-stayed section consists of a single 99-meter (325 ft) tall H-pylon which has a length of 368 meters (1,207 ft) and a main span of 172 meters (564 ft). This allows for a clearance of 32 meters (105 ft).

Kayamkulam is a municipality in the Alappuzha district of Kerala, India. It is located 90 km (55.9 mi) south of the district headquarters in Alappuzha and about 98 km (60.9 mi) north of the state capital Thiruvananthapuram. As per the 2011 Indian census, Kayamkulam has a population of 68,634 people, and a population density of 3,149/km2 (8,160/sq mi).

The Bandra–Worli Sea Link is a 5.6 km long, 8-lane wide cable-stayed bridge that links Bandra in the Western Suburbs of Mumbai with Worli in South Mumbai. It is the longest sea bridge, as well as the 5th longest bridge in India after Mumbai Trans Harbour Link, Bhupen Hazarika Setu, Dibang River Bridge and Mahatma Gandhi Setu. It contains pre-stressed concrete-steel viaducts on either side. It was planned as a part of the proposed Western Freeway that would link the Western Suburbs to Nariman Point in Mumbai's main business district, but is now planned to become part of the Coastal Road to Kandivali.

Alappuzha, also known as Alleppey, is a municipality in the Alappuzha district of Kerala, India. It is the district headquarters of the district, and is located about 130 km (80.8 mi) north of the state capital Thiruvananthapuram. As per the 2011 Indian census, Alappuzha has a population of 240,991 people, and a population density of 3,675/km2 (9,520/sq mi).

The M5 is an expressway in the City of Cape Town Metropolitan Municipality, South Africa. It connects Milnerton on the Western Seaboard in the north to Muizenberg in the south, and crosses both the N1 and the N2. For part of its length, from the N1 interchange to Plumstead, it is a limited-access freeway (motorway). From Mowbray to Muizenberg it is parallel to the M4 Main Road.
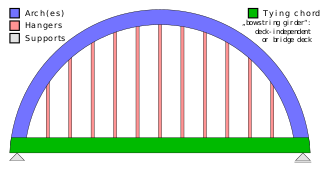
A tied-arch bridge is an arch bridge in which the outward-directed horizontal forces of the arch(es) are borne as tension by a chord tying the arch ends rather than by the ground or the bridge foundations. This strengthened chord may be the deck structure itself or consist of separate, independent tie-rods.

Luzhniki Metro Bridge, also known as Metromost (Метромост), is a concrete double-decked (two-level) arch bridge carrying a road and a Moscow Metro line across the Moskva River in Moscow, Russia. It connects the neighbourhood of Luzhniki Stadium to Sparrow Hills. The bridge houses Vorobyovy Gory, the only station of Moscow Metro located over water. Designed in 1958 by V.G. Andreyev and N.N. Rudomasin, the bridge rapidly decayed and was rebuilt in 1997–2002.

The Mumbai Trans Harbour Link, officially named as Atal Bihari Vajpayee Sewri–Nhava Sheva Atal Setu and colloquially known as Atal Setu, is a 21.8 km (13.5 mi) 6-lane grade separated expressway bridge, which connects Mumbai with Navi Mumbai, its satellite city. It is the longest sea bridge in India, and the world's 12th longest sea bridge. The bridge begins in Sewri, South Mumbai, crosses Thane Creek north of Elephanta Island, and terminates at Chirle near Nhava Sheva in Uran taluka, Navi Mumbai. The road is linked to the Mumbai–Pune Expressway in the east and to the Coastal Road in the west. The 6-lane highway is 27 meters in width, in addition to two emergency exit lanes, two edge strips, parallel crash barriers and noise barriers on both sides. The project costs a total of ₹17,843 crore (US$2.1 billion). The bridge has a capacity to handle 70,000 vehicles per day. Construction on the bridge began in April 2018, and was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 12 January 2024.

The Godavari Arch Bridge is a bowstring-girder bridge that spans the Godavari River in Rajahmundry, India. It is the latest of the three bridges that span the Godavari river at Rajahmundry. The Havelock Bridge being the earliest, was built in 1897, and having served its full utility, was decommissioned in 1997. The second bridge known as the Godavari Bridge is a truss bridge and is India's third longest road-cum-rail bridge crossing a water body.
Panakkattodil Devi Temple is a Hindu temple in Chavara Thekkumbhagom village in Kollam district of the Indian state of Kerala. Primary deity of this temple is Durga. The temple is managed by the Travancore Devaswom Board, Kerala. The Thalappoli in 'Meda Bharani' and the annual festival during the months of April and May are popular.

Ernakulam–Kayamkulam coastal line is a railway line which runs along the coastal areas of Alappuzha, Ernakulam districts in Kerala state of India. The coastal railway line starts as a branch line from Ernakulam Junction railway station towards Alappuzha and joins with the route via Kottayam at Kayamkulam Junction. This is the only main track in Kerala yet to be doubled and the single line traffic causes major delays in the route. The coastal line has a total distance of 102 km (63 mi).

The Ernakulam–Kottayam–Kayamkulam line is a railway line which runs through the districts of Ernakulam, Kottayam, Pathanamthitta and Alappuzha in Kerala state of India. This railway line starts as a branch line from Ernakulam Town railway station towards Kottayam and joins with the Ernakulam–Kayamkulam coastal line route via Alappuzha at Kayamkulam Junction. This line comes under the Thiruvananthapuram railway division of Southern Railway Zone of Indian Railways. The line has a total distance of 118 km (73 mi). The Ernakulam Town/Ernakulam Junction - Kottayam section opened in 1956-57 and Kottayam - Kollam section in 1957.
Waterways have always been an important mode of transport in Kerala. The total length of navigable route in Kerala was 1,900 kilometres and the navigable rivers constitute about 54 per cent of the waterways. The 41 West-flowing rivers together with the backwaters are an integrated part of the inland navigation system in Kerala. In Kerala water transportation through these channels are mainly small distant passenger services, informal country boats, freight transportation to PSU's such as Fertilisers and Chemicals Travancore, Kochi etc.
Vyttila flyover is a flyover, that is a part of the NH 66 in Kerala, India. The six lane flyover runs above the Vyttila junction in Kochi, which is one of the busiest junctions in the state.

The Neriamangalam Bridge is a bridge in the South Indian state of Kerala, that connects the Ernakulam and Idukki districts. Opened in 1935, it is the first Class A arch bridge in Asia. Popularly known as the gateway to the high ranges, it is located in Neriamangalam and presently a part of NH 85.

















