
Afghanistan is a landlocked mountainous country located on the Iranian Plateau, at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. The country is the 40th largest in the world in size. Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan, located in the Kabul Province. With a location at the intersection of major trade routes, Afghanistan has attracted a succession of invaders since the sixth century BCE.
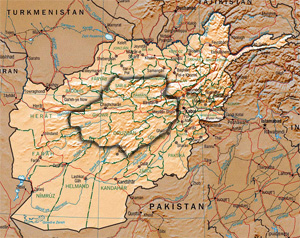
Hazarajat, also known as Hazaristan is a mostly mountainous region in the central highlands of Afghanistan, among the Kuh-e Baba mountains in the western extremities of the Hindu Kush. It is the homeland of the Hazara people who make up the majority of its population. Hazarajat denotes an ethnic and religious zone.

Ghazni is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in southeastern Afghanistan. The province contains 19 districts, encompassing over a thousand villages and roughly 1.3 million people, making it the 5th most populous province. The city of Ghazni serves as the capital. It lies on the important Kabul–Kandahar Highway, and has historically functioned as an important trade center. The Ghazni Airport is located next to the city of Ghazni and provides limited domestic flights to Afghanistan's capital, Kabul.

Ghōr, also spelled Ghowr or Ghur, is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan. It is located in the western Hindu Kush in central Afghanistan, towards the northwest. The province contains eleven districts, encompassing hundreds of villages, and approximately 764,472 settled people. Firuzkoh is the capital of the province.

Samangan is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located north of the Hindu Kush mountains in the central part of the country. The province covers 11,218 square kilometres (4,331 sq mi) and is surrounded by Sar-e Pol Province in the west, Balkh in the north, Baghlan in the east, and Bamyan in the south.

Paghman (Dari/Pashto:پغمان) is a town in the hills near Afghanistan's capital of Kabul. It is the seat of the Paghman District which has a population of about 120,000, mainly Pashtuns and Tajiks. The gardens of Paghman are a major tourist attraction, and why the city is also known as the garden capital of Afghanistan. The neighboring town of Qargha is to the southeast, which can be reached by several roads.

The Ghizer District, was a district in the westernmost part of the Gilgit-Baltistan province of Pakistan, before splitting into the current Ghizer and Gupis-Yasin districts in 2019. The capital of the district was Gahkuch.

Kunar is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northeastern part of the country. Its capital is Asadabad. Its population is estimated to be 508,224. Kunar's major political groups include Wahhabis or Ahl-e- Hadith, Nazhat-e Hambastagi Milli, Hezb-e Afghanistan Naween, Hezb-e Islami Gulbuddin.

The districts of Afghanistan, known as wuleswali, are secondary-level administrative units, one level below provinces. The Afghan government issued its first district map in 1973. It recognized 325 districts, counting wuleswalis (districts), alaqadaries (sub-districts), and markaz-e-wulaiyat. In the ensuing years, additional districts have been added through splits, and some eliminated through merges. In June 2005, the Afghan government issued a map of 398 districts. It was widely adopted by many information management systems, though usually with the addition of Sharak-e-Hayratan for 399 districts in total. It remains the de facto standard as of late 2018, despite a string of government announcements of the creation of new districts.

Jaghori is one of the main districts of the Ghazni province in Afghanistan. It is located in the highlands in the southern fringes of the Hazaristan region. It occupies 1,855 km2. in the upper Arghandab valley. The population is estimated to be around 560,000 in 2015. The district capital, Sange-e-Masha, is where major business transactions take place. The district is heavily dependent on agriculture, and migrant workers as the main sources of income. Other major marketplaces are in Ghojor and Anguri.

Nawur is one of the districts of Afghanistan, which is located in the northern part of Ghazni Province. With an area of approximately 5,234 km2 (2,021 sq mi), Nawur is the largest district of Ghazni province. Its population was estimated at 91,778 in 2002. Nawur's inhabitants are ethnic Hazaras followed by Kochis. The Jikhai River originates here.

Ajristan, also known as Dāya (دایه), or Dāya wa Folād, Ajristan also spelled as Ajeristan, is a district in the western part of Ghazni province, Afghanistan. Its population was estimated at 62,028 in 2001, of which 90% are Pashtun people with others from the Hazara people. Sangar, in the center of the district, is the capital. Most of the population live in the Jikhai River valley and depend upon agriculture, the main source of its economy. The last decade of severe winters and droughts have affected the economy and quality of life.

The Pech River is located in eastern Afghanistan.

Gizab also spelled as Gezab and Gizu, is a district in the Daykundi Province of Afghanistan. It has a population of about 75,503 and includes Hazara and Pashtun ethnic groups. The main town Gizab is at 1364 m altitude along the Helmand River.

Qarabagh or Qara Bagh, is a district in Ghazni province, 56 km to the south-west of Ghazni city in eastern Afghanistan. The 1,800 km2 area is one of the most populated at 109,000; some reports count more than 218,000. The ethnic composition of the district includes Hazaras and Pashtuns. The landscape varies in different parts of the district - deserts in the southwest, plains in the southeast and mountains in the north. The district is seriously affected by drought, especially farming and animal husbandry. Health and education need serious improvement.

The Baba Mountain range is the western extension of the Hindu Kush, and the origin of Afghanistan's Kabul, Arghandab, Helmand, Farah, Hari, Murghab, Balkh, and Kunduz rivers. The mountain range is crowned by Foladi peak rising 5048 m above sea level, and is located south of Bamyan.

Ramazan Bashardost is an Afghan politician who was the former planning minister in Afghanistan and a current member of the National Assembly of Afghanistan. He was an independent candidate in the 2009 Afghan presidential election.
Darah Sof was a district of Samangan Province in Afghanistan. It was located about 130 kilometres (81 mi) from the city of Samangan and 200 kilometres (120 mi) from the city of Mazar-i-Sharif, in Balkh Province. In 2005, the district was split into Dara-i Sufi Bala District or Darah Sof Balla District, and Dara-i Sufi Payin District or Darah Sof Payan District.

The central Afghan highlands, or the Afghan Highlands, is a geographic region of Afghanistan. Stretching from the Sabzak Pass near Herat in the west to the Little Pamir in the northeast, it includes the main Hindu Kush range and forms a western extension of the Himalayas. It is a highland area of more than 1,500 m above sea level, mostly situated between 2,000 and 3,000 m, with some peaks rising above 6,400 m. Usually, the valley bottoms in the area are used for cereal and horticultural production, and the mountains and high plateaus are used as pasture in summer for grazing sheep, goats, cattle, and camels. Its total area is about 414,000 km2.




















